Clock genes are a set of genes known to contribute to the regulation of the human body's internal 24-hour cycle, also known as the circadian rhythm. One of these genes is the so-called CLOCK gene, a protein that regulates the activity of other genes, contributing to...
Genetics
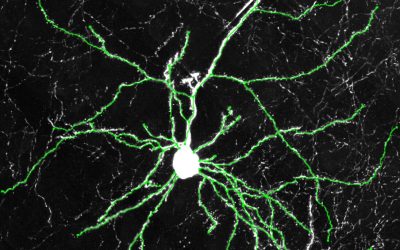
Study uncovers gene networks driving the development of distinct neuron subtypes in the human cerebral cortex
The human brain is known to contain a wide range of cell types, which have different roles and functions. The processes via which cells in the brain, particularly its outermost layer (i.e., the cerebral cortex), gradually become specialized and take on specific roles...
Study finds an overlap between genes linked to subjective well-being and psychiatric disorders
In psychology, the term subjective well-being (SWB) is used to describe the extent to which different people feel happy and satisfied with their lives. While some studies have found that there is a link between SWB and the diagnosis of some psychiatric disorders, such...
Genes, income and health: Unraveling the complex connections
Past research studies have consistently found that there are disparities in the health outcomes of people from different socio-economic backgrounds. More recently, some findings hinted at the possibility that genetics also play a role in the widely documented...
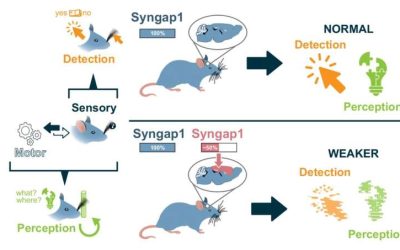
Mouse model unveils dynamics through which SYNGAP1 gene supports cognitive function
The SYNGAP1 gene, which supports the production of a protein called SynGAP (Synaptic Ras GTPase-Activating Protein), is known to play a key role in supporting the development of synapses and neural circuits (i.e., connections between neurons). Mutations in this gene...
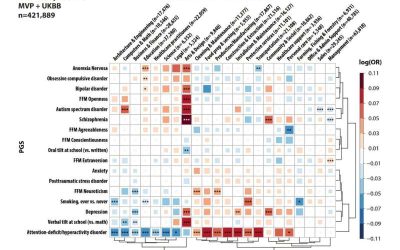
Study explores link between people’s professions and their genetic predisposition to neuropsychiatric traits
Polygenic scores (PGS) are metrics used to estimate the genetic predisposition of people to developing specific mental health conditions, personality traits or diseases. In recent years, these metrics have often been used to investigate the intricate connections...
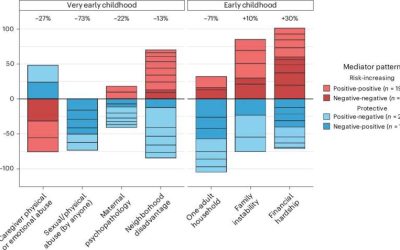
DNA methylation mediates the link between childhood adversity and depression, study suggests
Past psychology research suggests that there is a strong relationship between difficult experiences during childhood and the development of depressive symptoms. In fact, statistics suggest that adverse experiences during childhood can double the risk of being...
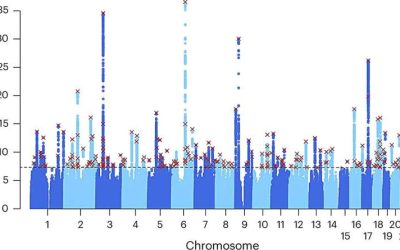
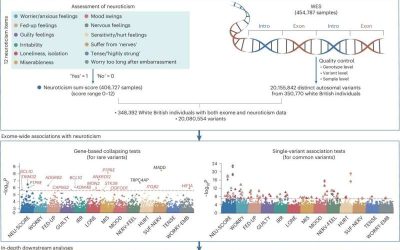
Large-scale genetic study identifies 14 genes linked to neuroticism
Neuroticism is a key personality trait described by well-established psychological theories, associated with a tendency towards emotional instability and negative emotions. Past studies found that this personality trait often goes hand in hand with various mental...
A histone post-translational modification linked to lifelong susceptibility to stress in mice
Chemical changes to histones, the proteins that help to pack and organize DNA inside cells, play a key role in determining what genes will be consistently activated over the course of an animal or human's life. Past studies have shed light on some chemical alterations...
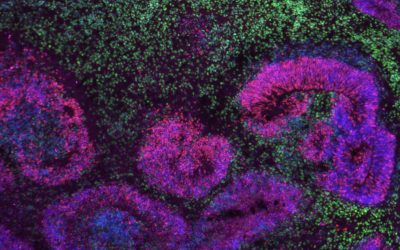
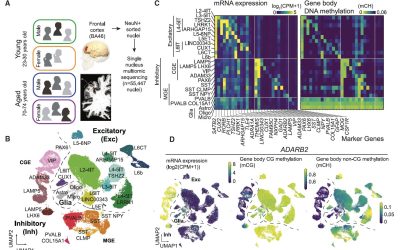
Study explores the cell-type-specific effects of aging and sex on human cortical neurons
Aging is known to have profound effects on the human brain, prompting changes in the composition of cells and the expression of genes, while also altering aspects of the interaction between genes and environmental factors. While past neuroscience studies have...