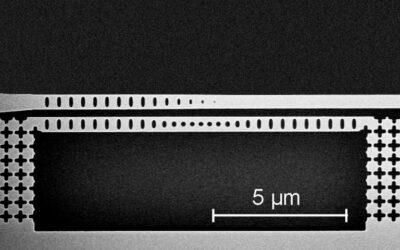
To create large quantum networks, researchers will first need to develop efficient quantum repeaters. A key component of these repeaters are quantum memories, which are the quantum-mechanical equivalents of more conventional computer memories, such as random-access...
PHYS.ORG
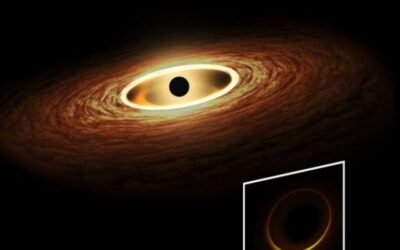
A new theorem predicts that stationary black holes must have at least one light ring
Black holes, regions in space with such an intense gravitational field that no matter or radiation can escape from them, are among the most mysterious and fascinating cosmological phenomena. Over the past five years or so, astrophysicists collected the first...
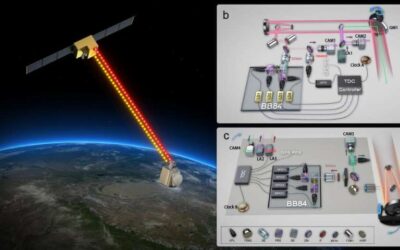
A new scheme for satellite-based quantum-secure time transfer
Researchers at the University of Science and Technology of China have recently introduced a new satellite-based quantum-secure time transfer (QSTT) protocol that could enable more secure communications between different satellites or other technology in space. Their...
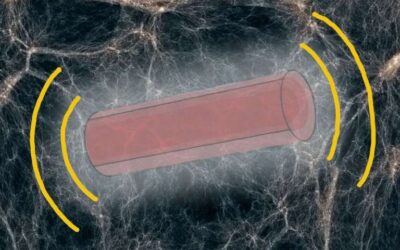
Searching for scalar dark matter using compact mechanical resonators
Researchers at University of Delaware, University of Arizona and Haverford College have recently introduced the idea of searching for scalar dark matter using compact acoustic resonators. Their paper, published in Physical Review Letters, theoretically demonstrates...
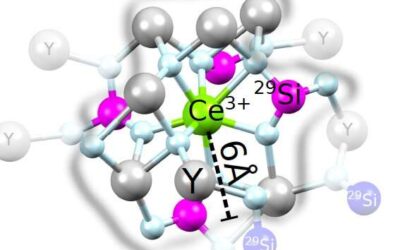
Detecting individual nuclear spins with single rare-earth ions hosted in crystals
Rare-earth minerals are a class of materials with similar properties that are currently used to build a variety of devices, including LEDs, rechargeable batteries, magnets, lasers, and much more. These materials' electron spins can be hosted in crystals, creating...
A system for robust and efficient wireless power transfer
Current methods for charging electronic devices via wireless technology only work if the overall system parameters are set up to match a specific transfer distance. As a result, these methods are limited to stationary power transfer applications, which means that a...
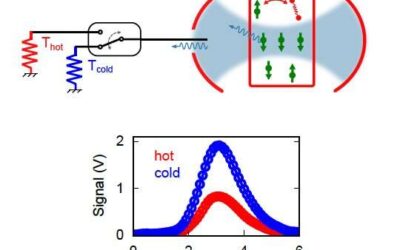
A new technique for the radiative cooling of spin ensembles
Researchers at CEA/CNRS/Université Paris Saclay, University College London and ETH Zurich have recently devised a new method to control the temperature of a spin ensemble by increasing electron spin polarization above its thermal equilibrium value. Their research,...
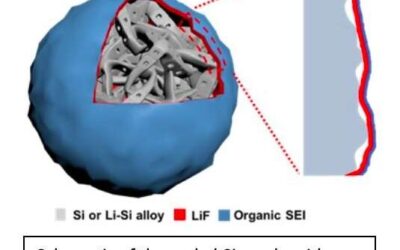
A new electrolyte design that could enhance the performance of Li-ion batteries
Most existing lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) integrate graphite anodes, which have a capacity of approximately 350 milliamp hours (mAh) per gram. The capacity of silicon anodes is almost 10 times higher than that of their graphite counterparts (around 2,800 mAh per...
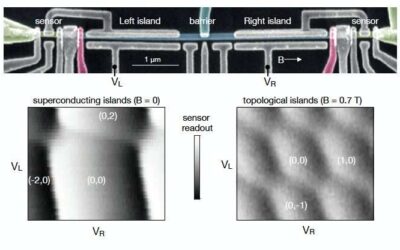
The observation of photon-assisted tunneling signatures in Majorana wires
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen and Microsoft Quantum Lab Copenhagen have recently carried out a study investigating the potential of Majorana zero modes, zero-energy quasiparticle states that can be found in superconductive hybrid nanowires, as a means of...
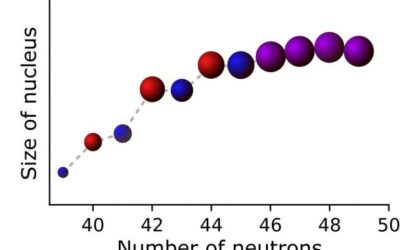
Measuring the charge radii of exotic copper isotopes
Researchers at Instituut voor Kern- en Stralingsfysica in Belgium and The University of Manchester, in collaboration with other institutes worldwide, have recently carried out a study aimed at measuring the size of the nucleus (i.e., nuclear charge radius) in...