In 2015, the LIGO/Virgo experiment, a large-scale research effort based at two observatories in the United States, led to the first direct observation of gravitational waves. This important milestone has since prompted physicists worldwide to devise new theoretical...
General Physics
Mapping the relations between Manhattan Project scientists using network science
The Manhattan Project was a top-secret program that culminated in the development of the first atomic bombs during World War 2. This covert and controversial research endeavor involved many gifted and reputable scientists, including physicist J. Robert Oppenheimer.
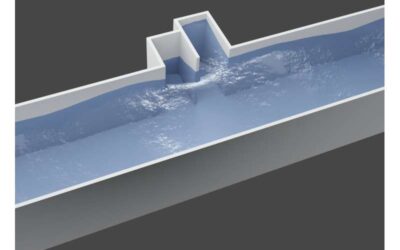
A strategy to realize the efficient resonant absorption of guided water waves
The absorption of water waves is the process through which water waves lose their energy, thus reducing their impact on shores or other solid structures surrounding them. Enabling this absorption process in real-world settings could help protect coasts and structures...
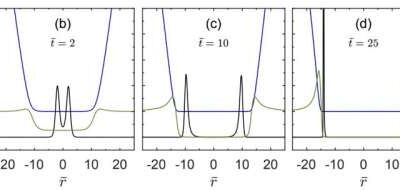
Study resolves puzzles in gravitational collapse of gravitational waves
Black holes are regions in space where the gravitational pull is so strong that nothing can escape them, not even light. These fascinating regions have been the focus of countless studies, yet some of the physics underlying their formation is not yet fully understood.
Muon g-2 experiment measures the positive muon anomalous magnetic moment to 0.20 ppm
The Muon g-2 Collaboration is a large group of researchers at different institutes worldwide collaborating on the Muon g-2 experiment. This is a research effort aimed at exploring the interactions of muons, short-lived particles that are essentially heavy electrons,...
A new formula to calculate the strength of thin conical structures
Conical structures can have advantageous applications in a variety of fields, ranging from robotics to civil engineering. Studies have found that conical shells made of liquid crystal elastomer films can be effective lifters; devices that can generate thrust for...
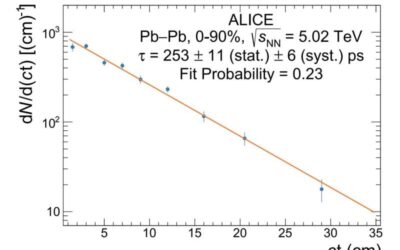
A new highly precise measurement of the hypertriton lifetime
A hypertriton is a tritium nucleus in which a neutron is replaced by a so-called Lambda hyperon. This type of hypernucleus was first discovered in the 1950s has since been the key focus of numerous studies.
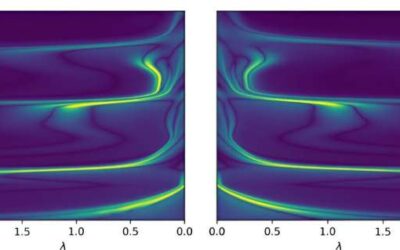
Theoretical study shows that Kerr black holes could amplify new physics
Black holes are regions in space characterized by extremely strong gravity, which prevents all matter and electromagnetic waves from escaping it. These fascinating cosmic bodies have been the focus of countless research studies, yet their intricate physical nuances...
A model probing the connection between entangled particles and wormholes in general relativity
Quantum entanglement is a physical process through which pairs of particles become connected and remain so even when separated by vast distances. This fascinating phenomenon has been the focus of numerous research studies, due to its mysterious nature and promising...
Study estimates the energy costs of information processing in biological systems
The behaviors, physiology and existence of living organisms is supported by countless biological processes, which entail the communication between cells and other molecular components. These molecular components are known to transmit information to each other in...