Current methods for charging electronic devices via wireless technology only work if the overall system parameters are set up to match a specific transfer distance. As a result, these methods are limited to stationary power transfer applications, which means that a...
Hi Tech & Innovation
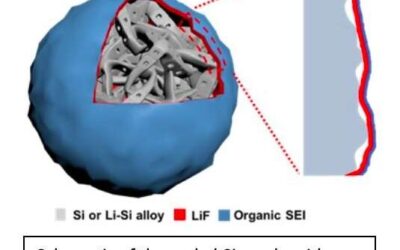
A new electrolyte design that could enhance the performance of Li-ion batteries
Most existing lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) integrate graphite anodes, which have a capacity of approximately 350 milliamp hours (mAh) per gram. The capacity of silicon anodes is almost 10 times higher than that of their graphite counterparts (around 2,800 mAh per...
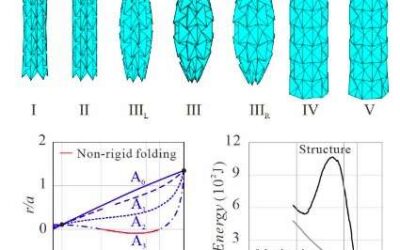
A model for the origami-inspired folding of a tubular waterbomb
In recent years, research teams worldwide have been trying to apply origami-folding strategies to mechanical structures, as this could allow them to change their shape both rapidly and efficiently. A key advantage of origami, the Japanese art that entails folding...
A technique to produce patterned transition metal ditelluride layers for 2-D devices
Researchers at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) in South Korea have recently introduced a method to produce thin and patterned transition metal ditelluride films to be integrated in 2-D metal semiconductors. Their synthesis technique,...
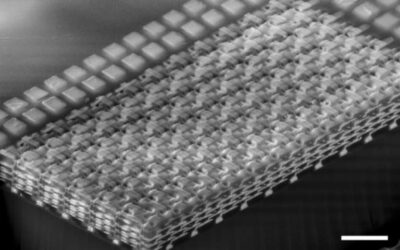
A new technique for the 3-D printing multimaterial devices
Three-dimensional printing techniques could potentially be used to fabricate a variety of objects with complex geometries, including electronic components. Most 3-D printing approaches developed so far, however, have merely proved effective for producing...
A 3-D memristor-based circuit for brain-inspired computing
Researchers at the University of Massachusetts and the Air Force Research Laboratory Information Directorate have recently created a 3-D computing circuit that could be used to map and implement complex machine learning algorithms, such convolutional neural networks...
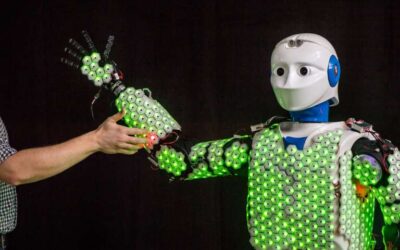
A highly performing and efficient e-skin for robotic applications
Researchers at Technische Universität München in Germany have recently developed an electronic skin that could help to reproduce the human sense of touch in robots. This e-skin, presented in a paper published in MDPI's Sensors journal, requires far less computational...
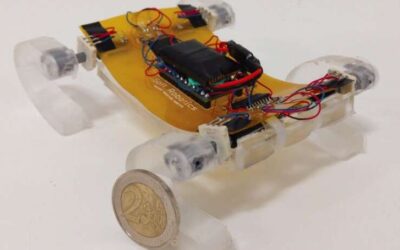
SQuad: A miniature robot that can walk and climb obstacles
Researchers at Bilkent University in Turkey have recently created a small quadruped robot called SQuad, which is made of soft structural materials. This unique robot, presented in a paper published in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, is more flexible than...
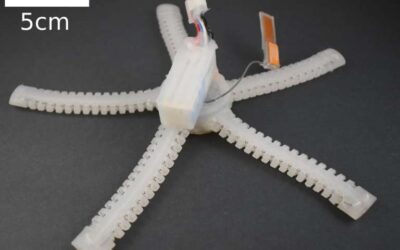
This is PATRICK: Meet the brittle star-inspired robot that can crawl underwater
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University have recently created PATRICK, an untethered soft robot that artificially replicates the structure and behavior of the brittle star, a marine invertebrate closely related to starfish. This unique bio-inspired robot, presented...
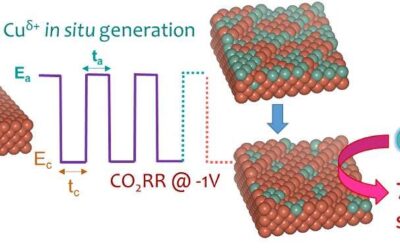
Simultaneously tuning the surface structure and oxidation state of copper catalysts
Electrical energy derived from renewable sources could be used to rearrange bonds in carbon dioxide (CO2) and water molecules into complex hydrocarbons, which can then be burnt to produce new energy and CO2, ultimately enabling a carbon cycle. Copper is a catalytic...