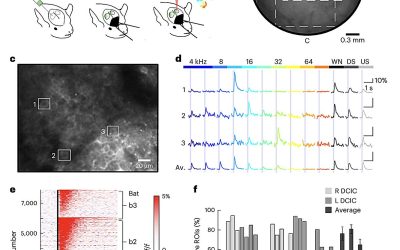
The ability to quickly recognize sounds, particularly the vocalizations made by other animals, is known to contribute to the survival of a wide range of species. This ability is supported by a process known as categorical perception, which entails the transformation...
Molecular & Computational biology
Molecular simulations provide new insights into the dynamics of supercoiled DNA
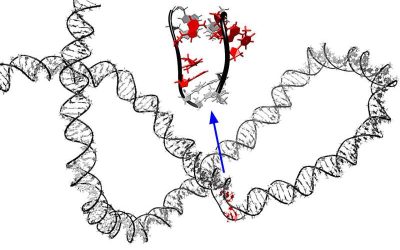
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), the molecular "blueprint" carrying the genetic instructions that influence the growth, development, reproduction and predispositions of individual humans, can undergo different types of mechanical stress inside cells. For instance, it can...
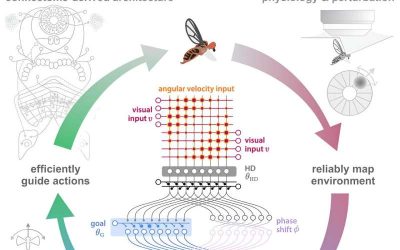
How fruit flies use internal representations of head direction to support goal-directed navigation
Animal behavior is known to rely on transforming sensory information into motor commands, often influenced by an animal's internal needs. While in mammals and other large animals this process is supported by complex brain processes, simpler versions of it might also...
The modeling and simulation of self-organized intracellular twisters in the Drosophila oocyte
Cytoplasmic streaming is the large-scale motion of cytoplasm (i.e., gelatinous liquid inside cells) inside a living cell. This flow, known to regulate various intracellular processes, can vary greatly between different cell types at different stages of a cell's...
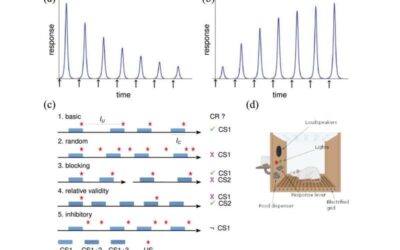
A new theory of learning integrates cognitive psychology and systems biology
Many neuroscientists, medical researchers and engineers specializing in artificial intelligence have been trying to understand the neural mechanisms underpinning learning. Although studies have unveiled some vital aspects of these mechanisms, numerous questions remain...
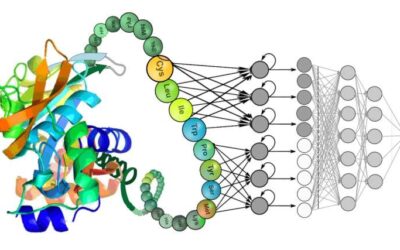
Study evaluates deep learning models that decode the functional properties of proteins
Deep learning–based language models, such as BERT, T5, XLNet and GPT, are promising for analyzing speech and texts. In recent years, however, they have also been applied in the fields of biomedicine and biotechnology to study genetic codes and proteins.
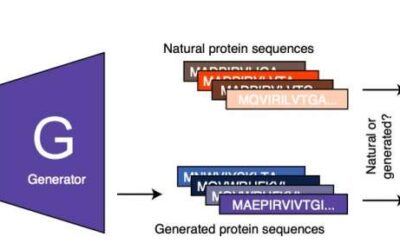
ProteinGAN: A generative adversarial network that generates functional protein sequences
Proteins are large, highly complex and naturally occurring molecules can be found in all living organisms. These unique substances, which consist of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds to form long chains, can have a variety of functions and properties.