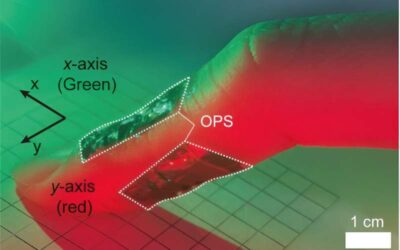
Devices that can detect, track and decode movements in their surroundings can have countless valuable applications in fields ranging from robotics to health care, the entertainment industry, sports, and more. Wearable sensors can be particularly effective in detecting...
Electronics & Semiconductors
A strategy to fabricate highly performing tin perovskite-based transistors
Metal halide perovskites are semiconducting materials with advantageous optoelectronic properties, low defects and low costs of production. In contrast with other emerging semiconductors, these materials can be easily synthesized via affordable solution processing...
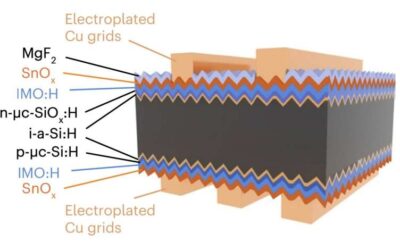
An affordable and scalable strategy to fabricate efficient silicon heterojunction solar cells
Silicon heterojunction (SHJ), solar cells based on a heterojunction between semiconductors with different band gaps, are among the most promising photovoltaic technologies. So far, these cells have exhibited remarkable power conversion efficiencies and good...
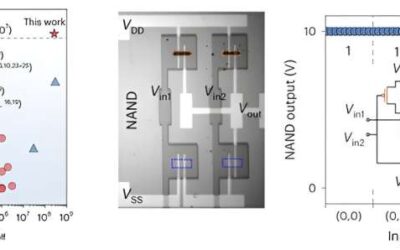
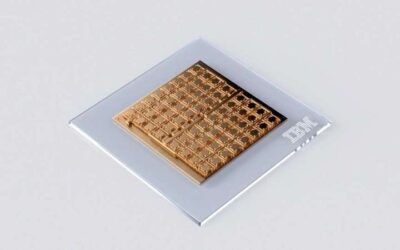
IBM develops a new 64-core mixed-signal in-memory computing chip
For decades, electronics engineers have been trying to develop increasingly advanced devices that can perform complex computations faster and consuming less energy. This has become even more salient after the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning...
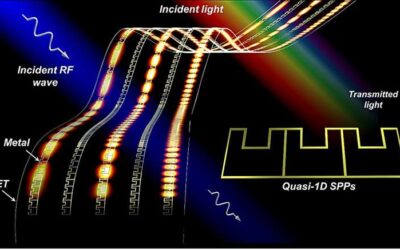
New transparent metadevices based on quasi-1D surface plasmon polariton structures
Transparent electronic devices could have numerous valuable real-world applications. Among other things, they could enable the creation of new optical devices, smart gear or wearables, invisible solar panels and integrated communication systems.
An approach to enhancing relaxors for energy storage devices
Relaxor ferroelectrics are materials with ferroelectric properties and high electrostriction (i.e., the ability to contract or deform in response to electric fields). These materials can be used to create highly efficient energy storage devices, such as capacitors.
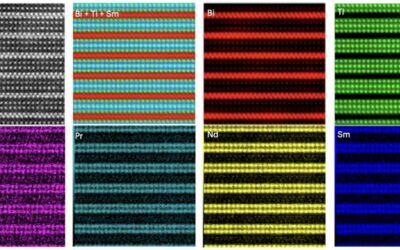
New gate-tunable and high-mobility devices based on strontium titanate
Strontium titanate (SrTiO3), an oxide of strontium and titanium with a perovskite structure, has many advantageous properties, including spin-orbit coupling, electrical tunability, and unconventional superconductivity. Compared to the superconductivity of conventional...
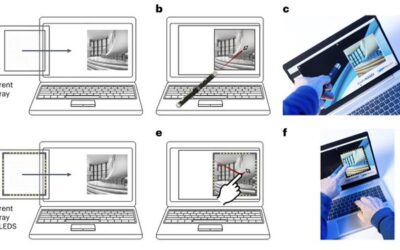
Researchers introduce transparent optical imager with near-infrared sensitivity and touchless interface
Most existing devices are operated via the sense of touch, either via touchscreens or mouse, remote controls, keyboards, and other equipment. Some engineers, however, have been trying to introduce alternative interfaces that do not require users to touch anything, as...
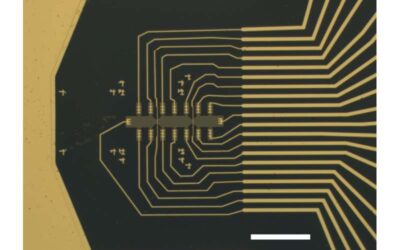
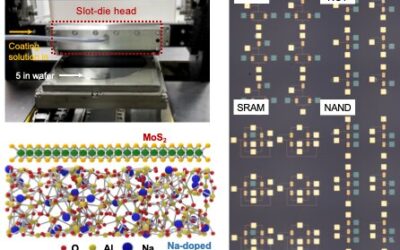
Wafer-scale transistor arrays created using slot-die printing
Engineers have been trying to devise increasingly efficient and low-cost methods to fabricate electronic components and devices on a large-scale. Recently, some studies explored the possibilities of creating electronics using solution processing techniques, which...
An origami-based haptic device that could enhance virtual reality experiences
The performance and realism of virtual reality (VR) technology has significantly improved over the past decade, allowing users to immerse themselves in digital content in ways that were previously inaccessible. The technology will most likely continue to evolve over...