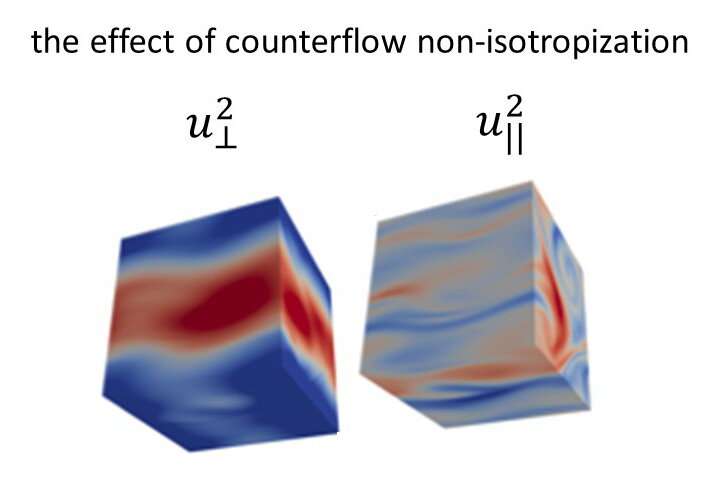
Researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science, the University of Rome, CNRS and the University of Helsinki have recently carried out a study investigating the difference between 3-D anisotropic turbulence in classical fluids and that in superfluids, such as helium....
PHYS.ORG
Study unveils a new supersolid phase in dipolar Bose-Einstein condensates
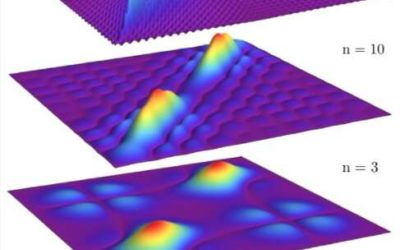
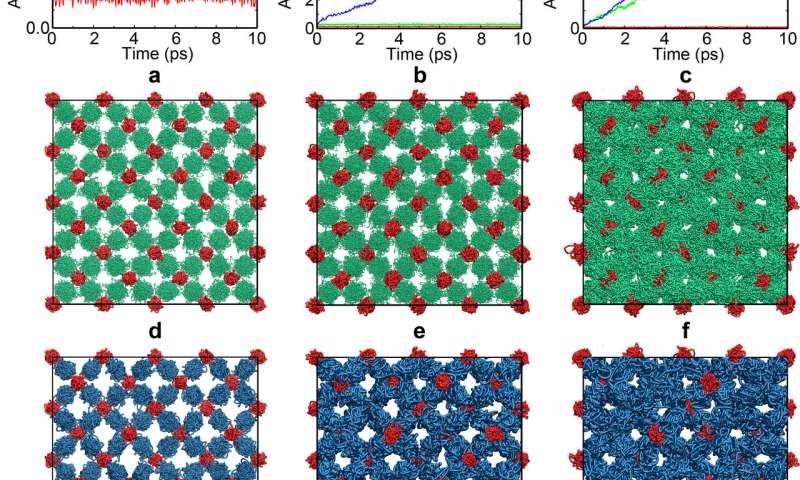
Generally, matter exists in three distinct forms: as a solid, a liquid or a gas. Past physics research, however, has unveiled other curious states of matter, one of which is supersolidity. In a supersolid state, particles are arranged into a rigid crystal and can...
A technique to measure mechanical motion beyond the quantum limit
Researchers at the University of Colorado have recently developed a new technique to measure mechanical motion using simultaneous electromechanical amplification and cooling processes. Their method, presented in a paper published in Physical Review Letters, allowed...
Study reports high-harmonic generation in an epsilon-near-zero material
High-harmonic generation (HHG) is a nonlinear optical phenomenon through which high harmonics of an intense laser beam are generated in a target material, typically a gas. Physicists have been studying HHG in atomic gases for decades, but more recently a team of...
Study unveils new supersymmetry anomalies in superconformal quantum field theories
Researchers at the University of Southampton and the Korea Institute for Advanced Study have recently showed that supersymmetry is anomalous in N=1 superconformal quantum field theories (SCFTs) with an anomalous R symmetry. The anomaly described in their paper,...
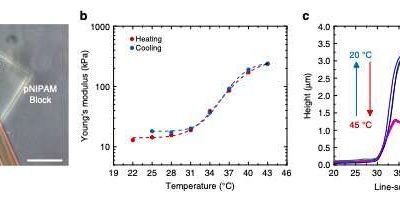
Researchers develop 3-D microstructures that respond to temperature and light
A team of researchers at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and Heidelberg University have recently introduced functional 3-D hetero-microstructures based on Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) (pNIPAM) a polymer that responds to changes in temperature close to its...
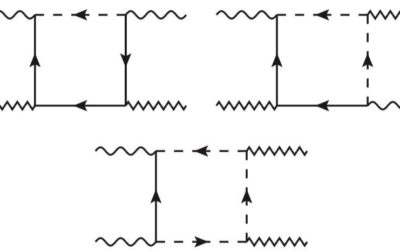
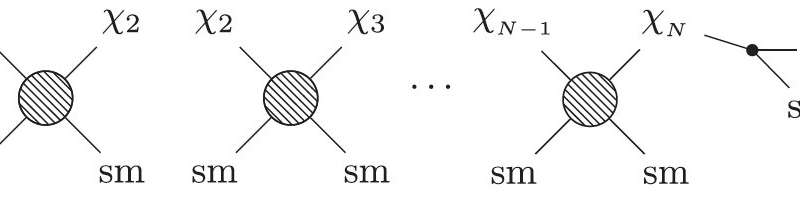
A new framework could aid the search for heavy thermal dark matter
Astrophysicists have been searching for dark matter for several decades, but these searches have so far yielded disappointing results. In a recent study, two researchers at Weizmann Institute of Science and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem in Israel have introduced...
Study sheds light on gauge invariance in ultrastrong-coupling cavity quantum electrodynamics
In quantum electrodynamics, the choice of gauge (i.e. specific mathematical formalism used to regulate degrees of freedom) can greatly influence the form of light-matter interactions. Interestingly, however, the "gauge invariance" principle implies that all physical...
Study unveils new superionic states of helium-water compounds
Helium and water are known to be abundant throughout the universe, particularly in giant planets such as Uranus and Neptune. Although helium is typically unreactive at common atmospheric conditions, past studies have found that it can sometimes react with other...
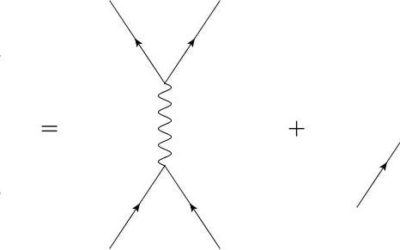
New research synthesizes different aspects of causality in quantum field theory
In current quantum field theory, causality is typically defined by the vanishing of field commutators for spacelike separations. Two researchers at the University of Massachusetts and Universidade Federal Rural in Rio de Janeiro have recently carried out a study...