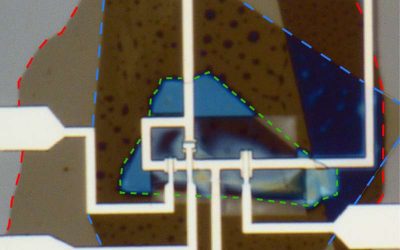
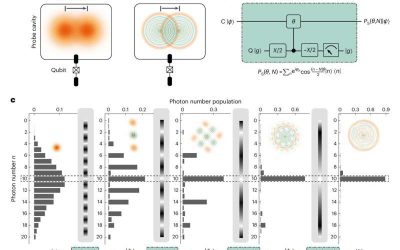
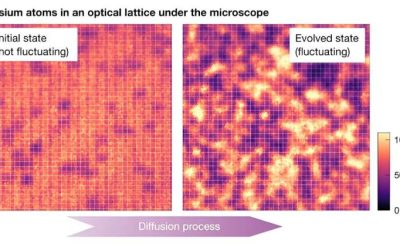
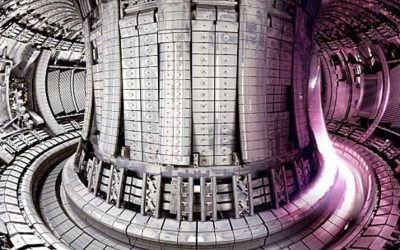
In recent years, quantum physicists and engineers have made significant strides toward the development of highly performing quantum computing systems. Realizing a quantum advantage over classical computing systems and enabling the stable operation of quantum devices,...
Physics
A versatile approach to realize quantum-enhanced metrology with large Fock states
Team studies the emergence of fluctuating hydrodynamics in chaotic quantum systems
Researchers at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität, Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik, Munich Center for Quantum Science and Technology (MCQST) and the University of Massachusetts recently carried out a study investigating the equilibrium fluctuations in large quantum...
Measuring the gamma-ray-to-neutron branching ratio in the deuterium-tritium reaction
Magnetic confinement fusion devices are technologies that can attain controlled nuclear fusion reactions, using magnetic fields to confine hot plasmas. These devices could contribute to the ongoing transition towards more sustainable energy production methods.
New Sisyphus cooling technique could enhance precision of atomic clocks
Researchers in the Neutral Atom Optical Clocks Group at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), University of Colorado and Pennsylvania State University recently devised a new sub-recoil Sisyphus cooling technique that could help to improve the...
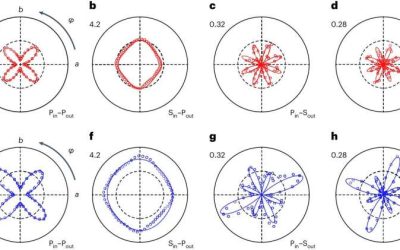
Study uncovers broken mirror symmetry in the Fermi-liquid-like phase of a cuprate
Materials that exhibit superconducting properties at high temperatures, known as high-temperature superconductors, have been the focus of numerous recent studies, as they can be used to develop new technologies that perform well at higher temperatures. Although...
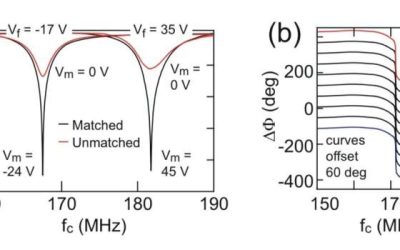
New varactor enhances quantum dot device measurements at millikelvin temperatures
The development of quantum computing systems relies on the ability to rapidly and precisely measure these systems' electrical properties, such as their underlying charge and spin states. These measurements are typically collected using radio-frequency resonators,...
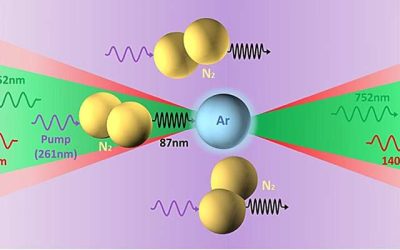
A mechanism that transfers energy from nitrogen to argon enables bidirectional cascaded lasing in atmospheric air
To produce light, lasers typically rely on optical cavities, pairs of mirrors facing each other that amplify light by bouncing it back and forth. Recently, some physicists have been investigating the generation of "laser light" in open air without the use of optical...
Physicists successfully observe Kibble–Zurek scaling in an atomic Fermi superfluid
The Kibble–Zurek (KZ) mechanism is a theoretical framework introduced by physicists Tom Kibble and Wojciech Zurek. This framework essentially describes the formation of topological defects while systems undergo non-equilibrium phase transitions.
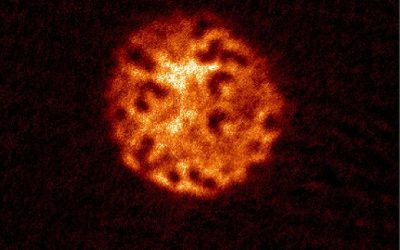
A first definitive demonstration of nonthermal particle acceleration in magnetorotational turbulence
Researchers at KU Leuven, the University of Colorado, Boulder, the Flatiron Institute, and the University of Wisconsin–Madison recently set out to answer a long-standing research question, specifically whether charged particles in the turbulent flows commonly...