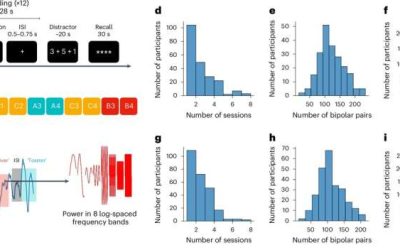
Past neuroscience and psychology studies have shown that after the human brain encodes specific events or information, it can periodically reactivate them to facilitate their retention, via a process known as memory consolidation. The reactivation of memories has been...
Neuroscience
Study shows that some voices are more memorable than others, irrespective of who is listening to them
The term "memorability" refers to the likelihood that a particular stimulus, such as an object, face or sound, will be remembered by those exposed to it. Over the past few years, some psychology studies have been exploring the extent to which some stimuli are...
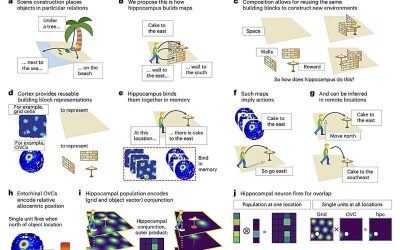
Memory composition and hippocampal replay: New insights into how the hippocampus helps shape future behavior
The hippocampal formation is a group of brain regions, including the hippocampus and some other structures closely connected to it. This set of brain regions is known to support various important brain functions, including the consolidation of memories,...
Sleep supports people’s ability to remember sequences of real-world experiences, immersive art tour experiment shows
Sleep is known to contribute to the healthy functioning of the brain and the consolidation of memories. Past psychology research specifically highlighted its role in retaining episodic memories, which are memories of specific events or experiences.
Study uncovers developmentally distinct neural architectures controlling avoidant behaviors
Over the course of their lives, humans and other animals typically learn to avoid situations and stimuli that are dangerous or are perceived as threatening. Past neuroscience studies have gathered evidence suggesting that the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), a brain...
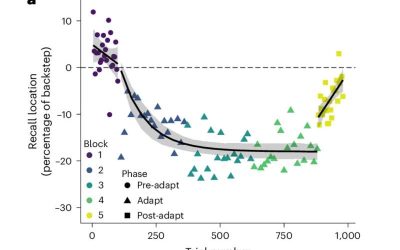
Errors in attention adaptively impact spatial working memory, study finds
Humans are known to rapidly adapt their mental processes and behavior based on feedback they receive from the world around them. For instance, some past studies have shown that people progressively adjust their movements while trying to move in specific ways or walk...
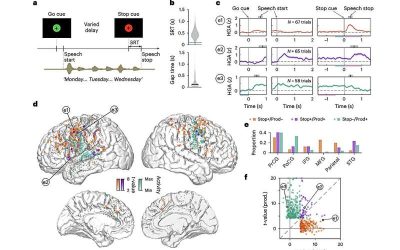
A premotor cortical network in the brain allows people to voluntarily stop speaking, study suggests
Speech is a unique human ability that is known to be supported by various motor and cognitive processes. When humans start speaking, they can decide to cease at any point; for instance, if they are interrupted by something happening or by another person speaking to...
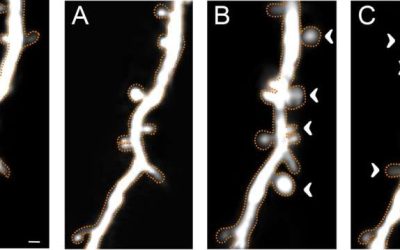
Study shows that dendritic plasticity contributes to the integration of memories
Past neuroscience studies suggest that memories of events that occurred at short time intervals from one another are often connected, via a process referred to as memory linking. While memory linking is now a well-documented phenomenon, its neural underpinnings have...
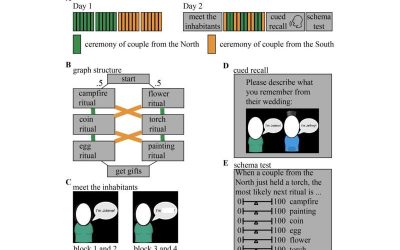
Encoding study reveals how the brain uses past experiences to predict the unfolding of similar events over time
The human brain continuously processes the wide range of information it acquires from the outside world. Over time, this information is organized into mental representations, referred to as "schema," which help us to understand what is happening at a given time and...
People’s spontaneous thought patterns fall into four main clusters, study finds
Thoughts that arise spontaneously when humans are not deliberately trying to think of something are known to play a key role in decision-making and various cognitive functions, as well as in some mental health disorders. In fact, psychology studies suggest that...