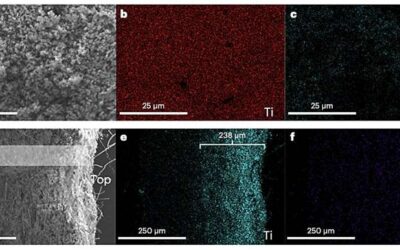
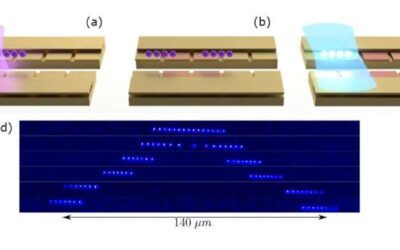
The hydrocarbon methane is highly abundant on Earth, yet its release is now known to contribute to surges in temperature and climate change. In recent years, researchers have been trying to devise reliable methods to directly convert methane into other fuels and...
PHYS.ORG
Dr Benjamin Scherlag | Could the Soul Be a Biophysical Reality?
The idea that human beings have souls that leave their body after death is an essential part of most religions and spiritual beliefs. However, this has been very difficult to prove scientifically. Benjamin Scherlag, Ronald Scherlag, Tarun Dasari and Sunny Po at the...
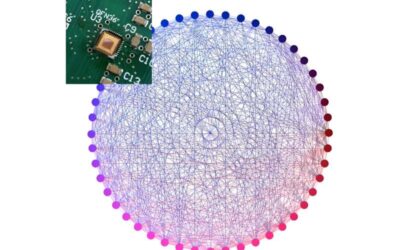
A physics-based Ising solver based on standard CMOS technology
Quantum computers, systems that perform computations by exploiting quantum mechanics phenomena, could help to efficiently tackle several complex tasks, including so-called combinatorial optimization problems. These are problems that entail identifying the optimal...
Study proves the difficulty of simulating random quantum circuits for classical computers
Quantum computers, technologies that perform computations leveraging quantum mechanical phenomena, could eventually outperform classical computers on many complex computational and optimization problems. While some quantum computers have attained remarkable results on...
A theory of strong-field non-perturbative physics driven by quantum light
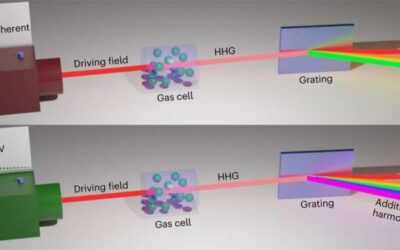
Non-perturbative interactions (i.e., interactions too strong to be described by so-called perturbation theory) between light and matter have been the topic of numerous research studies. Yet the role that quantum properties of light play in these interactions and the...
LHCb collaboration observes a doubly charged tetraquark and its neutral partner for the first time
The observation of elusive, exotic particles is the key objective of countless studies, as it could open new avenues for research, while also improving present knowledge of the matter contained in the universe and its underlying physics. The quark model, a theoretical...
A new protocol to reliably demonstrate quantum computational advantage
Quantum computers, devices that perform computations by exploiting quantum mechanical phenomena, have the potential to outperform classical computers on some tasks and optimization problems. In recent years, research teams at both academic institutions and IT...
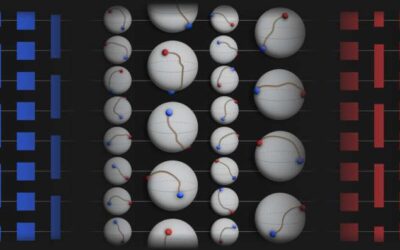
A dynamic matrix with DNA-encoded viscoelasticity to support the development of organoids and other biological tissues
Over the past few decades, material scientists and chemists have been working on designing increasingly sophisticated materials for a wide range of technological and scientific applications. These materials include synthetic polymers and hydrogels that could be...
The first observation of neutrinos at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider
Neutrinos are tiny and neutrally charged particles accounted for by the Standard Model of particle physics. While they are estimated to be some of the most abundant particles in the universe, observing them has so far proved to be highly challenging, as the...
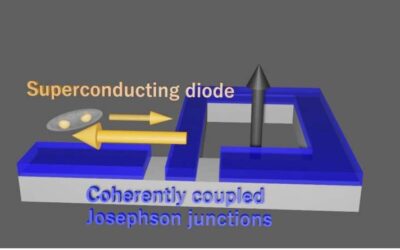
The superconducting diode effect in a device based on coupled Josephson junctions
The so-called superconducting (SC) diode effect is an interesting nonreciprocal phenomenon, occurring when a material is SC in one direction and resistive in the other. This effect has been the focus of numerous physics studies, as its observation and reliable control...