Humans are known to perceive the environment around them differently based on the situation they are in and their own feelings and sensations. Internal states, such as fear, arousal or hunger can thus affect the ways in which sensory information is processed and...
MEDICALXPRESS
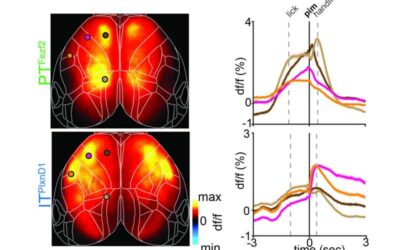
Study unveils the distinct activation patterns of glutamatergic projection neurons in the cortex of living mice
The cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the mammalian brain, is known to play a key role in numerous higher-level processes, including language, memory and decision-making. While countless studies have explored its structure and function, imaging its neuronal dynamics...
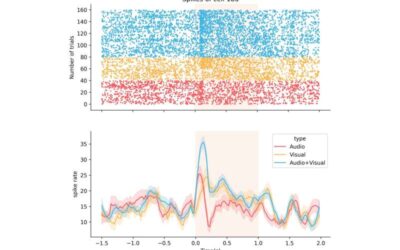
Exploring the integration of audiovisual information in the primate amygdala and adjacent regions
Humans and other primates can jointly make sense of different types of sensory information, including sounds, smells, shapes and so on. By integrating sensory stimuli in the brain, they can better understand the world around them, detecting potential threats, food and...
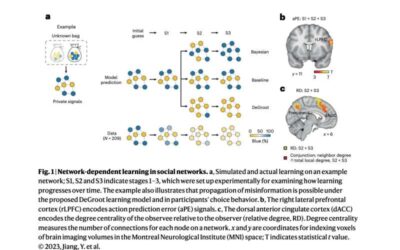
Exploring the neural mechanisms behind how social networks shape our decisions
Over the past decade or so, social scientists have been trying to understand how social networks can influence people's beliefs and behavior. Despite the many studies on this topic, currently very little is known about how the human brain makes decisions in networked...
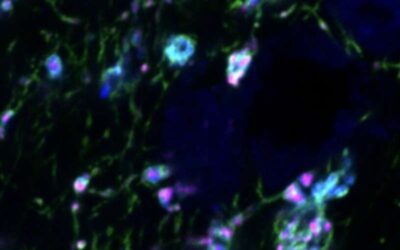
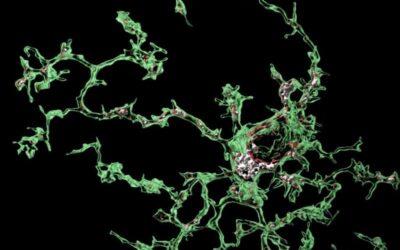
Perivascular cells could induce microglial malfunction associated with Alzheimer’s disease
Microglia are primary immune cells that safeguard the mammalian brain, partly by devouring or 'phagocytosing' pathogens and toxic debris. Recent genetic studies have consistently highlighted the role of microglia in the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and...
Study hints at the promise of non-hallucinogenic LSD for treating mood disorders
Mood disorders are mental health conditions characterized by persistently dysregulated moods, such as recurring feelings of depression or euphoria. According to statistics by the National Institutes of Health, approximately 1 in 5 people in the United States will...
A wearable device that records single-neuron activity while humans are walking
New technologies can greatly advance research in various fields, including medicine and neuroscience. In recent years, for instance, engineers have created increasingly sophisticated devices to record brain activity and other biological signals with high precision.
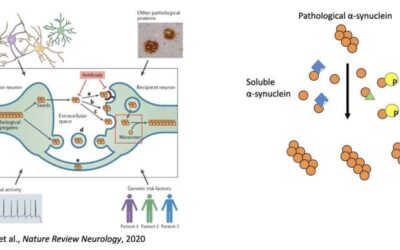
Study unveils mechanism regulating the transmission of a protein associated with the progression of Parkinson’s disease
Proteins, long polymers comprised of smaller constituents known as amino acids, play a crucial role in the functioning of the human body. Over the course of a human's life, these "strings" of proteins fold into unique 3D structures or conformations, and this folding...
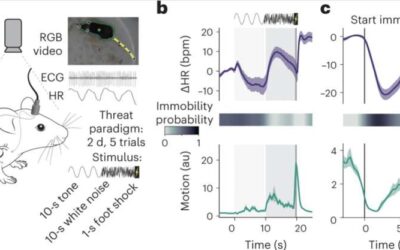
A framework characterizing the cardio-behavioral responses associated with fear and anxiety
Anxiety disorders are becoming increasingly common, with estimates suggesting that almost one in three people in the U.S. will experience high levels of anxiety at some point in their life. Anxiety is essentially a feeling of unease, worry or psychological discomfort,...
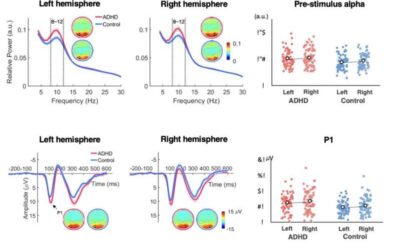
A single dose of methylphenidate does not affect the contextual visual perception of children with ADHD, shows study
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder estimated to affect approximately 2.5% of children and adults worldwide. The disorder is characterized by the inability to pay attention to stimuli for prolonged periods of time, along...