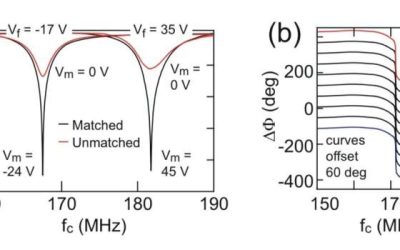
The development of quantum computing systems relies on the ability to rapidly and precisely measure these systems' electrical properties, such as their underlying charge and spin states. These measurements are typically collected using radio-frequency resonators,...
PHYS.ORG
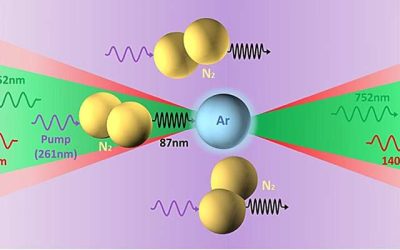
A mechanism that transfers energy from nitrogen to argon enables bidirectional cascaded lasing in atmospheric air
To produce light, lasers typically rely on optical cavities, pairs of mirrors facing each other that amplify light by bouncing it back and forth. Recently, some physicists have been investigating the generation of "laser light" in open air without the use of optical...
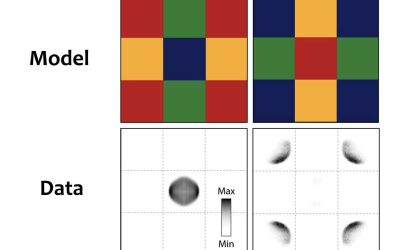
Study uncovers condensed-matter dark states in a quantum system with two pairs of sublattices
Dark states are quantum states in which a system does not interact with external fields, such as light (i.e., photons) or electromagnetic fields. These states, which generally occur due to interferences between the pathways through which a system interacts with an...
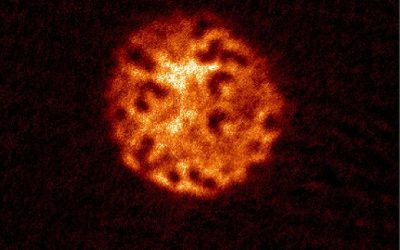
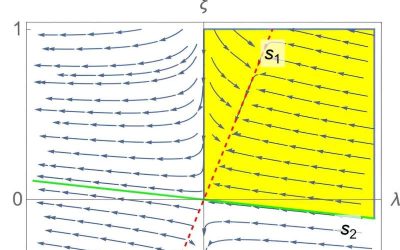
Physicists successfully observe Kibble–Zurek scaling in an atomic Fermi superfluid
The Kibble–Zurek (KZ) mechanism is a theoretical framework introduced by physicists Tom Kibble and Wojciech Zurek. This framework essentially describes the formation of topological defects while systems undergo non-equilibrium phase transitions.
A first definitive demonstration of nonthermal particle acceleration in magnetorotational turbulence
Researchers at KU Leuven, the University of Colorado, Boulder, the Flatiron Institute, and the University of Wisconsin–Madison recently set out to answer a long-standing research question, specifically whether charged particles in the turbulent flows commonly...
A new robotic platform to reproduce and study complex ciliary behavior
Cilia are sensory structures extending from the surface of some cells. These hair-like structures are known to contribute to the sensorimotor capabilities of various living organisms, including humans.
Study unveils limits on the extent to which quantum errors can be ‘undone’ in large systems
Quantum computers have the potential of outperforming conventional computers on some practically relevant information processing problems, possibly even in machine learning and optimization. Yet their large-scale deployment is not yet feasible, largely due to their...
Cosmic microwave background experiments could probe connection between cosmic inflation, particle physics
Various large-scale astrophysical research projects are set to take place over the next decade, several of which are so-called cosmic microwave background (CMB) experiments. These are large-scale scientific efforts aimed at detecting and studying CMB radiation, which...
A new technique to calculate the physical running of couplings in quadratic gravity
Researchers at the International School for Advanced Studies in Trieste, University of Massachusetts, and Instituto de Física Teórica at Universidade Estadual Paulista in Brazil recently introduced an alternative approach to derive the correct physical beta functions...
Exploring what happens when different spherical objects hit the water
When an object hits a body of water vertically, it is accompanied by a strong hydrodynamic force fueled by the flow of water around it, which propels it forward. The magnitude of this force is known to vary depending on the mass of the object hitting the water.