The term dementia is used to describe various debilitating neurological disorders characterized by a progressive loss of memory and a decline in mental abilities. Estimates suggest that over 55 million people worldwide are currently living with dementia, and...
Alzheimer’s disease & dementia
Nasal microbiome may help explain link between olfactory dysfunction and cognitive decline
As humans age, particularly after middle age, their brain functions, cognitive abilities and memory can deteriorate to varying degrees. Aging-related disorders marked by cognitive decline, particularly dementia, have become increasingly widespread over the past decades.
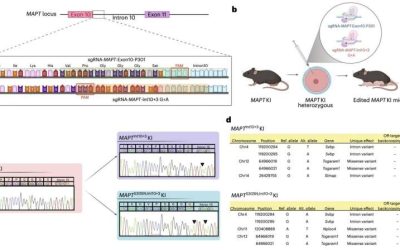
Genetically modified mice hint at tau hyperphosphorylation’s early role in neurodegenerative diseases
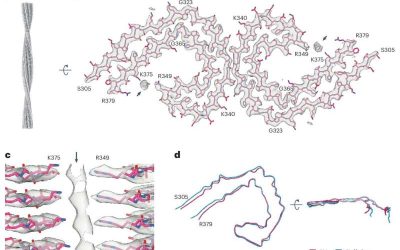
Tau is a microtubule-associated protein that helps to stabilize the structure of neurons, specifically by supporting microtubules, cylindrical structures that contribute to cell motility, intracellular transport and the maintenance of a cell's shape over time. While...
Study explores association between Tau filaments and extracellular vesicles in Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a debilitating neurodegenerative disorder associated with a progressive decline in memory and mental abilities, which can significantly hinder people's ability to complete daily tasks. Past studies found that patients diagnosed with AD, as...
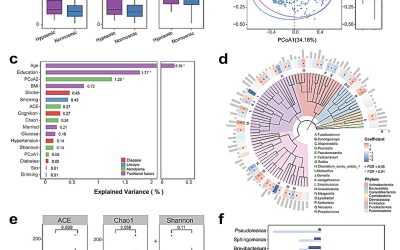
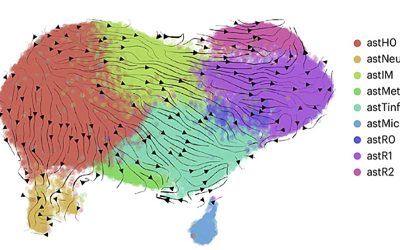
Detailed mapping shows how astrocytes change throughout the progression of Alzheimer’s disease
Astrocytes are star-shaped glial cells in the central nervous system that support neuronal function, maintain the blood-brain barrier, and contribute to brain repair and homeostasis. The evolution of these cells throughout the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD)...
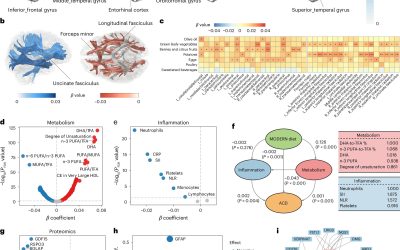
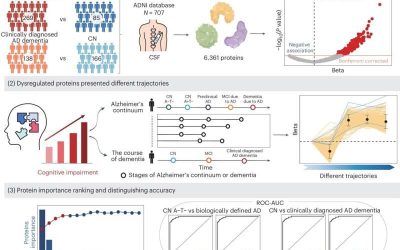
Study identifies new biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease
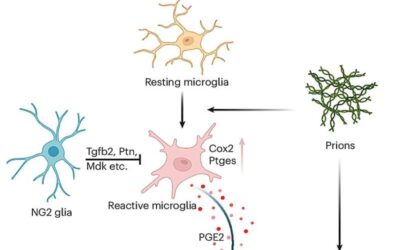
NG2 glia cells shown to protect against prion-induced neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration
Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD) are highly debilitating medical conditions arising from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Studies exploring the neural underpinnings of these diseases and how...
Perivascular cells could induce microglial malfunction associated with Alzheimer’s disease
Microglia are primary immune cells that safeguard the mammalian brain, partly by devouring or 'phagocytosing' pathogens and toxic debris. Recent genetic studies have consistently highlighted the role of microglia in the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and...
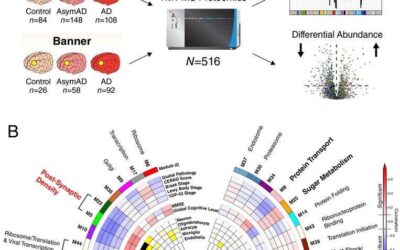
Study unveils new protein-related changes in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease
Researchers at Emory University School of Medicine have recently carried out a large-scale analysis of the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Their findings, published in Nature Neuroscience, unveiled a series of disease-related changes in protein...