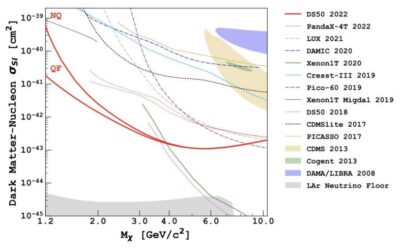
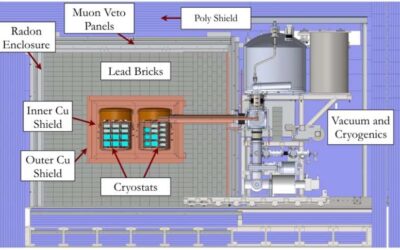
The DarkSide experiment is an ambitious research effort aimed at detecting dark matter particle interactions in liquid argon using a dual-phase physics detector located at the underground Gran Sasso National Laboratory. These interactions could be observed by...
General Physics
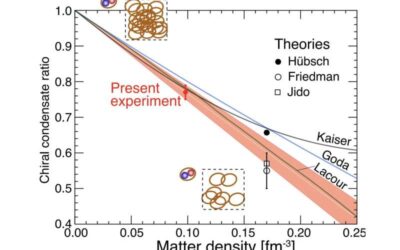
New experimental evidence of the restoration of chiral symmetry at high matter density
The QCD vacuum (i.e., the ground state of vacuum in the quantum chromodynamics regime) is theoretically characterized by the presence of non-zero expectation values of condensates, such as gluons and quark–antiquark pairs. Instead of being associated with a lack of...
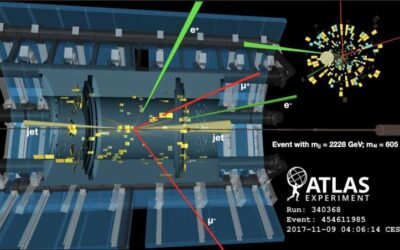
The ATLAS collaboration observes the electroweak production of two jets and a Z-boson pair
The ATLAS collaboration, the large research consortium involved in analyzing data collected by the ATLAS particle collider at CERN, recently observed the electroweak production of two Z bosons and two jets. This crucial observation, presented in Nature Physics,...
The SNO+ collaboration gathers the first evidence of antineutrinos in a water Cherenkov detector
Antineutrinos, the antimatter counterpart of neutrinos, have an almost non-existent mass and charge, and almost never interact with other particles, which makes them particularly difficult to detect. Physicists have been studying neutrinos from reactors for many...
A universal protocol that inverts the evolution of a qubit with a high probability of success
Researchers at the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information (IQOQI) in Vienna recently devised a universal mechanism to invert the evolution of a qubit with a high probability of success. This protocol, outlined in Physical Review Letters, can...
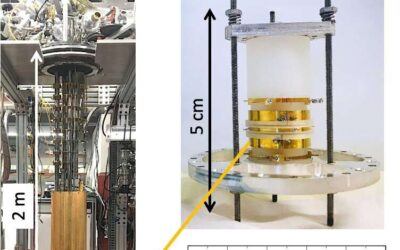
The final results of the Majorana collaboration’s search for neutrinoless double-beta decay
For more than half a decade, the Majorana Collaboration, a large consortium of researchers from different universities worldwide, have been trying to observe neutrinoless double-beta decay, one of the rarest forms of radioactive decay. This was done using the Majorana...
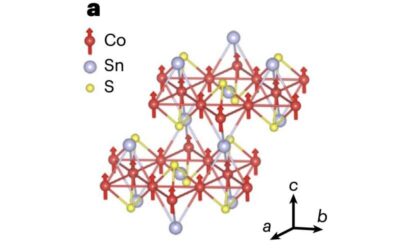
Modulating magnetism in a Weyl semi-metal using current-assisted domain wall motion
Spintronic devices are emerging technologies that exploit the intrinsic spin of electrons to store and process data. These technologies have the potential to outperform conventional electronics both in terms of speed and energy-efficiency.
Study demonstrates a new method to search for meV dark photons
Approximately 85% of the mass of our galaxy is comprised by dark matter, matter that does not emit, absorb or reflect light and thus cannot be directly observed. While several studies have hinted at or theorized about its composition, it remains one of the greatest...
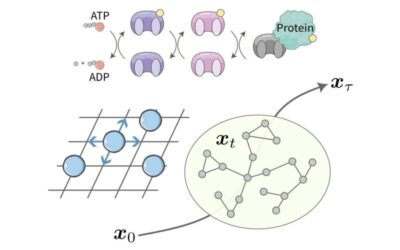
Researchers derive a unified topological speed limit for the evolution of physical states
Physical systems evolve at a particular speed, which depends on various factors including the system's so-called topological structure (i.e., spatial properties that are preserved over time despite any physical changes that occur). Existing methods for determining the...
Could axion decay underlie excess cosmic optical background?
The cosmic optical background (COB) is the visible light emitted by all sources outside of the Milky Way. This faint glow of light, which can only be observed using very precise and sophisticated telescopes, could help astrophysics to learn more about the origins of...