In recent years, physicists worldwide have been conducting studies exploring the characteristics and dynamics of topological phases of matter that could enable the development of quantum devices and other new technologies. Some of these phases are supported by what is...
PHYS.ORG
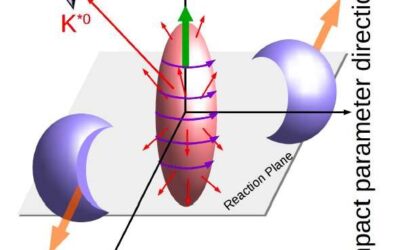
The first evidence of vector meson spin alignment in heavy-ion collisions
The ALICE collaboration is a large group of researchers from over 100 physics institutes worldwide that focuses on the study of quark-gluon plasma using data collected by the ALICE (A Large Ion Collider Experiment) detector. ALICE is a heavy-ion detector designed to...
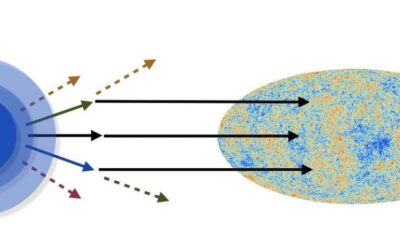
A new test to investigate the origin of cosmic structure
Many cosmologists believe that the universe's structure is a result of quantum fluctuations that occurred during early expansion. Confirming this hypothesis, however, has proven highly challenging so far, as it is hard to discern between quantum and classical...
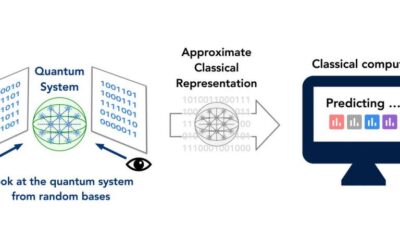
A method to predict the properties of complex quantum systems
Predicting the properties of complex quantum systems is a crucial step in the development of advanced quantum technologies. While research teams worldwide have already devised a number of techniques to study the characteristics of quantum systems, most of these have...
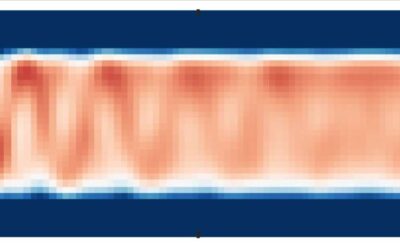
Probing the properties of a 2-D fermi gas
When a new physical system is created or uncovered, researchers generally study it in depth to unveil its distinctive properties and characteristics. For example, they might try to determine how the system reacts when it is disturbed, and in what ways this disturbance...
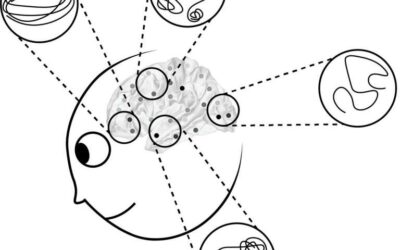
A new framework for understanding dynamic representations in networked neural systems
Groups of neurons in the human brain produce patterns of activity that represent information about the stimuli that one is perceiving and then convey these patterns to different brain regions via nerve cell junctions known as synapses. So far, most neuroscience...
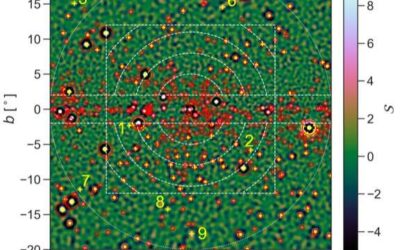
Could recently spotted dim point sources explain the galactic center excess (GCE)?
Over the past decade or so, a number of astrophysics studies have detected an excess of gamma-ray radiation at the center of our galaxy. Despite the many attempts to understand this unexpected surplus of radiation, now known as the galactic center excess (GCE), its...
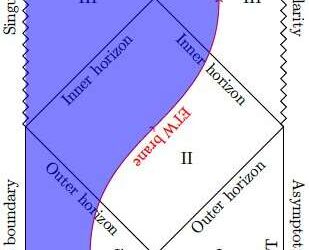
Researchers apply the anti-de Sitter/conformal field theory to cosmology
The anti-de Sitter/conformal field theory (AdS/CFT) correspondence, also referred to as gauge/gravity duality, hypothesizes the existence of a relationship between two types of physics theories, namely gravity theories in AdS spacetimes and CFTs. Over the past few...
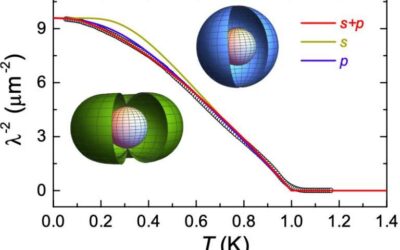
Simultaneous nodal superconductivity and broken time-reversal symmetry in CaPtAs
In the vast majority of superconducting materials, Cooper pairs have what is known as even parity, which essentially means that their wave function does not change when electrons swap spatial coordinates. Conversely, some unconventional superconductors have been found...
A quantum metrology protocol for locating noncooperative targets in 3-D space
Radar technology, which stands for radio detection and ranging, has been around for several decades and has a wide range of real-world applications. Radar is currently used to detect targets or other objects in many settings. For instance, it is employed during...