Over the past decades, numerous studies have investigated the neural and cognitive processes underpinning intergroup conflict, as this could help to explain what fuels belligerent behavior, political clashes, and wars. While these works gathered some interesting...
MEDICALXPRESS
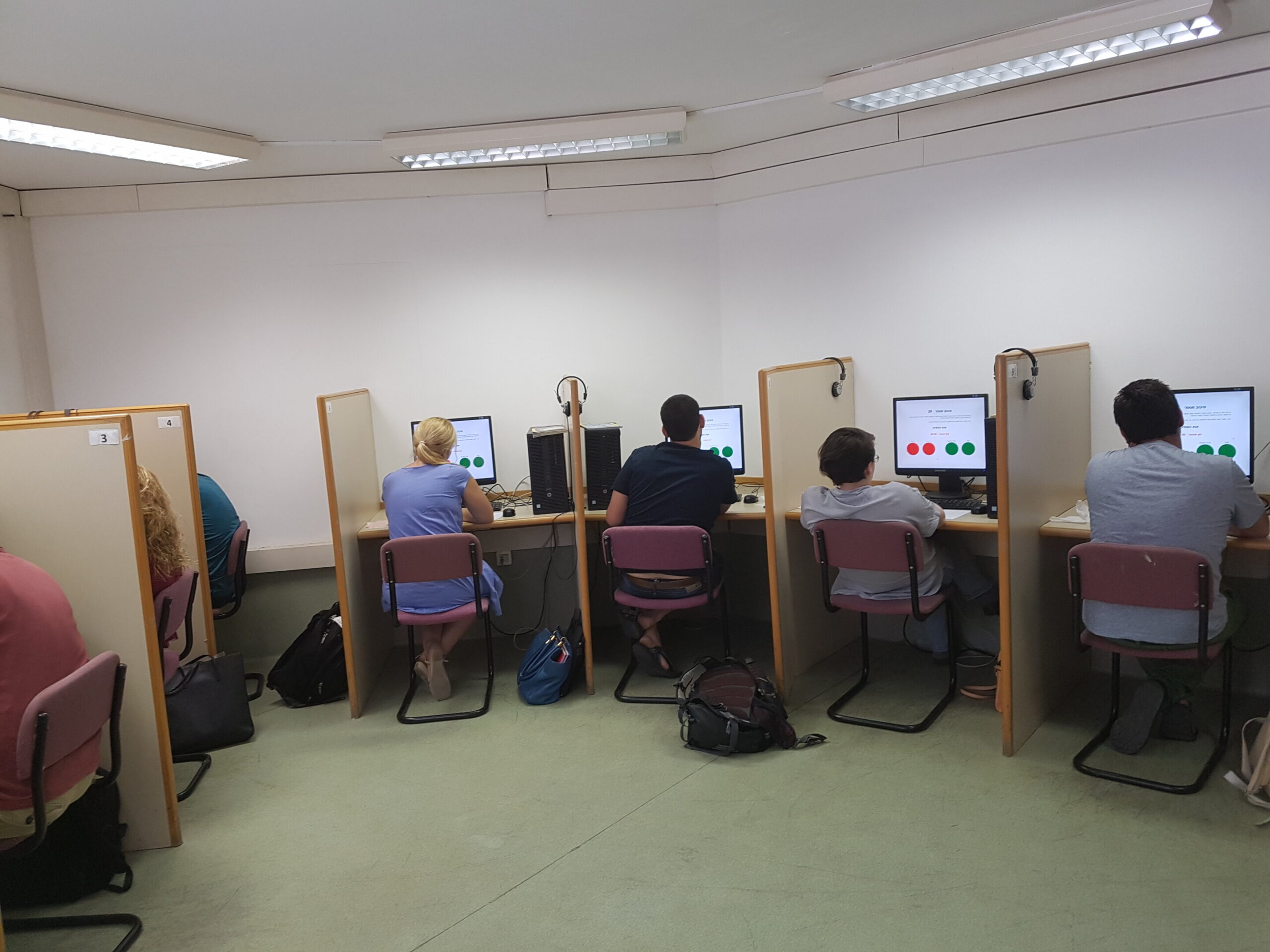
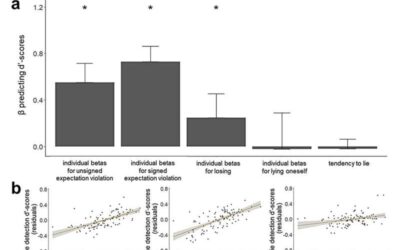
Exploring the factors that influence people’s ability to detect lies online
The internet has given rise to new forms of deceit and misinformation, including phishing attacks, romance scams and fake news. While many psychological studies have investigated the factors that influence people's ability to tell if others are lying in person, lie...
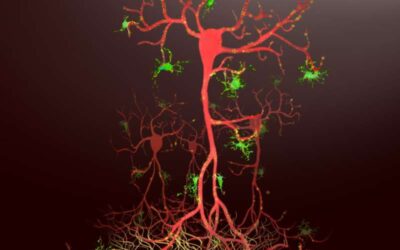
Reorganization of prefrontal cortex circuitry during adolescence enables cognitive maturation of mice
Neuroscientists have been trying for decades to understand how the brains of humans and other animals develop throughout the lifespan. While their work has gathered much insight into brain maturation and development, many questions remain unanswered.
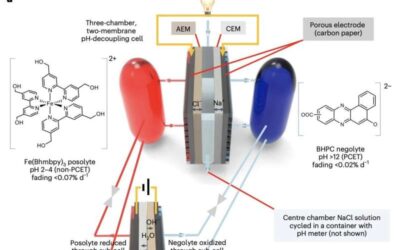
The realization of aqueous flow batteries with mild pH decoupling
Technologies that can store the energy produced by photovoltaics and wind turbines could play a key role in the decarbonization of the energy sector. The operation of both solar cells and wind turbines relies on suitable weather conditions, and grid-scale energy...
Study offers insights into neural mechanisms involved in progression from aggressive motivation to action
The social behaviors of humans and animals often unfold over two distinct phases, namely a motivational and an action phase. The first of these phases entails instinctual and reward-seeking mental states, characterized by sexual or aggressive drives to perform...
Dopamine fluctuations in distinct brain subregions predict rewards over a range of time-scales
Previous neuroscience studies suggest that transient increases in brain dopamine are critical signals for learning about reward, and the motivation to obtain more rewards. Researchers at University of California San Francisco carried out a study exploring transient...
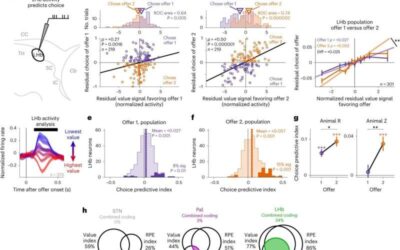
Study unveils the role of a neural substrate in the lateral habenula in value-based decision-making
In their everyday lives, humans often weigh the value of different options and decide how to act based on this mental evaluation. This process, known as value-based decision-making, has been the topic of numerous studies rooted in psychology, neuroscience and economics.
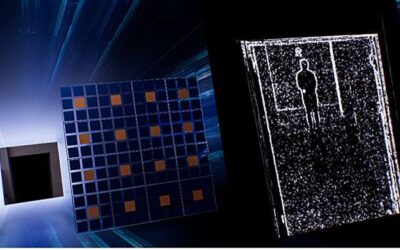
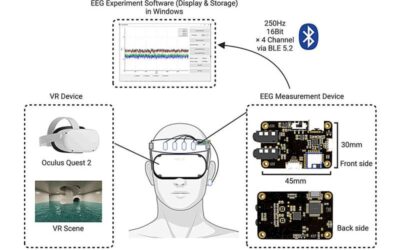
A low-cost system to collect EEG measurements during VR experiences
Recent technological advances have enabled the development of increasingly advanced systems and devices for measuring brain activity in both research and medical settings. A concept that has been widely explored and yet not effectively realized is that of collecting...
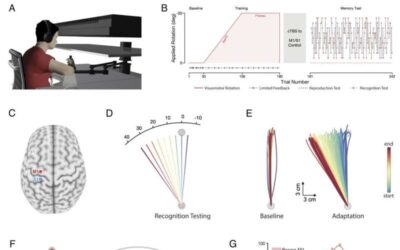
Exploring how the somatosensory cortex contributes to the encoding of newly learned movements
The somatosensory cortex is a brain region known to play a role in the detection of tactile information, changes in temperature, and pain sensations. Some recent studies found that this crucial brain region is also involved in the human ability to learn and retain new...
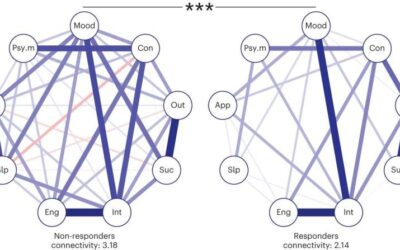
Network analysis highlights the key role of plasticity in the transition from depression to mental health
Surveys and statistics suggest that mental illnesses are becoming increasingly widespread, as the number of people worldwide accessing mental health services has increased in recent years. Understanding the factors that can predict well-being and contribute to the...