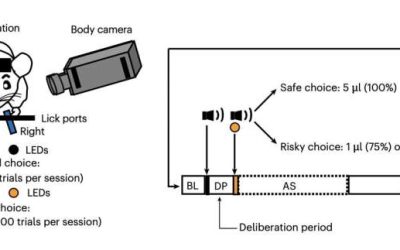
To survive in complex and unpredictable environments, humans and other animals need to learn to predict the consequences of their actions, so that they can reduce risks and maximize their gains. In humans, this risk evaluation process is known to be highly...
MEDICALXPRESS
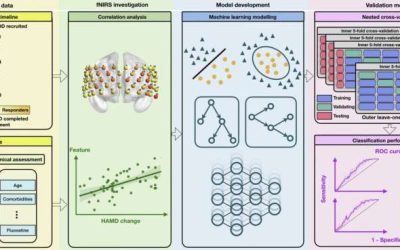
Using machine learning to predict how people diagnosed with major depressive disorder respond to treatment
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a debilitating mental health condition characterized by persistent low mood, loss of interest in everyday activities, appetite changes, sleep disturbances and, in extreme cases, suicidal thoughts. Millions of individuals worldwide...
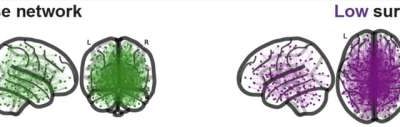
Meditation, art and nature: Neuroimaging reveals distinct patterns of brain activation
Past research suggests that meditation and exposure to art or nature can positively impact people's well-being and brain health, in some cases even reducing stress and supporting the processing of emotions. Yet most past studies focused on each of these experiences...
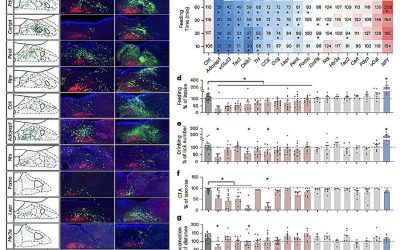
Neuronal subtypes study uncovers parallel gut-to-brain pathways that regulate feeding behaviors
The ability to regulate one's own food intake is essential to the survival of both humans and other animals. This innate ability ensures that the body receives the nutrients it needs to perform daily activities, without significantly exceeding calorie intake, which...
Brain network model can predict when people will feel surprised
Surprise is a key human emotion that is typically felt when something that we are witnessing or experiencing differs from our expectations. This natural human response to the unexpected has been the focus of numerous psychology studies, which uncovered some of its...
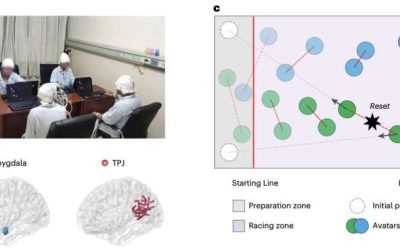
Study gathers new insight into the neural underpinnings of human cooperation
Collaboration and cooperation are key elements of human social interactions, which can contribute to the efficient achievement of shared goals. While many psychology and neuroscience studies have investigated cooperative behaviors among humans, the complex interplay...
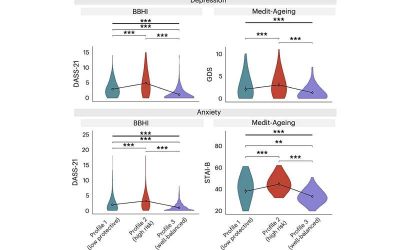
Study uncovers psychological profiles associated with mental and brain health in middle-aged and older adults
As humans age, their brain function can progressively decline and they become more vulnerable to developing neurodegenerative diseases, such as dementia. Dementia and other progressive neurological conditions can significantly impair their memory, thinking skills and...
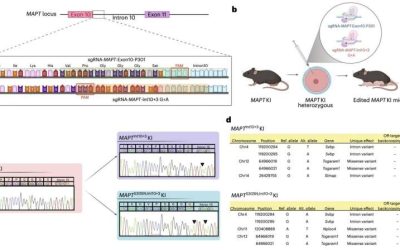
Genetically modified mice hint at tau hyperphosphorylation’s early role in neurodegenerative diseases
Tau is a microtubule-associated protein that helps to stabilize the structure of neurons, specifically by supporting microtubules, cylindrical structures that contribute to cell motility, intracellular transport and the maintenance of a cell's shape over time. While...
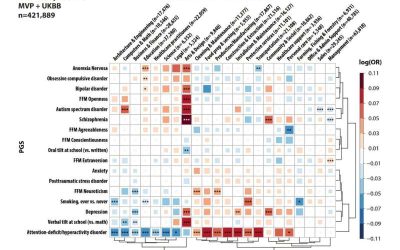
Study explores link between people’s professions and their genetic predisposition to neuropsychiatric traits
Polygenic scores (PGS) are metrics used to estimate the genetic predisposition of people to developing specific mental health conditions, personality traits or diseases. In recent years, these metrics have often been used to investigate the intricate connections...
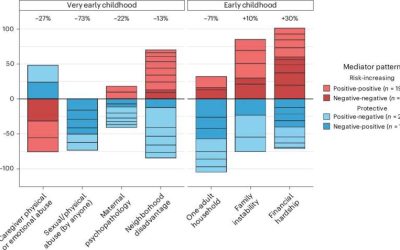
DNA methylation mediates the link between childhood adversity and depression, study suggests
Past psychology research suggests that there is a strong relationship between difficult experiences during childhood and the development of depressive symptoms. In fact, statistics suggest that adverse experiences during childhood can double the risk of being...