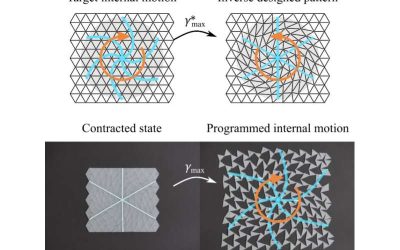
Kirigami is a traditional Japanese art form that entails cutting and folding paper to produce complex three-dimensional (3D) structures or objects. Over the past decades, this creative practice has also been applied in the context of physics, engineering, and...
General Physics
Results of the HAYSTAC Phase II search for dark matter axions
Axions, hypothetical subatomic particles that were first proposed by theoretical physicists in the late 1970s, remain among the most promising dark matter candidates. Physics theories suggest that the interactions between these particles and regular matter are...
Results of the first search for dark photons using a MADMAX prototype
While many research groups worldwide have been searching for dark matter over the past decades, detecting it has so far proved very challenging, thus very little is known about its possible composition and physical properties. Two promising dark matter candidates...
Study uncovers origin of the large neutron-capture cross section in ⁸⁸Zr using new methodology
Studies that explore how the denser sections of atoms, known as atomic nuclei, interact with neutrons (i.e., particles with no electric charge) can have valuable implications both for the understanding of these atoms' underlying physics and for the development of...
AMoRE experiment sets new limits on neutrinoless double beta decay of ¹⁰⁰Mo
In recent years, some large physics experiments worldwide have been trying to gather evidence of a nuclear process known as neutrinoless double beta (0νββ) decay. This is a rare process that entails the simultaneous decay of two neutrons in a nucleus into two protons,...
Thermomajorization theory provides new framework for quantifying mysterious Mpemba effect
The Mpemba effect is an intriguing physical phenomenon that causes some systems to cool faster when they are hot than when they are warm or colder. This effect was observed in various systems, including water, which sometimes freezes faster when it is hot than when it...
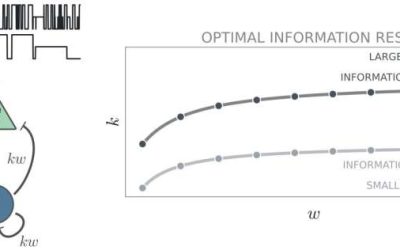
Optimal brain processing requires balance between excitatory and inhibitory neurons, study suggests
The brain's ability to process information is known to be supported by intricate connections between different neuron populations. A key objective of neuroscience research has been to delineate the processes via which these connections influence information processing.
First dark matter search using WINERED spectrograph sets new lifetime constraints
Dark matter is an elusive type of matter that does not emit, absorb or reflect light and is thus impossible to detect using conventional techniques employed in particle physics. In recent years, groups of physicists worldwide have been trying to observe this matter...
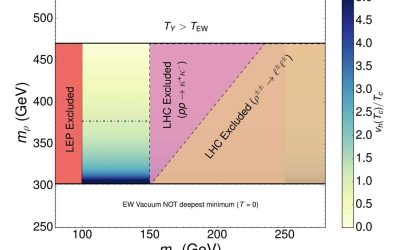
Hypercharge breaking scenarios could explain the baryon asymmetry of the universe
The Standard Model (SM), the main physics framework describing elementary particles and the forces driving them, outlines key patterns in physical interactions referred to as gauge symmetries. One of the symmetries it describes is the so-called U(1)Y hypercharge:...
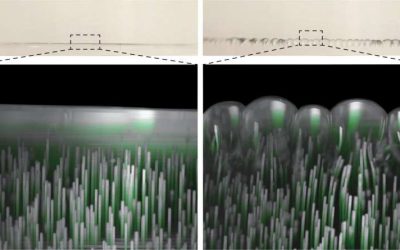
Study unveils new extrusion-induced instabilities in viscoelastic materials
Soft viscoelastic solids are flexible materials that can return to their original shape after being stretched. Due to the unique properties driving their deformation, these materials can sometimes behave and change shape in unexpected ways.