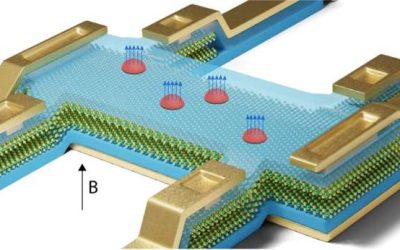
Semiconducting transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) are a class of layered materials exhibiting unique optoelectronic properties that could be leveraged to develop transistors, sensors and other nanoelectronics. Despite their advantages, creating robust ohmic...
nanomaterials
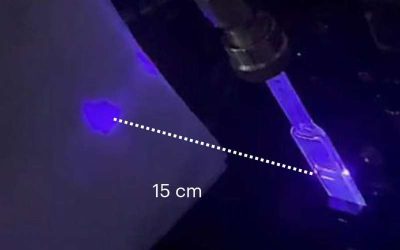
New blue light-emitting lasers leverage low-toxicity colloidal quantum dots
Blue lasers, lasers that emit a light beam with a wavelength between 400 nm and 500 nm, are key components of various technologies, ranging from high-resolution displays to printers, medical imaging tools and data storage solutions. A key advantage of these lasers is...
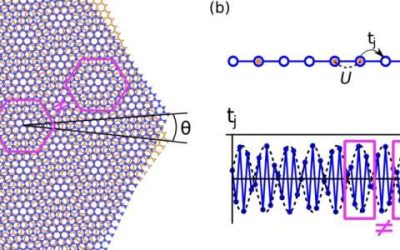
Quasiperiodicity changes the ground-state properties of 1D narrow-band moiré systems, study demonstrates
Moiré materials, such as twisted bilayer graphene, are materials generally formed by stacking two or more layers of 2D materials on top of each other with a small lattice mismatch. This slight mismatch creates a unique pattern known as the moiré pattern, which is...
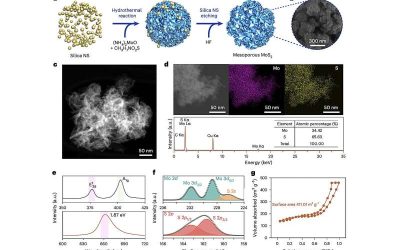
Mesoporous MoS₂ strategy boosts efficiency and stability of perovskite solar cells
The efficiency and performance of photovoltaics (PVs) have improved significantly over the past decades, which has led to an increase in the adoption of solar technologies. To further enhance the performance of solar cells, energy researchers worldwide have been...
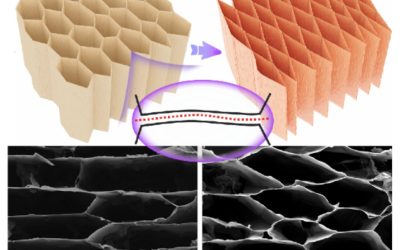
New fabrication strategy enhances graphene aerogel sensitivity and durability for human-machine interfaces
In recent years, researchers have synthesized various new materials that could be used to develop more advanced robotic systems, devices and human-machine interfaces. These materials include graphene aerogels, ultralight, porous and graphene-based materials comprised...
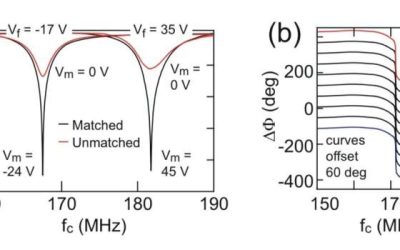
New varactor enhances quantum dot device measurements at millikelvin temperatures
The development of quantum computing systems relies on the ability to rapidly and precisely measure these systems' electrical properties, such as their underlying charge and spin states. These measurements are typically collected using radio-frequency resonators,...
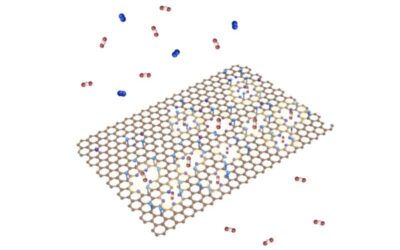
High-selectivity graphene membranes enhance CO₂ capture efficiency
Reducing carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions is a crucial step towards mitigating climate change and protecting the environment on Earth. One proposed technology for reducing CO₂ emissions, particularly from power plants and industrial establishments, is carbon capture.
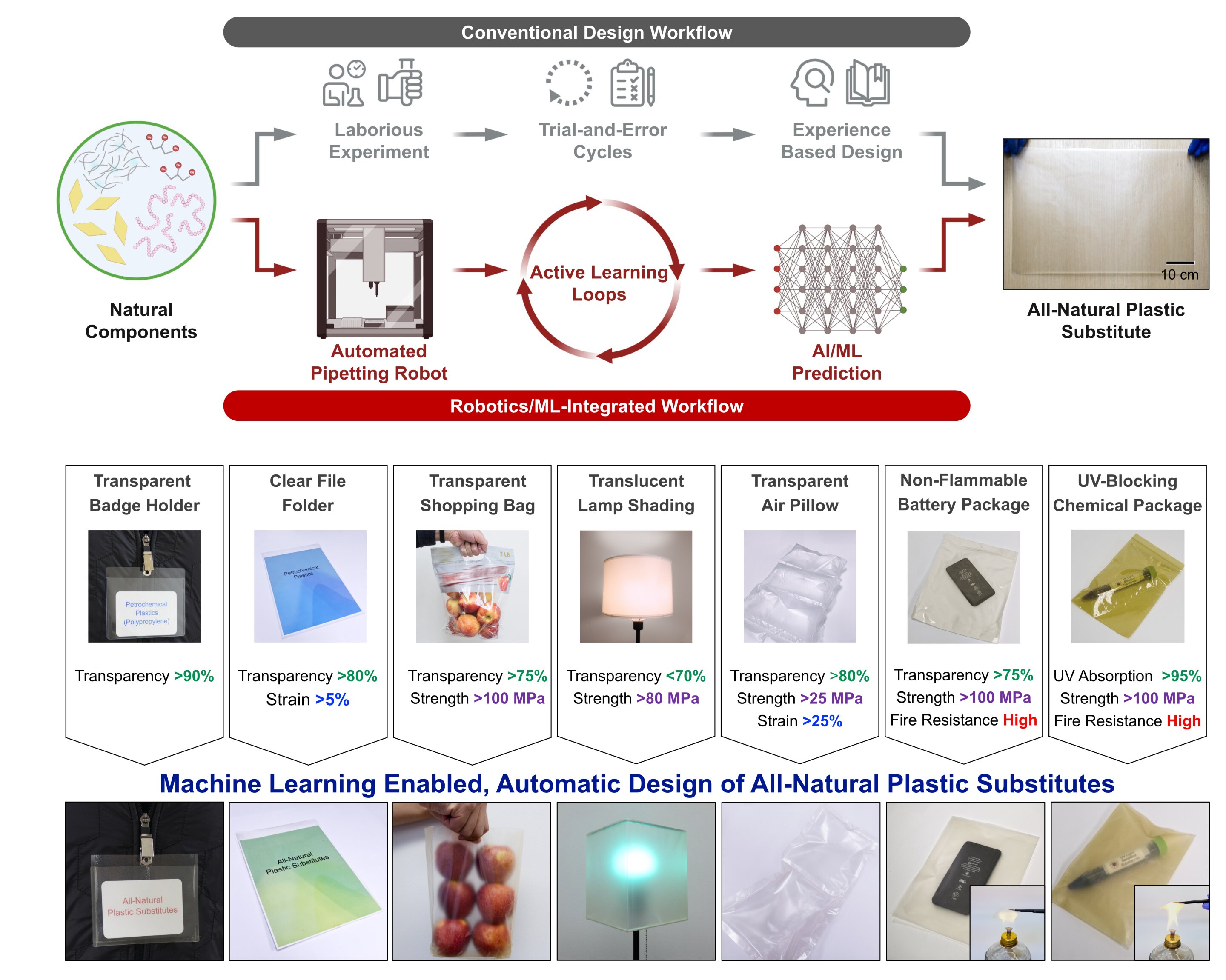
A machine learning-based approach to discover nanocomposite films for biodegradable plastic alternatives
The accumulation of plastic waste in natural environments is of utmost concern, as it is contributing to the destruction of ecosystems and is causing harm to aquatic life. In recent years, material scientists have thus been trying to identify all-natural alternatives...
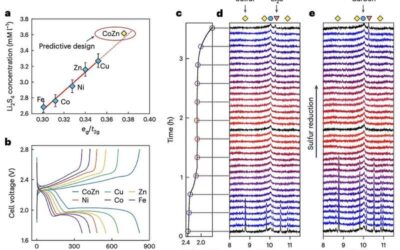
An approach to design high-power lithium sulfur batteries
Lithium–sulfur (Li–S) batteries are a promising alternative to lithium–ion batteries (LiBs), the most common rechargeable battery technology. As sulfur is abundant on Earth, these batteries could be cheaper and more environmentally friendly than LiBs, while also...
A method to fabricate long rolls of subnanocomposite dielectric polymers
Engineers and material scientists have been trying to develop increasingly advanced devices, to meet the growing needs of the electronics industry. These devices include electrostatic capacitors, devices that can store electrical energy in a dielectric between a pair...