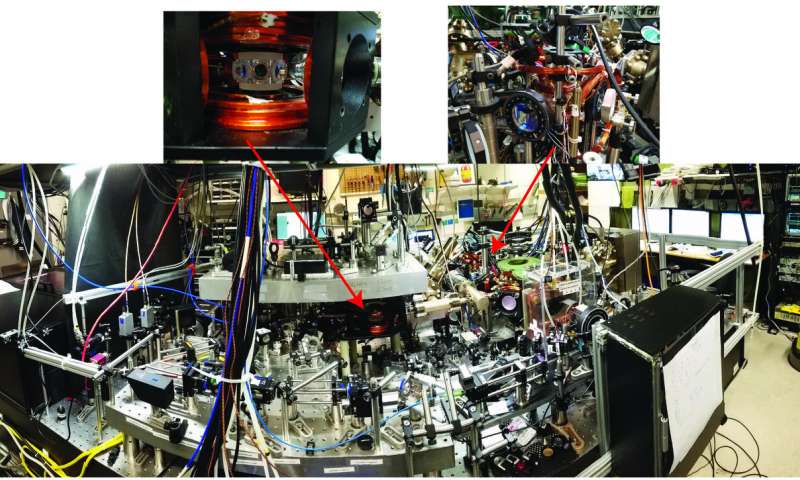
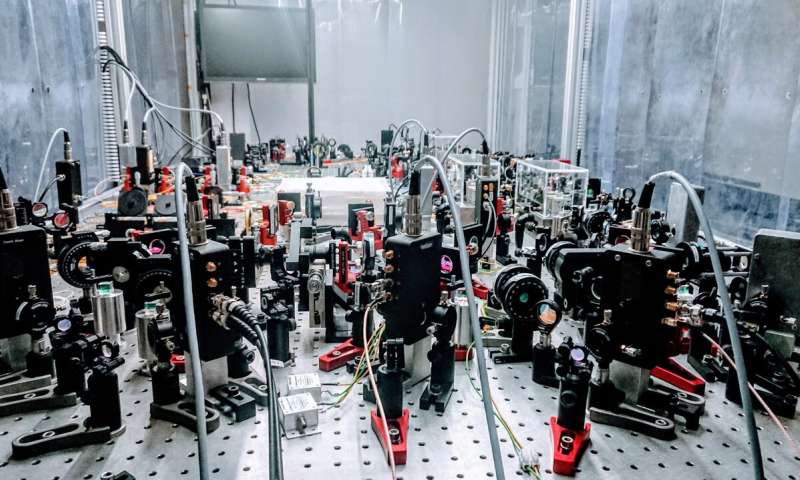
The concept of universal physics is intriguing, as it enables researchers to relate physical phenomena in a variety of systems, irrespective of their varying characteristics and complexities. Ultracold atomic systems are often perceived as ideal platforms for...
PHYS.ORG
The experimental observation of echoes in a single molecule
Echoes, sounds that are repeated or reverberate as a result of waves reflected back to the listener, occur in several physical systems. In physics research, echoes are typically used to eliminate the effects of dephasing caused by a system's interactions with the...
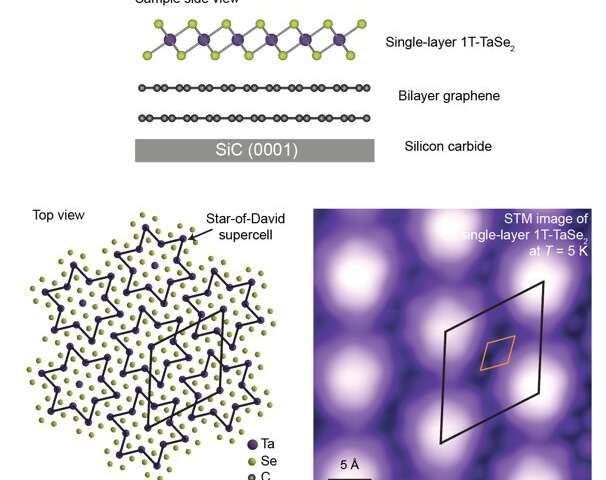
Researchers discover a unique orbital texture in single-layer of 3-D material
New physical behavior, such as Mott insulating behavior, unconventional superconductivity and quantum spin liquid behavior, occurs when electrons inside a material interact with each other. When electrons are confined to lower dimensions such as 2-D planes, these...
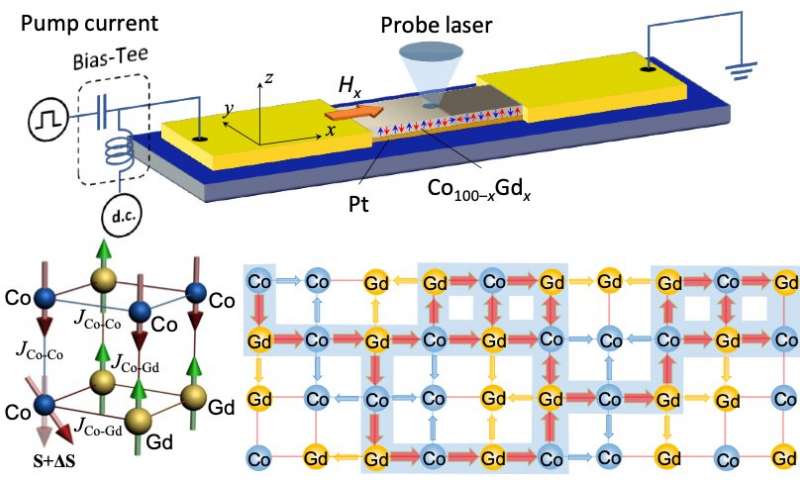
Researchers achieve ultrafast spin-orbit torque switching in ferrimagnetic devices
Spin-orbit torque (SOT) magnetization switching is a phenomenon induced by a spin current, which is in turn generated by a charge current. Eliciting this phenomenon could help to manipulate the magnetization in spintronic devices, potentially increasing their...
3-D trapping of Rydberg atoms in holographic optical bottle beam traps
Researchers at CNRS, Université Paris-Saclay in France have recently demonstrated the 3-D trapping of atoms in a Rydberg state inside holographic optical bottle beam traps. Their demonstration, outlined in a paper published in Physical Review Letters, could have...
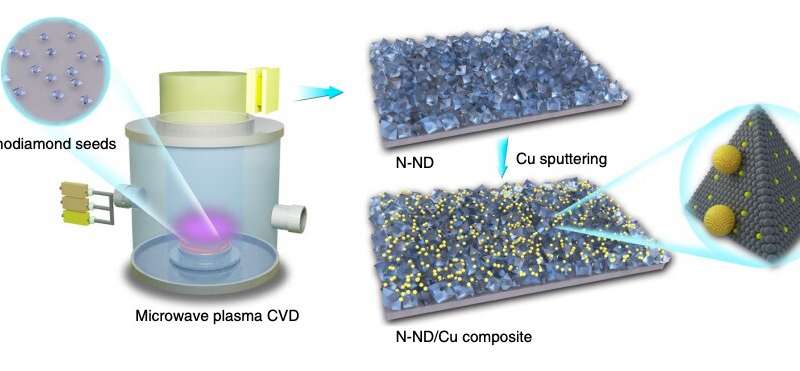
A design principle for creating selective and robust electrocatalytic interfaces
To effectively counteract climate change and meet rising global energy requirements, humans must drastically change their methods for generating energy. New catalysts for a carbon-neutral conversion of energy could be of great help in facing these challenges,...
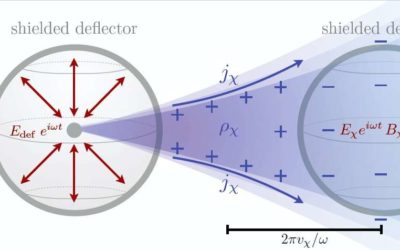
A new strategy for directly detecting light particle dark matter
For almost a century, astronomers have hypothesized that the universe contains more matter than what can be observed by the human eye. It is now believed that approximately 80 percent of the universe's mass is made up of a type of matter that does not emit light or...
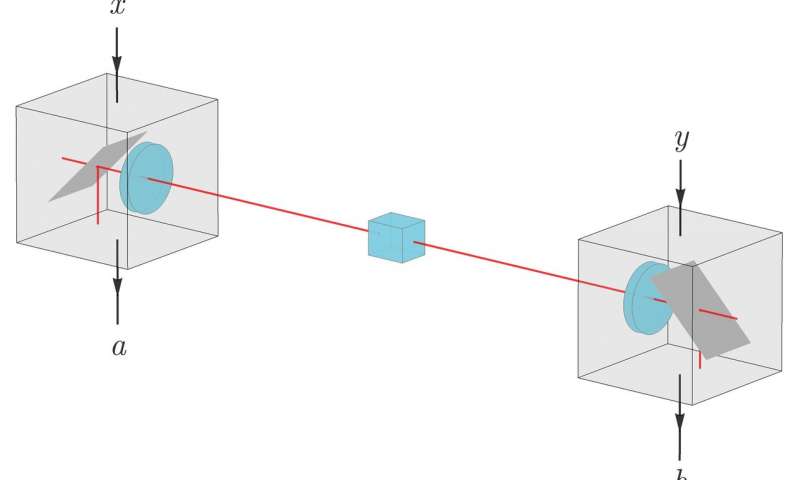
Applying advantage distillation to device-independent quantum key distribution (DIQKD)
Researchers at ETH Zürich and National University of Singapore have carried out a study investigating whether advantage distillation, a classical cryptography technique that has so far never been successfully implemented, can be applied to device-independent quantum...
High-precision distributed sensing using an entangled quantum network
Quantum-enhanced metrology has been an active area of research for several years now due to its many possible applications, ranging from atomic clocks to biological imaging. Past physics research established that having a non-classical probe, such as squeezed light or...
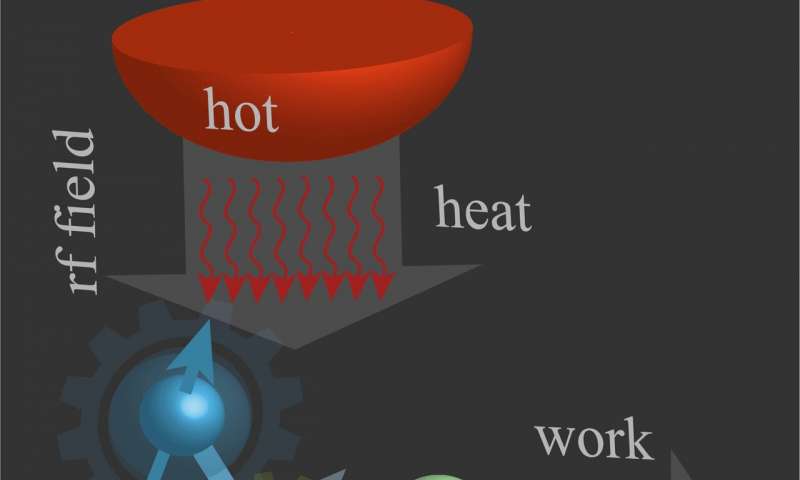
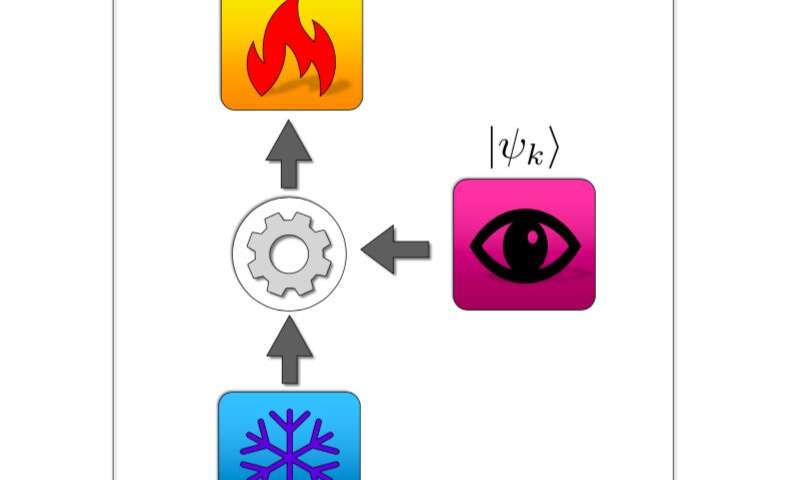
Using quantum measurements to fuel a cooling engine
Researchers at the University of Florence and Istituto dei Sistemi Complessi, in Italy, have recently proved that the invasiveness of quantum measurements might not always be detrimental. In a study published in Physical Review Letters, they showed that this invasive...