Conversations allow humans to communicate their thoughts, feelings and ideas to others. This in turn enables them to learn new things, deepen their social connections, and co-operate with peers to solve specific tasks.
Neuroscience
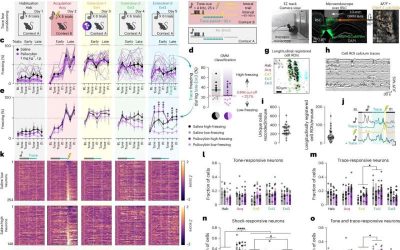
Psilocybin rewires brain circuits to boost fear extinction and behavioral flexibility in mice
Psilocybin, a psychedelic compound contained in some varieties of mushrooms, has recently been found to be promising for the treatment of some neuropsychiatric disorders, including depression, some anxiety disorders and post-traumatic...
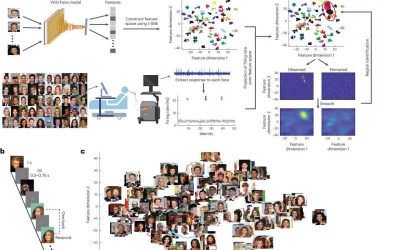
Individual neurons in amygdala and hippocampus encode visual features that help recognize faces, study finds
Humans are innately capable of recognizing other people they have seen before. This capability ultimately allows them to build meaningful social connections, develop their sense of identity, better cooperate with others, and identify individuals who could pose a risk...
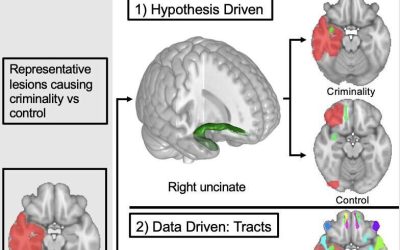
Injury to specific brain connections could explain some people’s criminal behavior, study finds
Over the past decades, some lawyers have started using brain imaging scans as evidence during criminal trials, to provide a possible explanation for the criminal behavior of defendants. This was justified by recent neuroscientific studies, which found that some people...
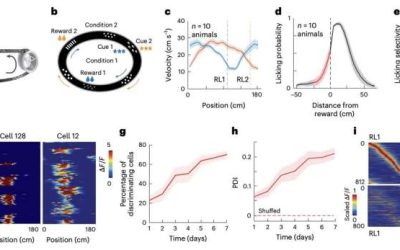
How hippocampal place cells and synaptic plasticity contribute to the progressive acquisition of memories
The human brain is known to store various memories for long periods of time, progressively learning from new experiences and forming adaptive representations that ultimately guide decision-making and behavior. When people experience new things, their brain...
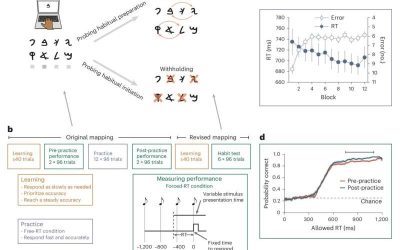
Habits supported by two different aspects of action control could resolve past discrepancies
When humans repeat specific patterns of behavior on a regular basis, these behaviors can become habits. Some habits, such as exercising in the morning, hygienic rituals, eating healthy or meditation practices, can be beneficial. Others, such as smoking, eating while...
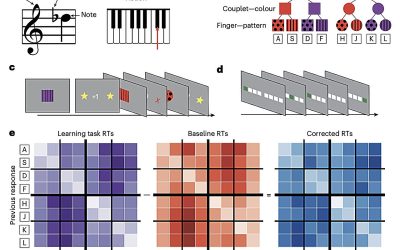
Brain organizes visuomotor associations into structured graph-like mental schemes, study finds
Graphs, visual representations outlining the relationships between different entities, concepts or variables, can be very effective in summarizing complex patterns and information. Past psychology studies suggest that the human brain stores memories and...
Eye-tracking exhibit helps map gaze behavior development across different life stages
Understanding how people visually browse their surroundings and direct their gaze in specific situations is a long-standing goal among psychology researchers. Past studies suggest that humans exhibit oculomotor biases, which are tendencies that guide the way they look...
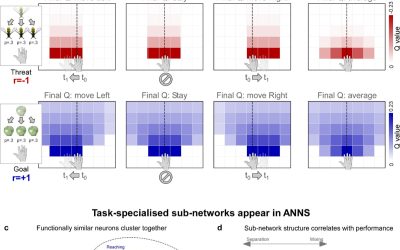
Artificial neural networks reveal how peripersonal neurons represent the space around the body
The brains of humans and other primates are known to execute various sophisticated functions, one of which is the representation of the space immediately surrounding the body. This area, also sometimes referred to as "peripersonal space," is where most interactions...
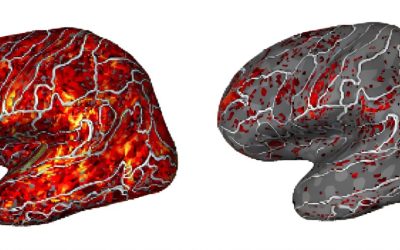
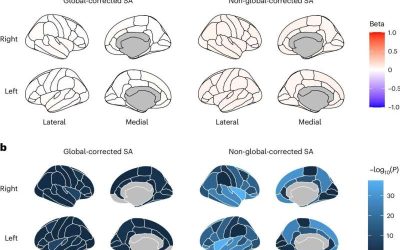
Brain cortex structure linked to mental abilities and psychiatric disorders
The cerebral cortex, the outermost layer of the brain, is the central driver of various human capabilities, including decision-making, perception, language and memory. Understanding how the morphology (i.e., structure and shape) of people's cerebral cortex is...