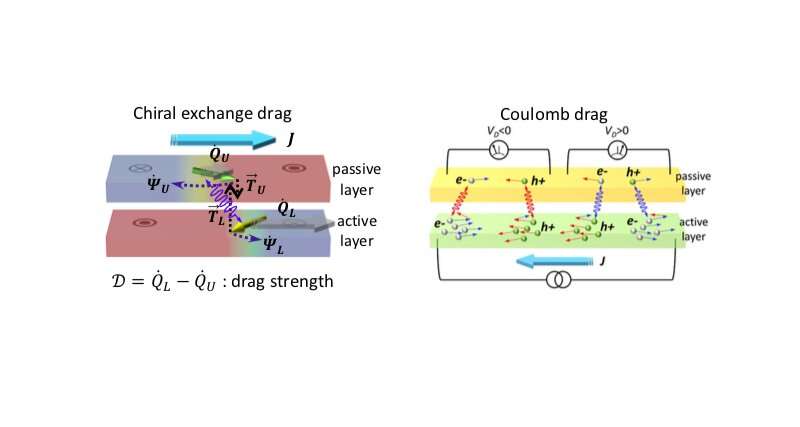
A quasiparticle is a disturbance or excitation (e.g. spin waves, bubbles, etc.) that behaves as a particle and could therefore be regarded as one. Long-range interactions between quasiparticles can give rise to a 'drag,' which affects the fundamental properties of...
Physics
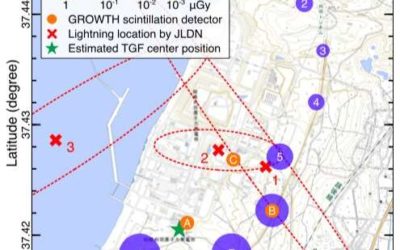
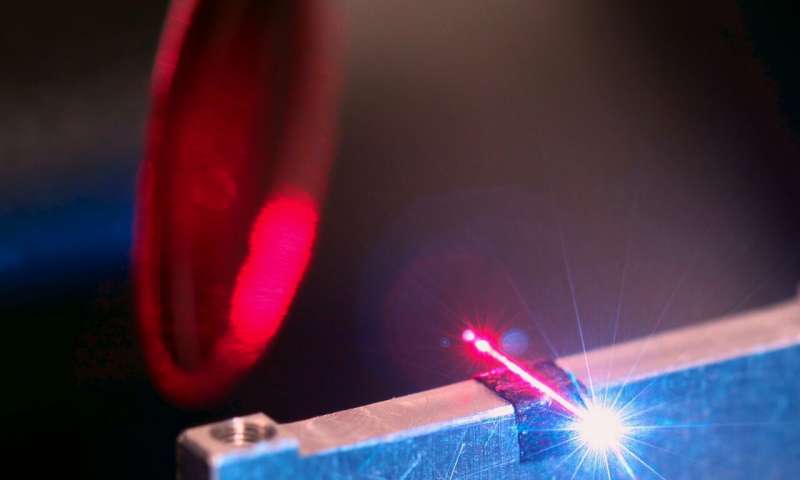
Studying downward terrestrial gamma-ray flashes during a winter thunderstorm
Lightning is a unique and fascinating phenomenon that has been studied for centuries. Although we now have a better understanding of this naturally occurring spectacle, many of its secrets are yet to be uncovered.
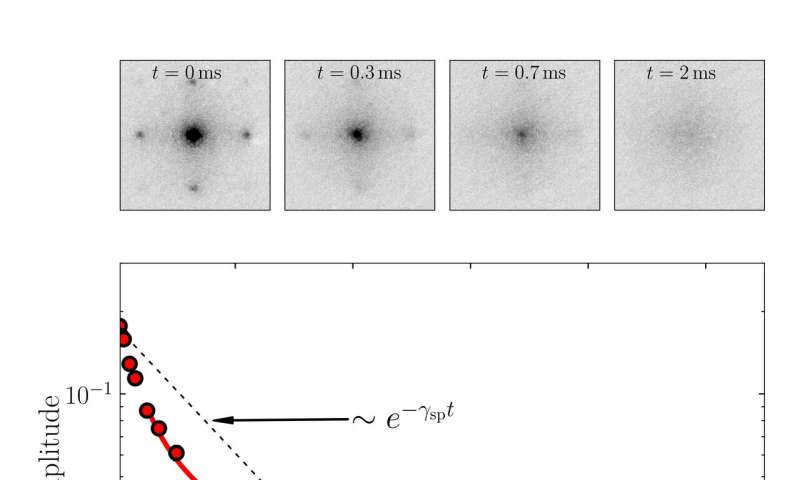
Studying the excitation spectrum of a trapped dipolar supersolid
Supersolids, solid materials with superfluid properties (i.e., in which a substance can flow with zero viscosity), have recently become the focus of numerous physics studies. Supersolids are paradoxical phases of matter in which two distinct and somewhat antithetical...
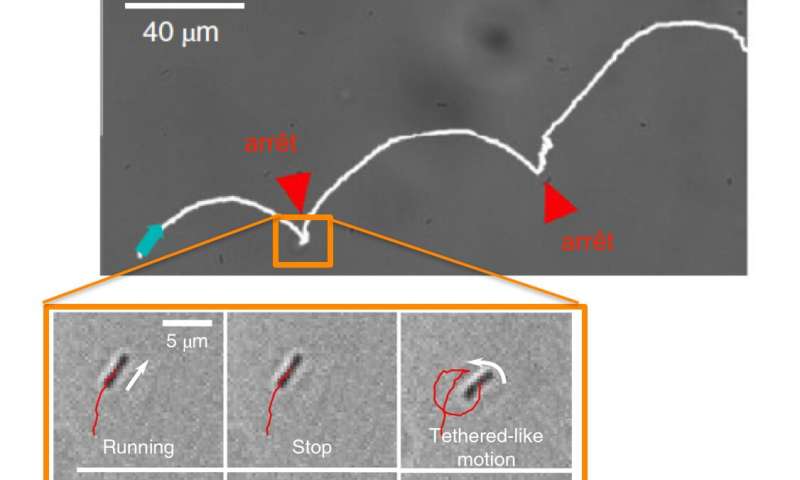
Studying the swimming patterns of bacteria near surfaces
A team of researchers at Université Côte d'Azur and Centre Scientifique de Monaco has recently carried out a study aimed at better understanding the near-surface swimming patterns of bacteria. Their paper, published in Nature Physics, could shed some light on how...
Study observes anomalous decay of coherence in a dissipative many-body system
In quantum physics, some of the most interesting effects are the result of interferences. Decoherence, or loss of coherence, occurs when a quantum system eventually loses the ability to produce interferences, due to external noise or coupling to a larger and...
Testing Hawking radiation in laboratory black hole analogues
Researchers at Weizmann Institute of Science and Cinvestav recently carried out a study testing the theory of Hawking radiation on laboratory analogues of black holes. In their experiments, they used light pulses in nonlinear fiber optics to establish artificial event...
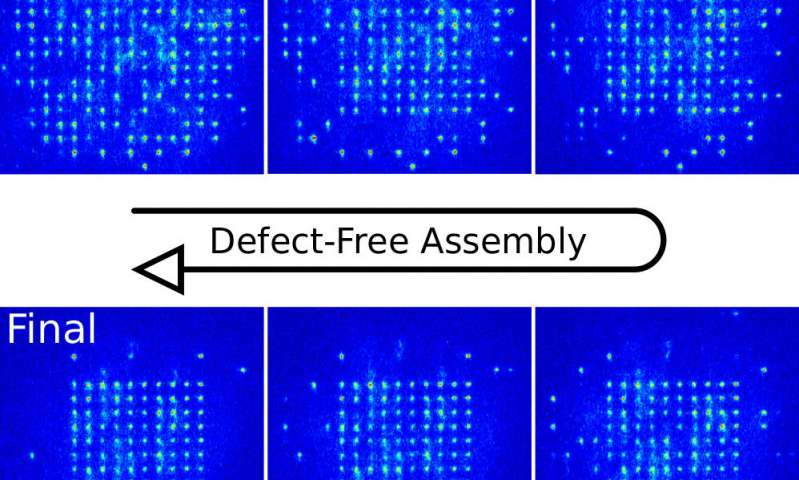
The defect-free assembly of 2-D clusters with over 100 single-atom quantum systems
Researchers at Technische Universität Darmstadt have recently demonstrated the defect-free assembly of versatile target patterns of up to 111 single-atom quantum systems. Their findings, outlined in a paper published in Physical Review Letters, could drive...
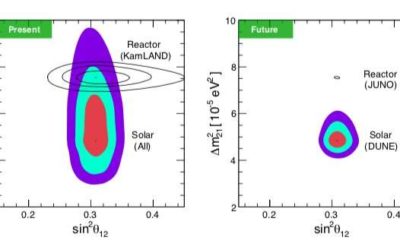
The DUNE experiment could lead to new discoveries about solar neutrinos
The Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment (DUNE) is an international research collaboration aimed at exploring topics related to neutrinos and proton decay, which should start collecting data around 2025. In a recent study featured in Physical Review Letters, a team of...
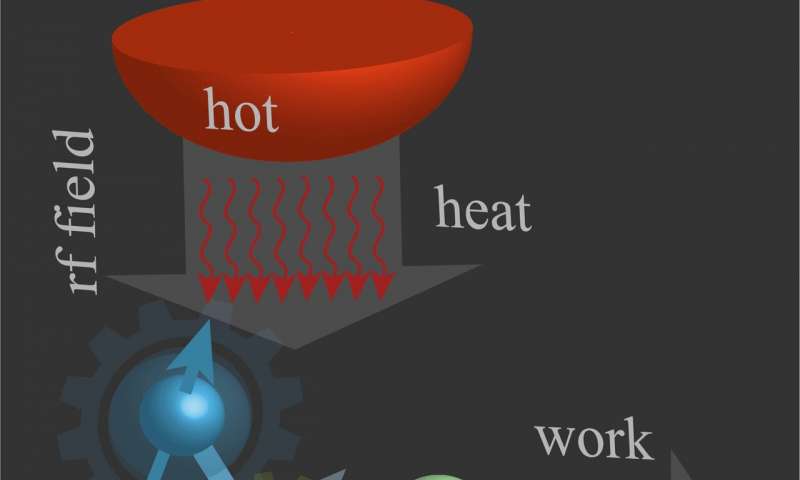
The experimental demonstration of a spin quantum heat engine
The theoretical notion of a 'quantum heat engine' has been around for several decades. It was first introduced around sixty years ago by Scovil and Schulz-DuBois, two physicists at Bell Labs who drew an analogy between three-level masers and thermal machines.
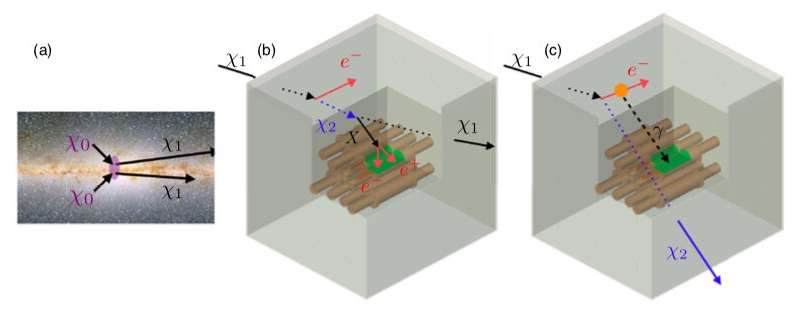
The first direct search for inelastic boosted dark matter with a terrestrial detector
A team of researchers in the Republic of Korea, the U.S., Brazil, Indonesia and the U.K. have recently carried out a direct search for inelastic boosted dark matter (IBDM) using a terrestrial detector. Their study, published in Physical Review Letters (PRL), is the...