Conical structures can have advantageous applications in a variety of fields, ranging from robotics to civil engineering. Studies have found that conical shells made of liquid crystal elastomer films can be effective lifters; devices that can generate thrust for...
Soft Matter
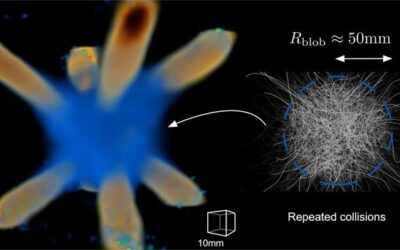
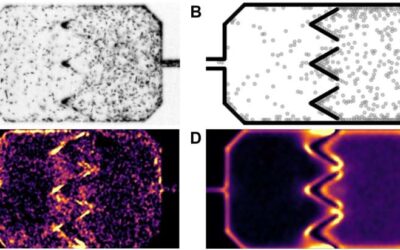
A new approach to controlling the properties of turbulence
Turbulence, a fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in flow velocity and pressure, has been the topic of countless physics studies. Although turbulence is a very common phenomenon that occurs in nature, manipulating it and controlling its properties had so far...
A numerical protocol to estimate local entropy production
In physics, equilibrium is a state in which a system's motion and internal energy do not change over time. Videos of systems in equilibrium would look exactly the same if they were watched in their normal chronological progression or backwards. This symmetry means...
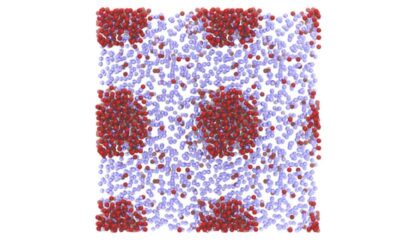
Using machine learning to infer rules for designing complex mechanical metamaterials
Mechanical metamaterials are sophisticated artificial structures with mechanical properties that are driven by their structure, rather than their composition. While these structures have proved to be very promising for the development of new technologies designing...
A new experimental study tackles the unsolved mystery of ‘nanobubbles’
Nanobubbles are extremely small (i.e., nanoscopic) gaseous cavities that some physicists observed in aqueous solutions, typically after specific substances were dissolved in them. While some studies reported the observation of these incredibly tiny bubbles, some...
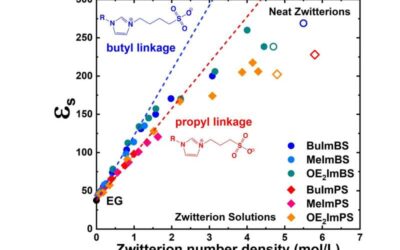
Study shows that zwitterions can raise the dielectric constant of soft materials
To create efficient energy storage solutions and actuators, engineers need materials with a high dielectric constant. The dielectric constant is essentially the ratio of a substance's permittivity (i.e., its ability to store electrical energy in an electric field) to...
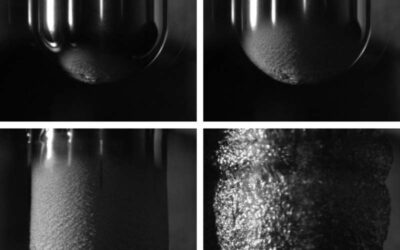
Study unveils the minimum temperature for droplets levitating from smooth surfaces
The Leidenfrost effect is a well-known physical phenomenon first discovered in 1756. It occurs when a liquid is in the proximity of a surface that is significantly warmer than its boiling point. This produces an insulating vapor layer that prevents the liquid from...