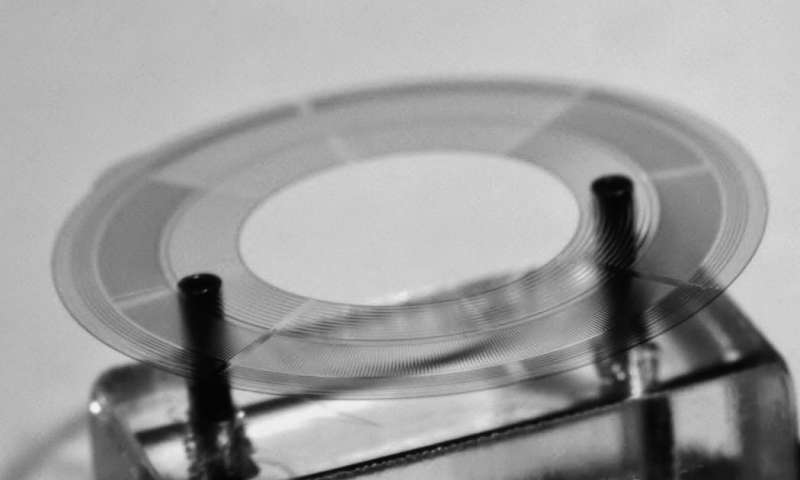
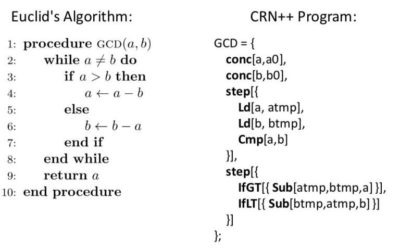
Synthetic biology is a relatively new area of research that could significantly impact a number of fields, including biology, nanofabrication and medicine. A primary challenge in this emerging field is that of embedding computation in molecular contexts, in situations...
TECHXPLORE
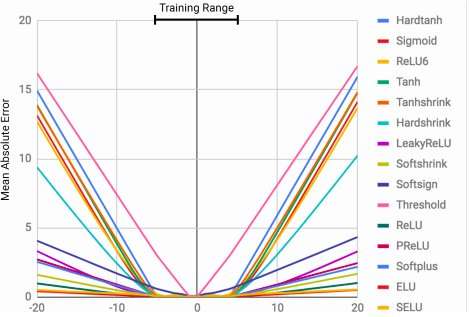
DeepMind researchers develop neural arithmetic logic units (NALU)
The ability to represent and manipulate numerical quantities can be observed in many species, including insects, mammals and humans. This suggests that basic quantitative reasoning is an important component of intelligence, which has several evolutionary advantages.
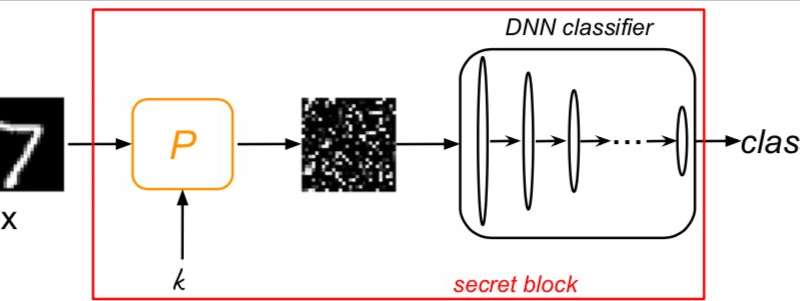
Defense against adversarial attacks using machine learning and cryptography
Researchers at the University of Geneva have recently developed a new defense mechanism that works by bridging machine learning with cryptography. The new system, outlined in a paper pre-published on arXiv, is based on Kerckhoffs' second cryptographic principle, which...
Droidbugs: A new benchmark to evaluate automated repair methods for Android apps
Automated program repair (APR) is an emerging field of research that sets out to develop methods of fixing software bugs automatically, without intervention by human programmers. After development, APR techniques are typically evaluated on several benchmarks,...
Emotion recognition based on paralinguistic information
Researchers at the University of Texas at Arlington have recently explored the use of machine learning for emotion recognition based solely on paralinguistic information. Paralinguistics are aspects of spoken communication that do not involve words, such as pitch,...
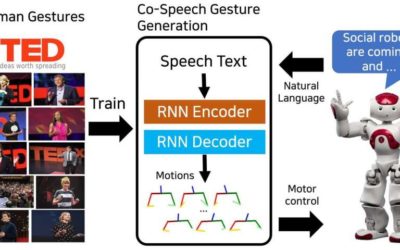
End-to-end learning of co-speech gesture generation for humanoid robots
Researchers at the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) in South Korea have recently developed a neural network model that can generate sequences of co-speech gestures. Their model, trained on 52 hours of TED talks, successfully produced...
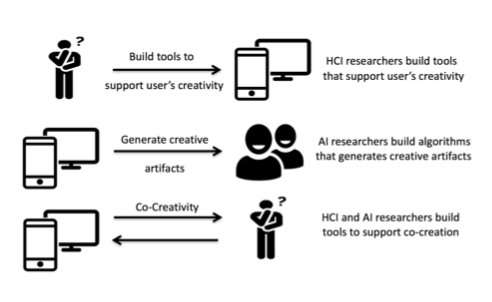
Evaluating creativity in computational co-creative systems
Computer programs assist humans in a variety of ways, including in their creative endeavors. Researchers at UNC Charlotte and the University of Sydney have recently developed a new framework for evaluating creativity in co-creative systems in which humans and...
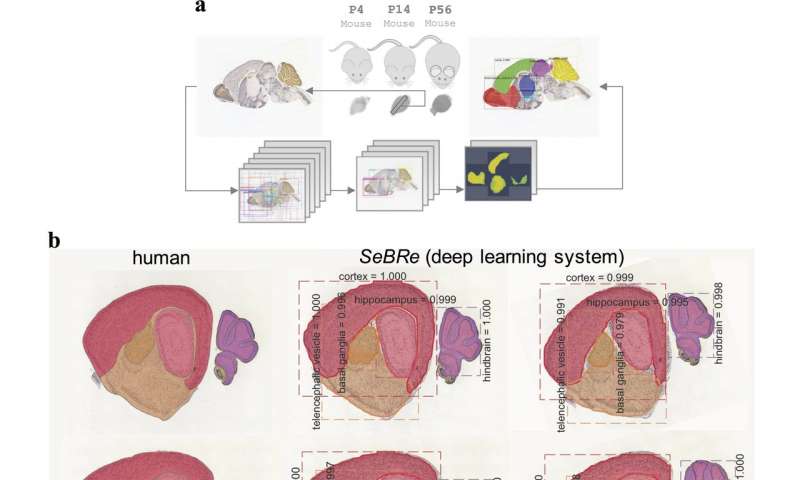
Developing brain atlas using deep learning algorithms
A team of researchers from the Brain Research Institute of the University of Zurich and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) have developed a fully automated brain registration method that could be used to segment brain regions of interest in mice.
Evaluating linear and rotational microhydraulic actuators driven by electrowetting
Microhydraulic actuators are designed to convert electrical power into mechanical power on a microscale with more power density and higher efficiency. Essentially, these new actuators work by combining the surface tension force derived from a large number of droplets...
BrambleBee: An autonomous robot to pollinate bramble plants
Natural pollinators, particularly honey bees, are disappearing at an unprecedented rate. This poses serious risks for agriculture, the economy, and the sustenance of humans and animals. Bees are the primary pollinators of a vast variety of crops, so their...