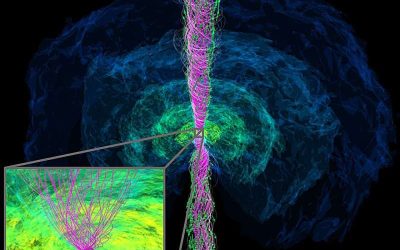
Binary neutron star mergers, cosmic collisions between two very dense stellar remnants made up predominantly of neutrons, have been the topic of numerous astrophysics studies due to their fascinating underlying physics and their possible cosmological outcomes. Most...
Astronomy
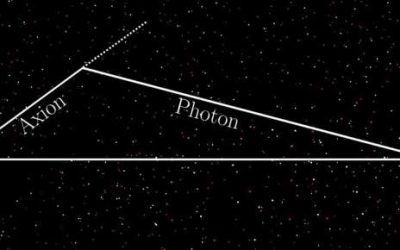
Searching for axions by analyzing X-ray observations of entire galaxies
The ongoing search for dark matter, the elusive type of matter that does not emit, absorb or reflect light and is estimated to account for most of the universe's mass, has not yet yielded conclusive results. Axions, hypothetical elementary particles that were first...
TeV halos could be a common feature of middle-aged pulsars, study shows
Pulsars are rapidly rotating neutron stars that emit regular radio wave pulses and beams of magnetic radiation, which can sometimes be detected from Earth. These pulsating stars are dense remnants of massive stars whose life terminated in a supernova explosion.
Astrobee learns to transport soft cargo: Open-source simulator models real ISS challenges
Astrobee is a free-flying robotic system developed by NASA that is made up of three distinct cube-shaped robots. This system was originally designed to help astronauts who are working at the International Space Station (ISS) by automating some of their routine manual...
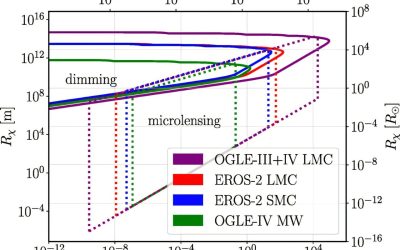
Dark matter search: Dimming starlight may signal passage of dark compact objects
The detection of dark matter, an elusive form of matter believed to account for most of the universe's mass, remains a long-standing goal within the physics research community. As this type of matter can only emit, reflect or absorb light very weakly, it cannot be...
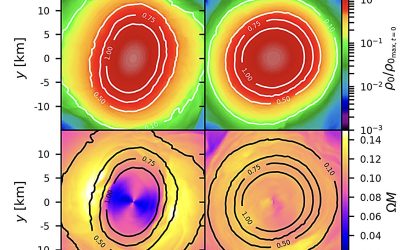
Rethinking neutron star mergers: Study explores the effects of magnetic fields on their oscillating frequencies
Neutron star mergers are collisions between neutron stars, the collapsed cores of what were once massive supergiant stars. These mergers are known to generate gravitational waves, energy-carrying waves propagating through a gravitational field, which emerge from the...
Astrophysicists propose new method to directly detect ultralight dark matter
The detection of dark matter, the elusive type of matter predicted to make up most of the universe's mass, is a long-standing goal in the field of astrophysics. As dark matter does not emit, reflect or absorb light, it cannot be observed using conventional...
Supernova simulations show that low-mass star in binary system J0453+1559 could be a neutron star
In 2015, astrophysicists discovered a system consisting of two compact stars orbiting each other: a pulsar (i.e., a highly magnetized rapidly rotating, light-emitting neutron star) and a so-called companion star. The companion star in this system has a mass that is...
Sub-GeV dark matter hunt: SENSEI collaboration reports first findings
Detecting dark matter particles and understanding their underlying physics is a long-standing research goal for many researchers worldwide. Dark matter searches have been aimed at detecting different possible signals that could be associated with the presence of these...
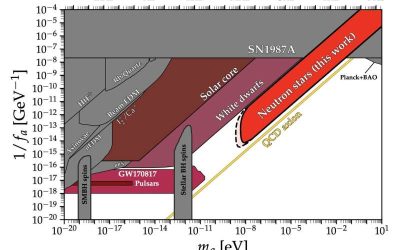
Neutron star cooling simulations set new constraints on light QCD axions
Neutron stars, the remnants of massive stars after a supernova explosion, have often been the focus of studies aimed at testing and unveiling exotic physics. This is because these stars are among the densest objects in the universe, so they host extremely high...