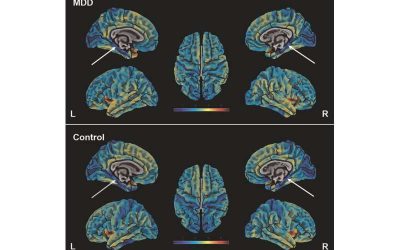
Depression is a mental health disorder characterized by a recurrent or persistent sadness and a loss of interest in activities that were previously deemed pleasurable, sometimes accompanied by changes in sleep, appetite and perceived energy levels. One of the...
Neuroscience
How the brain stores ‘unattended’ information: Neuronal firing disproves activity-silent hypothesis
Understanding how the human brain stores information and later uses it to complete various tasks has been a long-standing goal of neuroscience and psychology research. Past studies have identified different types of memory processes that have distinct roles...
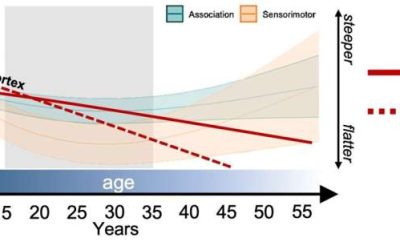
Study maps changes in brain’s ‘neural noise’ from childhood to adulthood
For over a century, neuroscientists and psychologists have been trying to understand the neurophysiological mechanisms underpinning the human brain's development from birth to late adulthood. While past studies have shed light on some of these mechanisms, several...
Human CLOCK gene enhances brain connectivity and mental flexibility in mice, study finds
Clock genes are a set of genes known to contribute to the regulation of the human body's internal 24-hour cycle, also known as the circadian rhythm. One of these genes is the so-called CLOCK gene, a protein that regulates the activity of other genes, contributing to...
Genetic variants linked with higher risk of developing bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder is a mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings, with alternating periods of depression and manic episodes. Past research suggests that bipolar disorder has a strong genetic component and is among the most...
Electrical stimulation of facial muscles influences how people perceive others’ emotions, study finds
Psychology research suggests that the human body, particularly the muscles on our face, plays a key part in the processing of others' emotions. For instance, past findings suggest that when we see another person smiling or frowning, we often unconsciously mimic their...
Dietary intervention optimized using machine learning could lower risk of dementia
The term dementia is used to describe various debilitating neurological disorders characterized by a progressive loss of memory and a decline in mental abilities. Estimates suggest that over 55 million people worldwide are currently living with dementia, and...
Mathematical model reveals how humans store narrative memories using ‘random trees’
Humans can remember various types of information, including facts, dates, events and even intricate narratives. Understanding how meaningful stories are stored in people's memory has been a key objective of many cognitive psychology studies.
Computational models explore how regions of the visual cortex jointly represent visual information
Understanding how the human brain represents the information picked up by the senses is a longstanding objective of neuroscience and psychology studies. Most past studies focusing on the visual cortex, the network of regions in the brain's outer layer known...
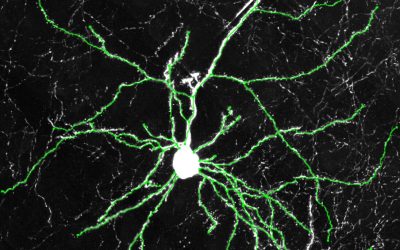
Roundworm study identifies proteins that could mediate neuron-glia communication as brain ages
The human brain is comprised of two main types of cells, known as neurons and glia. The first are responsible for transmitting electrical and chemical signals, while the latter support and protect neurons.