Fatigue, which can be defined as lacking energy and the motivation to do things during the day, is a very common symptom that most humans will experience at least once in their life. While it is sometimes linked to medical conditions, in most cases it is caused by...
Neuroscience
Study finds that the release of endocannabinoids is mediated by postsynaptic synucleins
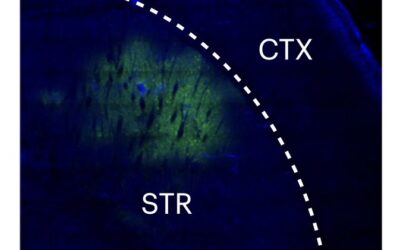
Endogenous cannabinoids, also known as endocannabinoids, are neurotransmitters (i.e., chemical messengers naturally produced by the body) that transmit specific signals from one neuron to another. These neurotransmitters are known to support several vital...
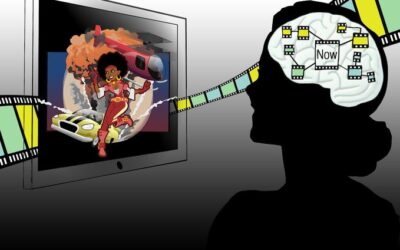
Study finds that the human brain reactivates mental representations of past events during new experiences
Neuroscience studies have showed that as mice and other rodents navigate a maze, their brain often "replays" relevant past events. This mental replaying of events, such as the route taken until reaching their current position, could help rodents create a mental map of...
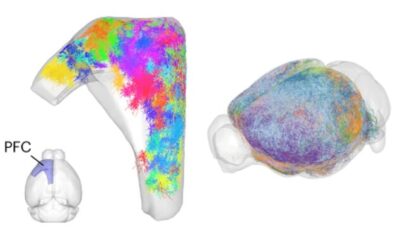
Study reconstructs thousands of dendrites and axons in the mouse prefrontal cortex
The prefrontal cortex (PFC) is a crucial part of the mammalian brain, known to be involved in decision-making, planning, complex social behavior and integrating the activity of other brain regions. While countless neuroscience studies have investigated the function...
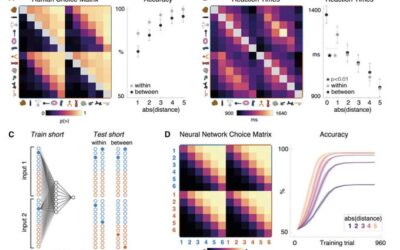
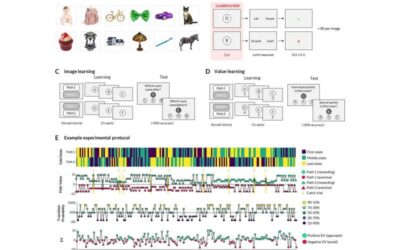
Exploring how the human brain and artificial neural networks assemble knowledge
As humans explore the world around them and experience new things, they innately start to make sense of what they encounter, creating mental connections between the objects, people, places, and events they encounter. Neuroscientists have been trying to identify the...
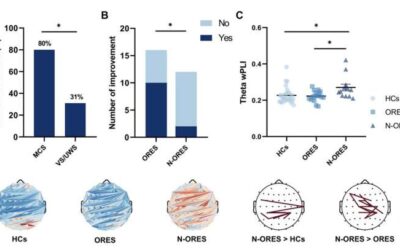
Are the olfactory responses of patients in a coma or vegetative state signs of consciousness?
Severe brain injuries or head traumas in humans can lead to various stages of so-called disorders of consciousness (DoC). These are states in which consciousness is either partly or entirely absent, such as a coma; unresponsive wakefulness syndrome, also known as a...
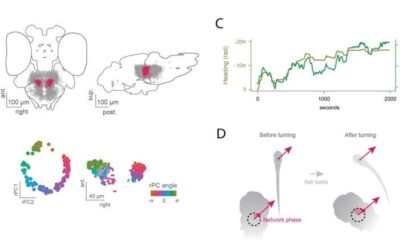
A neuronal network that represents the direction in which zebrafish are traveling
Past studies have found that the brains of some animals generate representations of the direction in which they are headed. For instance, the heading direction of insects is represented by the activity of neurons in a region at the center of their brain, known as the...
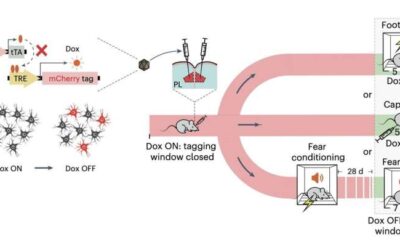
Fearful memories of pain stored in the prefrontal cortex could shape the experience of pain later in life
While pain and fear are very different experiences, past studies showed that they can sometimes be closely related to one another. For instance, when many animals and humans are in dangerous or life-threatening situations, acute fear can suppress their perception of...
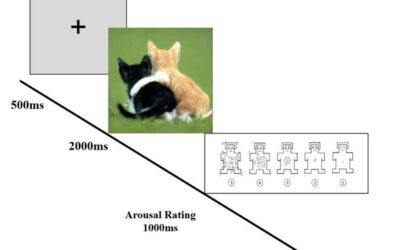
Replaying outcomes in the brain could predict whether we approach or avoid situations
Past neuroscience studies suggest that when deciding their next actions, mice and other rodents tend to replay past outcomes of similar situations in their brain, which is reflected in a rapid activation of certain brain regions in a sequence. Recently, some studies...
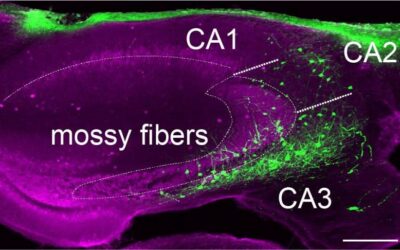
Study explores activity of distinct interneuron populations in a mouse hippocampus during memory consolidation
The hippocampus is a key region of the mammalian brain, which has been found to be involved in the formation of episodic memories. These are long-term memories of events or experiences that can be consciously remembered and mentally re-experienced, such as...