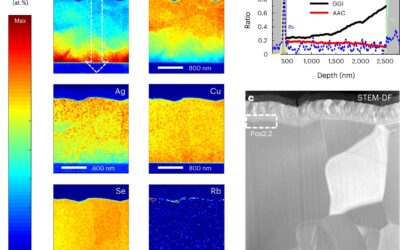
Until recently, chalcopyrite-based solar cells have achieved a maximum energy conversion efficiency of 23.35%, as reported in 2019 by Solar Frontier, a former Solar Energy company based in Japan. Further boosting this efficiency, however, has so far proved challenging.
Chemistry
Towards the selective and energy-efficient synthesis of ethylene via carbon dioxide reduction
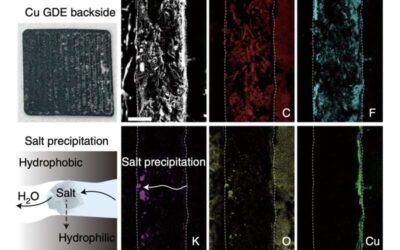
The synthesis of carbon-based chemicals via the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) has become the key objective of numerous recent energy research efforts. While these studies have yielded promising results, enabling the production of various widely...
Promising electrolytes for solid-state batteries based on viscoelastic inorganic glass
Recent advancements in the development of hybrid and electric vehicles have increased the need for highly performing battery technologies. Research teams worldwide have thus been working on a wide range of alternative battery solutions, while also trying to identify...
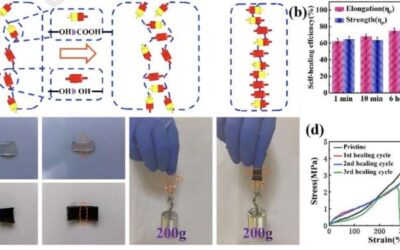
A conductive self-healing hydrogel to create flexible sensors
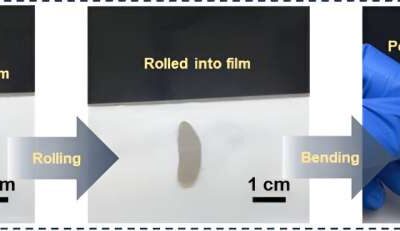
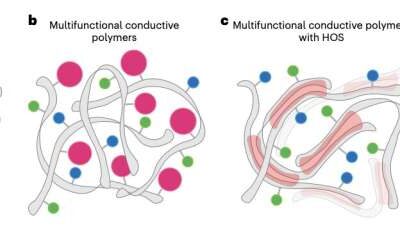
A method to change the mechanical and transport properties of conductive polymers
Conductive polymers, synthetic substances with large molecules that can conduct electricity, can have a broad range of valuable applications. For instance, they have been used to create sensors, light-emitting diodes, photovoltaics and various other devices.
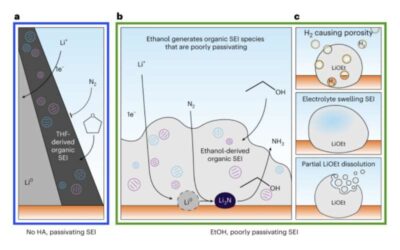
Using cryogenic electron microscopy to study the lithium SEI during electrocatalysis
Ammonia (NH3), the chemical compound made of nitrogen and hydrogen, currently has many valuable uses, for instance serving as a crop fertilizer, purifying agent, and refrigerant gas. In recent years, scientists have been exploring its potential as an energy carrier,...
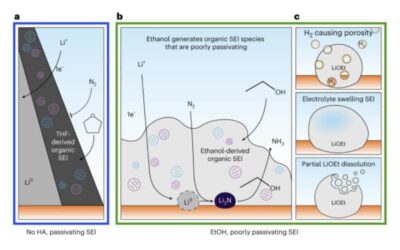
Using cryogenic electron microscopy to study the lithium SEI during electrocatalysis
Ammonia (NH3), the chemical compound made of nitrogen and hydrogen, currently has many valuable uses, for instance serving as a crop fertilizer, purifying agent, and refrigerant gas. In recent years, scientists have been exploring its potential as an energy carrier,...
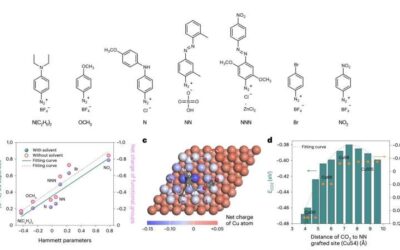
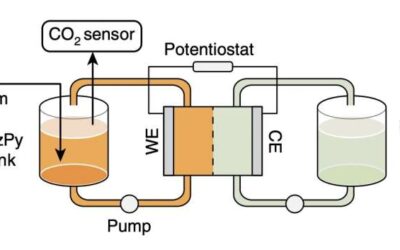
A strategy to fine-tune the properties of Lewis bases for electrochemical carbon dioxide capture
In recent years, many engineers and material scientists have been trying to develop sustainable energy solutions that could help to mitigate climate change on Earth. This includes carbon capture technologies, which are specifically designed to capture or absorb carbon...
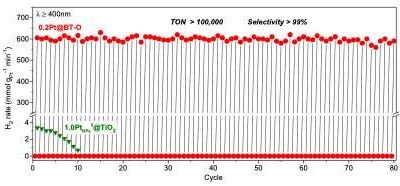
A new method to dehydrogenate alkanes at ambient conditions
The chemical term alkanes, or paraffins, refers to organic compounds that consist of single-bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms, such as methane, ethane, and propane, and several other hydrocarbons. Over the years, alkanes have become widely used in organic chemistry,...
Using bifunctional ionomers as electrolytes to synthesize ethylene from carbon dioxide
Over the past century or so, human activities have led to the rapid deterioration of the environment on Earth, with detrimental effects such as climate change and a rise in atmospheric CO2. Many scientists worldwide have thus been trying to devise new technologies and...