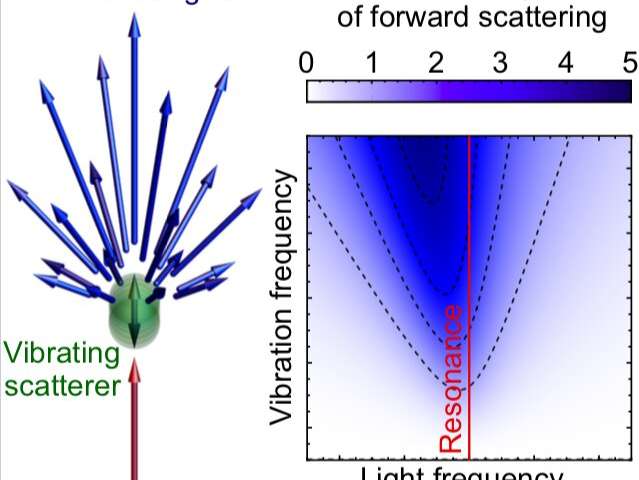
For the Kerker effect to occur, particles need to have electric and magnetic polarizabilities of the same strength. This, however, is very challenging to achieve, as magnetic optical resonances in small particles are relatively weak. Researchers at Ioffe Institute, in...
PHYS.ORG
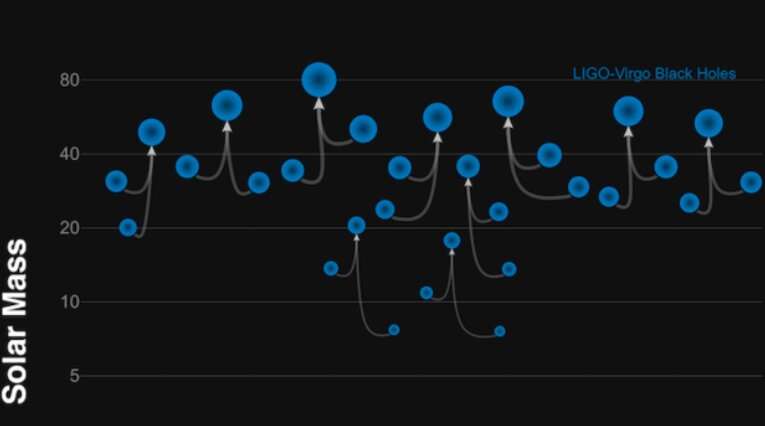
Theory proposes that LIGO/Virgo black holes originate from a first order phase transition
A few years ago, the LIGO/Virgo collaboration detected gravitational waves arising from a binary black hole merger using the two detectors of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO). This eventually led to the observation of black holes with...
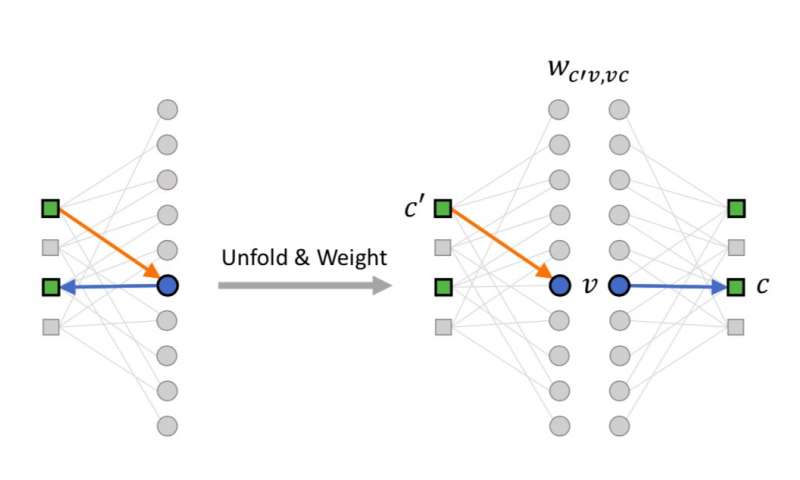
Training neural belief-propagation decoders for quantum error-correcting codes
Two researchers at Université de Sherbrooke, in Canada, have recently developed and trained neural belief-propagation (BP) decoders for quantum low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes. Their study, outlined in a paper published in Physical Review Letters, suggests that...
Turning an organic molecule into a coherent two-level quantum system
Researchers at Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light and Friedrich Alexander University in Erlangen, Germany have recently demonstrated that a molecule can be turned into a coherent two-level quantum system. In their study, published in Nature Physics, they...
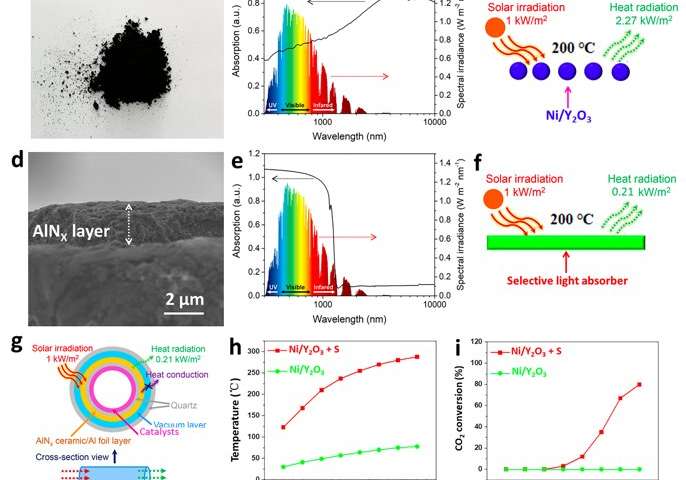
Using a selective light absorber to build a photothermal catalysis system
Researchers at Hebei University in China and Hakkaido University in Japan have recently used a selective light absorber to construct a photothermal system that can generate temperatures up to 288°C under weak solar irradiation (1 kW m-2). This system, presented in...
Using QMC simulations to examine the dynamic spin structure of planar coupled spin ladders
Recent polarized inelastric neutron scattering experiments have identified the amplitude (i.e. Higgs) mode in C9H18N2CuBr4, a 2-D, near-quantum-critical spin ladder compound that exhibits a weak easy-axis exchange anisotropy. Inspired by these findings, researchers at...
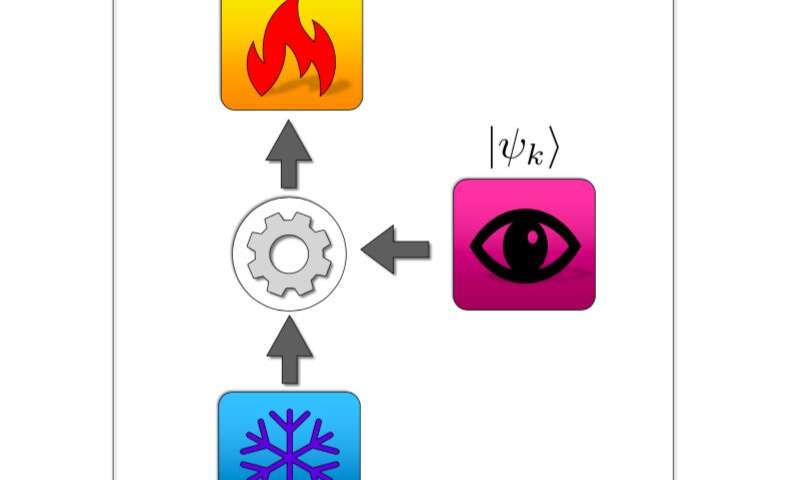
Using quantum measurements to fuel a cooling engine
Researchers at the University of Florence and Istituto dei Sistemi Complessi, in Italy, have recently proved that the invasiveness of quantum measurements might not always be detrimental. In a study published in Physical Review Letters, they showed that this invasive...
Using velocity-induced acoustic oscillations as a standard ruler at cosmic dawn
Our current understanding of physics suggests that there are two main types of matter in the universe known as dark and baryonic matter. Dark matter is made up of material that scientists cannot directly observe, as it does not emit light or energy. On the other hand,...
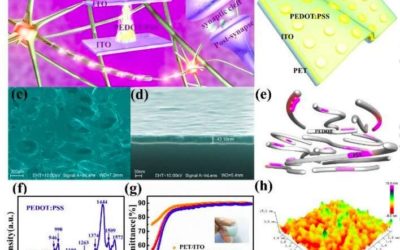
Waterproof artificial synapses for pattern recognition in organic environments
Most artificial intelligence (AI) systems try to replicate biological mechanisms and behaviors observed in nature. One key example of this is electronic synapses (e-synapses), which try to reproduce junctions between nerve cells that enable the transmission of...
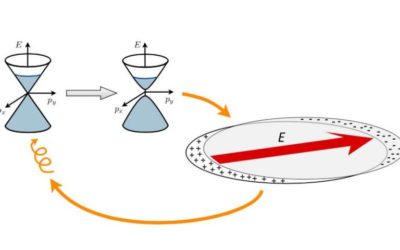
Spontaneous magnetization in a non-magnetic interacting metal
Over the past decade, numerous physics studies have explored how oscillating electric fields produced by lasers or microwave sources can be used to dynamically alter the properties of materials on demand. In a new study featured in Nature Physics, two researchers at...