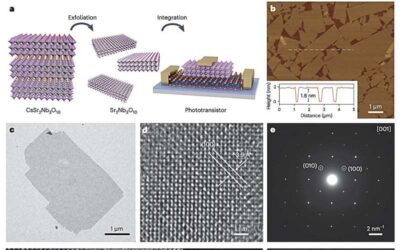
Two-dimensional (2D) superconducting materials have been found to be promising for the development of miniaturized optoelectronic devices. To perform well while consuming less energy, however, these smaller devices require a higher gate capacitance (i.e., gates that...
Engineering
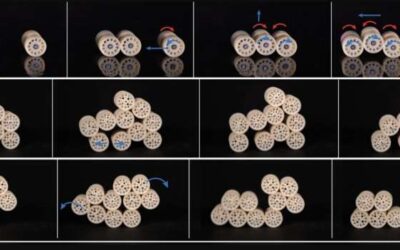
Self-organizing robotic aggregate design inspired by flowing and rigid behaviors of sandpiles
Researchers at the University of Chicago and the Illinois Institute of Technology recently developed Granulobot, a new modular robotic system that can change its physical shape to best navigate different environments.
A skating, tri-pedal robot capable of highly stable locomotion
Researchers at University of Michigan recently developed SKOOTR, a tri-pedal skating robot that can efficiently move around in its surroundings without repeatedly flipping over. This robot, introduced in a paper posted to the preprint server arXiv, was...
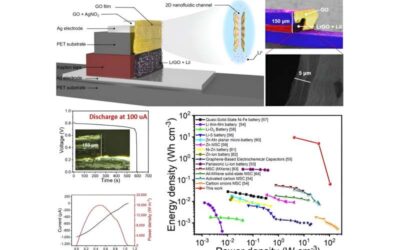
A strategy to realize vertical iontronic energy storage via osmotic effects and electrode redox reactions
In recent years, engineers have been trying to identify new technologies to sustainably generate and store energy. One promising solution leverages the energy produced by osmosis when two fluids with a different salt concentration meet, such as when a freshwater body...
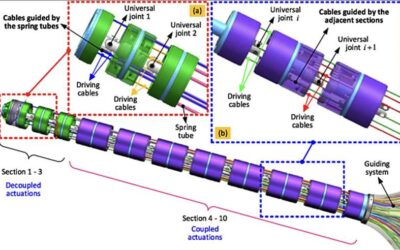
A new strategy to regulate the stiffness of snake-inspired robots
Robotic systems inspired by nature can help to efficiently tackle a wide range of problems, ranging from navigating complex environments to seamlessly completing missions as a team. In recent years, roboticists have created a growing number of bio-inspired systems...
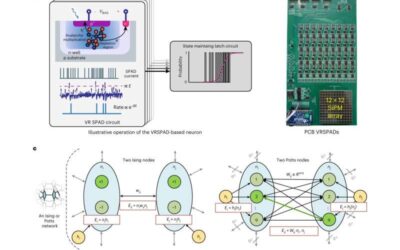
An approach to realize Potts annealing using single-photon avalanche diodes
Massively parallel annealing processors, where the computing nodes on a single processor can simultaneously perform a series of coordinated operations, could have a huge potential for tackling complex sampling and optimization problems. Electronics engineers and...
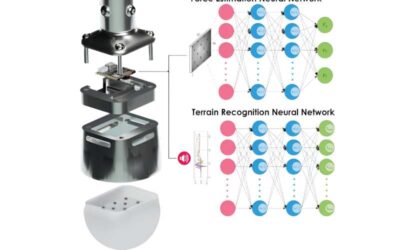
A sensing paw that could improve the ability of legged robots to move on different terrains
Legged robots that artificially replicate the body structure and movements of animals could efficiently complete missions in a wide range of environments, including various outdoor natural settings. To do so, however, these robots should be able to walk on different...
A tin-based tandem electrocatalyst for the synthesis of ethanol via CO₂ reduction
The electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) into various multi-carbon products is highly desirable, as it could help to easily produce useful chemicals for a wide range of applications. Most existing catalysts to facilitate CO2 reduction are based on...
A wearable robot that assists people with walking
In recent years, roboticists have introduced increasingly advanced systems, which could open exciting new possibilities for surgery, rehabilitation, and health care assistance. These robotic systems are already helping to improve the quality of life of many people...
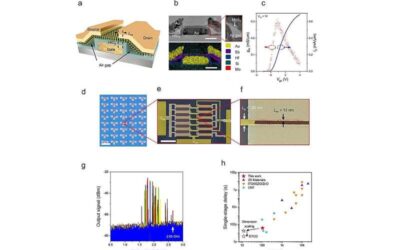
Integrated circuits based on a 2D semiconductor operating at GHz frequencies
Transistors are crucial electronic components that regulate, amplify and control the flow of current inside most existing devices. In recent years, electronics engineers have been trying to identify materials and design strategies that could help to further improve...