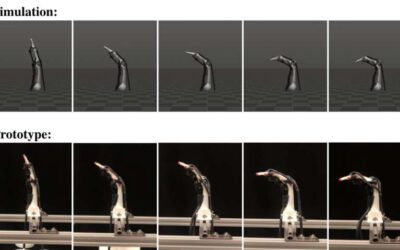
To perform tasks that involve moving or handling objects, robots should swiftly adapt their grasp and manipulation strategies based on the properties of these objects and the environment surrounding them. Most robotic hands developed so far, however, have a fixed and...
Engineering
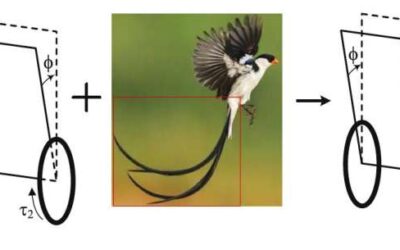
A self-balancing robot with a tail-like component
Nature is one of the greatest sources of inspiration for engineers and computer scientists developing new technological tools. Over the past decade or so, roboticists have developed countless robots inspired by the behavior and biological mechanisms of snakes, fish,...
A gecko-adhesive gripper for the Astrobee free-flying robot
Robots that can fly autonomously in space, also known as free-flying robots, could soon assist humans in a variety of settings. However, most existing free-flying robots are limited in their ability to grasp and manipulate objects in their surroundings, which may...
RoomShift: A room-scale haptic and dynamic environment for VR applications
Researchers at University of Colorado Boulder's ATLAS Institute have recently created RoomShift, a haptic and dynamic environment that could be used to support a variety of virtual reality (VR) experiences. This new haptic environment, introduced in a paper...
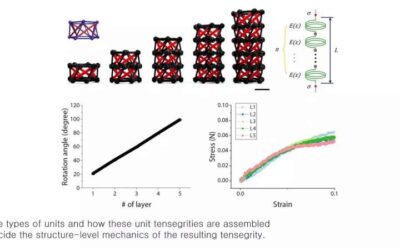
A 3D-printed tensegrity structure for soft robotics applications
Tensegrity is a design principle that has often been applied by artists, architects and engineers to build a wide range of structures, including sculptures, frames and buildings. This principle essentially describes the dynamics that occur when a structure maintains...
A three-agent robotic system for Mars exploration
Mars, also known as the red planet, has been the focus of numerous research studies, as some of its characteristics have sparked discussions about its possible inhabitability. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and a few other space agencies have...
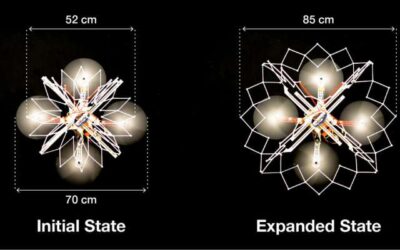
PufferBot: A flying robot with an expandable body
Researchers at University of Colorado Boulder's ATLAS Institute and University of Calgary have recently developed an actuated, expandable structure that can be used to fabricate shape-changing aerial robots. In a paper set to be presented at the 2020 IEEE/RSJ...
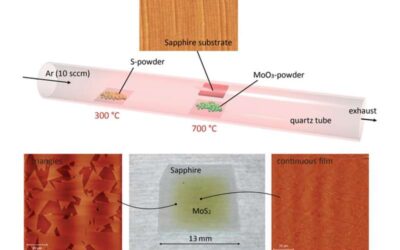
An operational amplifier fabricated using a 2-D semiconductor
Analog electronics are electronic systems that operate with currents and voltages that continuously change over time, rather than switching only between two levels, like digital electronics. Most existing analog devices are made of silicon. Due to the pressing demand...
A biomimetic robotic finger created using 3-D printing
Humans are innately capable of performing complex movements with their hands via the articulation of their endoskeletal structure. These movements are made possible by ligaments and tendons that are elastically connected to a fairly rigid bone structure.
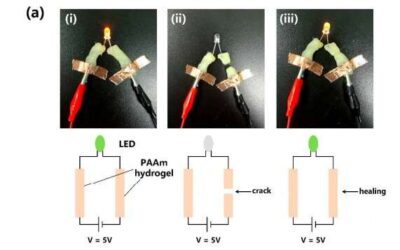
A highly stretchable and self-healing strain sensor for motion detection
Strain sensors are devices that can convert force, pressure, tension and weight into a change in electrical resistance (i.e., capacitance), which can then be measured. Over the past few years, these sensors have been used to create a variety of devices that can detect...