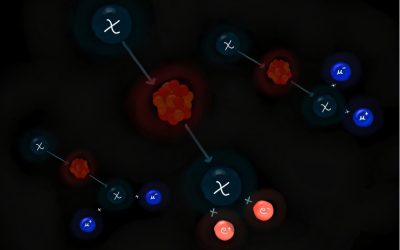
Dark matter (DM) is a type of matter estimated to account for 80% of the universe's total mass, but it cannot be directly detected using conventional experimental techniques. As DM does not emit, reflect or absorb light, most previous dark matter searches were aimed...
PHYS.ORG
Cross-country study gathers new insight about the psychology of social class
Understanding the effects of social class on people's attitudes, thoughts, feelings and behaviors could have valuable implications, as it could help to tailor social and behavioral interventions around the unique psychological characteristics of target populations....
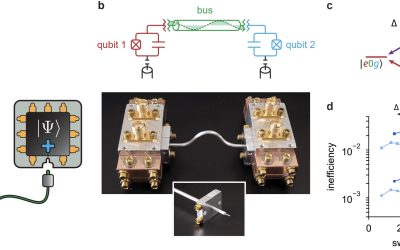
Modular network offers fault-tolerant scaling of superconducting qubit devices
Quantum computers, devices that can perform computations relying on the principles of quantum mechanics, are expected to outperform classical computers on some types of optimization and processing tasks. While physicists and engineers have introduced various quantum...
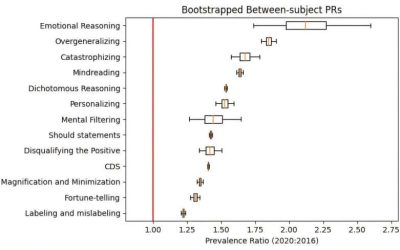
Rigid and negative thought patterns linked to increasing political polarization online
The ideological divide between opposing political groups has been drastically increasing in various countries worldwide. This phenomenon, known as political polarization, can lead to greater social division, extremism and political violence.
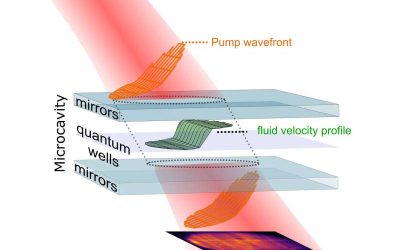
Simulating the Hawking effect and other quantum field theory predictions with polariton fluids
Quantum field theory (QFT) is a physics framework that describes how particles and forces behave based on principles rooted in quantum mechanics and Albert Einstein's special relativity theory. This framework predicts the emergence of various remarkable effects in...
IceCube neutrino search sets first constraints on proton fraction of ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays
Neutrinos are subatomic particles with no charge and very little mass that are known to weakly interact with other matter in the universe. Due to their weak interactions with other particles, these particles are notoriously difficult to detect.
A new method to measure ultrafast relaxation processes in single molecules
Quantum stochastic rectification is a process observed in some physical systems, which entails the conversion of random quantum fluctuations (i.e., quantum noise) and a small oscillating signal, such as a weak alternating current or AC voltage, into a steady output...
Researchers uncover a topological excitonic insulator with a tunable momentum order
Topological materials are a class of materials that exhibit unique electronic properties at their boundary (surface in 3D materials; edge in 2D materials) that are robust against imperfections or disturbances and are markedly different from their bulk properties. In...
New approach to engineering crumpled GO membranes for separating hydrogen and other gases
The reliable separation of some gases from others could be highly advantageous for a wide range of applications. For instance, it could help to produce hydrogen (H2) for fuel cells and chemical applications or to capture the carbon dioxide (CO2) emitted by industrial...
New scheme mitigates self-discharging in quantum batteries
Quantum batteries (QBs) are energy storage devices that could serve as an alternative to classical batteries, potentially charging faster and enabling the extraction of more energy. In contrast with existing batteries, these batteries leverage effects rooted in...