Over the past decades, roboticists have introduced a wide range of systems with distinct body structures and varying capabilities. As the number of developed robots continuously grows, being able to easily learn about these many systems, their unique characteristics,...
Robotics
Sony’s aibo dog could soon walk quietly and perform elaborate dance routines
Aibo, the cute-looking robot puppy developed by Sony, was designed to be a household companion. The robot can already emulate many of the movements and behaviors of real dogs, such as walking on four legs, responding when it is called by its name, reacting to toys,...
Robots with eyes more likely to be perceived as having a ‘mind’
Over the past few years, engineers have developed increasingly advanced robotic systems already introduced in some public spaces and could soon be deployed in home environments. Many of these robots are humanoids, meaning that their body structure and physical...
A new high-quality dataset to train robotics algorithms on textile manipulation tasks
Many industrial processes and household tasks currently completed by humans entail the manipulation of textiles, including clothes, sheets, towels, cloths and other fabric-based objects. Most robotic systems developed so far do not reliably manipulate all types of...
Humanoid robots can swiftly get up after they fall with new learning framework
Humanoid robots, which have a body structure that mirrors that of humans, could rapidly and effectively tackle a wide range of tasks in real-world settings. These robots and their underlying control algorithms have improved considerably in recent years. Many of them...
H-shaped bionic robot mimics cheetah’s sprint using electric charge
In recent years, roboticists and computer scientists have developed a wide range of systems inspired by nature, particularly by humans and animals. By reproducing animal movements and behaviors, these robots could navigate real-world environments more effectively.
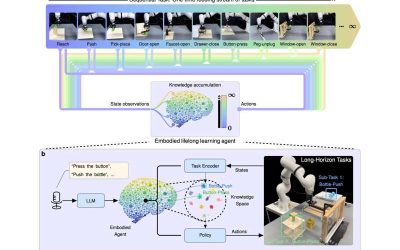
Continuous skill acquisition in robots: New framework mimics human lifelong learning
Humans are known to accumulate knowledge over time, which in turn allows them to continuously improve their abilities and skills. This capability, known as lifelong learning, has so far proved difficult to replicate in artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics systems.
Neuromechanics-inspired control solution boosts robot adaptability
To be successfully deployed on a large-scale and in a wide range of real-world settings, robots should be able to rapidly adjust their movements while interacting with humans and their surroundings, responding to changes in their environment. Many robots developed so...
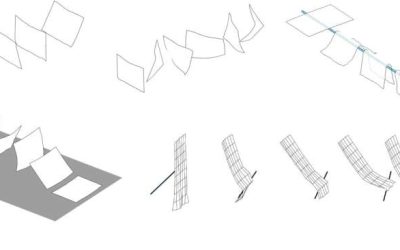
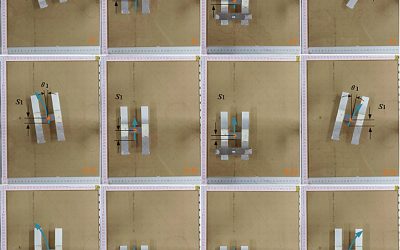
Modular robot design uses tethered jumping for planetary exploration
Recent technological advances have opened new possibilities for the development of robotic systems, including spacecraft for the exploration of other planets. These new systems could ultimately contribute to our understanding of our galaxy and the unique...
Smart robotic wheelchair offers enhanced autonomy and control
Recent advances in the fields of human-infrastructure interaction, electronic engineering, robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) have opened new possibilities for the development of assistive and medical technologies. These include devices that can assist...