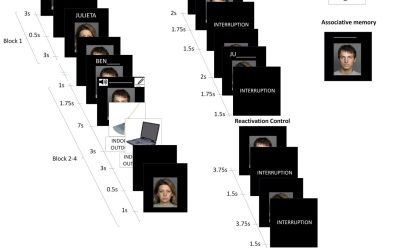
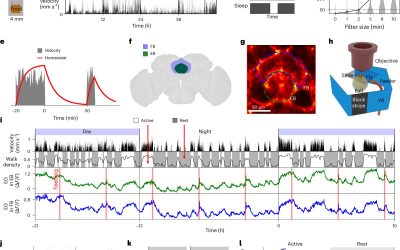
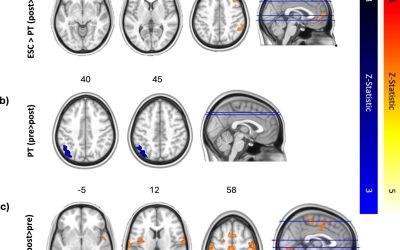
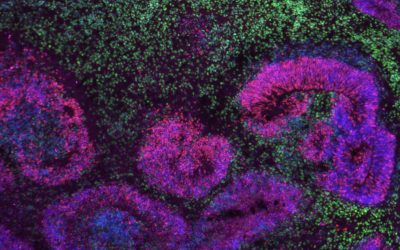
Most humans can recall specific events and past experiences for long periods of time. This capability, referred to as episodic memory, is known to be in great part supported by the activity of neurons in the hippocampus and medial temporal lobe.
MEDICALXPRESS
Exposure to gun violence linked to widespread psychological distress in US adults
Psychology research has consistently emphasized the adverse effects of enduring or witnessing violent acts, showing that exposure to different forms of violence can increase the risk of developing various mental health conditions. Many of the most gruesome violent...
Glial cells may play key role in managing sleep and metabolism, fruit fly study suggests
Homeostasis is the ability of living organisms to maintain stable internal conditions, such as temperature, hydration and blood sugar levels, irrespective of any changes in their surroundings. Homeostatic mechanisms also regulate behaviors that are central to the...
The words of health care providers during prenatal care visits can influence how parents see their children
Pregnancy is often a unique experience, marked by anticipation and mental representations of what will happen after a baby's birth. Understanding how people's experiences while pregnant influence their parenting skills and how they perceive their children after birth...
Psilocybin better preserves depressed patients’ emotional response to music than standard drug, study finds
Depression is among the most widespread mental health disorders worldwide, typically characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, a lack of interest in daily activities and dysregulated sleep and/or eating habits. There are now a wide range of pharmacological...
Distinct neuron populations in the hypothalamus encode states associated with predator-related threats
The ability to detect imminent threats and execute behaviors aimed at protecting oneself, such as hiding, running away or defending oneself, is central to the survival of most animal species. A region of the mammalian brain known to play a key role in threat response...
Study uncovers gene networks driving the development of distinct neuron subtypes in the human cerebral cortex
The human brain is known to contain a wide range of cell types, which have different roles and functions. The processes via which cells in the brain, particularly its outermost layer (i.e., the cerebral cortex), gradually become specialized and take on specific roles...
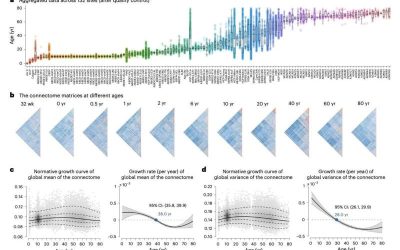
Large-scale study explores lifespan changes in the human brain’s functional connectivity
From birth to the last moments of life, the human brain is known to change and evolve significantly, both in terms of its physical organization (i.e., structural connectivity) and the coordination between different brain regions (i.e., functional connectivity)....
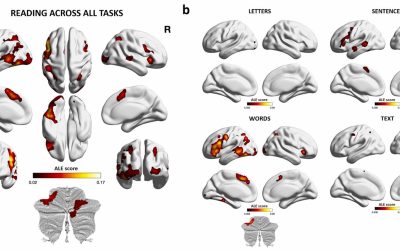
A comprehensive look at what happens in the brain when we’re reading
Reading is a highly valuable skill that allows humans to acquire new knowledge, pursue an education and complete a wide range of real-world tasks. Many past psychology and neuroscience studies set out to better understand the neural underpinnings of reading and the...
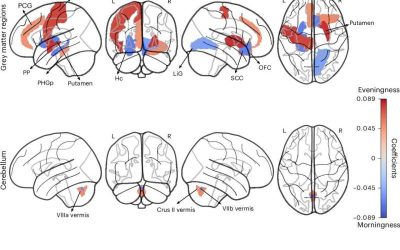
New insight into the neurobiological roots of being a ‘morning person’ or ‘night owl’
Human beings exhibit marked differences in habits, lifestyles and behavioral tendencies. One of these differences, known as chronotype, is the inclination to sleep and wake up early or alternatively to sleep and wake up late.