Our current, well-established understanding of phases of matter primarily relates to systems that are at or near thermal equilibrium. However, there is a rich world of systems that are not in a state of equilibrium, which could host new and fascinating phases of matter.
PHYS.ORG
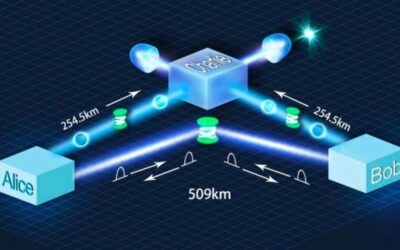
Study achieves a new record fiber QKD transmission distance of over 509 km
The sending-or-not-sending twin-field (SNS-TF) protocol has so far proved to be a highly promising strategy for achieving high rates over long distances in quantum key distribution (QKD) applications. In fact, by tolerating large misalignment errors, this protocol can...
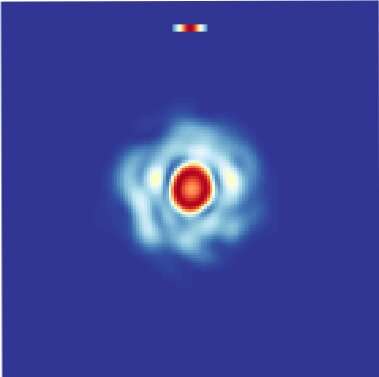
A theoretical approach to understand the mechanisms of 3-D spatiotemporal mode-locking
Laser technology confines light inside a resonator containing a gain medium, a material with quantum properties that can amplify light. As laser resonators are generally far larger than the wavelength of light, lasing inside their cavities can occur in a wide range of...
Reviewing recent developments in the electrolysis of saline water
Solar-powered technology, such as photovoltaics (PVs), could address some of the environmental challenges of our times, enabling the sustainable production of electrical energy in many geographical areas, including arid or desert regions. Many arid regions are located...
Cooling of a trapped ion to the quantum regime
Neutral atoms and charged ions can be cooled down to extremely low temperatures (i.e., to microkelvins, 1 millionth of a degree above absolute zero) using laser techniques. At these low temperatures, the particles have often been found to behave in accordance with the...
Compact dark object search: Scanning Earth’s core with superconducting gravimeters
Physics theory suggests that the universe is made up in great part by a type of matter that does not emit, absorb or reflect light, and hence cannot be observed using conventional detection methods. This type of matter, referred to as dark matter, has so far never...
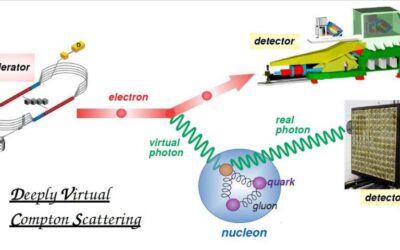
3-D imaging the flavor content of the nucleon
The Jefferson Lab Hall A Collaboration, in an experiment led by researchers at Faculté des Sciences de Monastir in Tunisia, Institut de Physique Nucléaire d'Orsay in France and Old Dominion University in the United States, has recently gathered the first experimental...
A theoretical approach to understand the mechanisms of 3-D spatiotemporal mode-locking
Laser technology confines light inside a resonator containing a gain medium, a material with quantum properties that can amplify light. As laser resonators are generally far larger than the wavelength of light, lasing inside their cavities can occur in a wide range of...
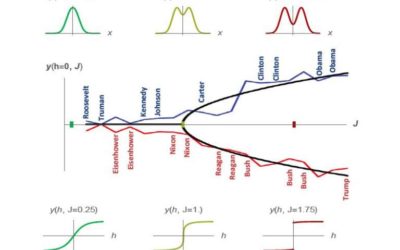
Investigating dynamics of democratic elections using physics theory
Sometimes, physics theories and constructs can also be used to study seemingly unrelated phenomena, such as social behaviors or dynamics. While human beings are not necessarily similar to specific physical particles, theories or techniques that physicists typically...
New phase diagrams of superfluid helium under varying degrees of confinement
Physicists have been studying superfluid 3He under nanoscale confinement for several years now, as this unique liquid presents a rich variety of phases with complex order parameters that can be stabilized. While past studies have gathered many interesting...