Superconductivity is an advantageous property observed in some materials, which entails the ability to conduct electricity without resistance below specific critical temperatures. One particularly fascinating phenomenon observed in some unconventional superconductors...
Condensed Matter
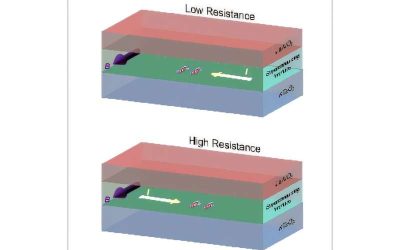
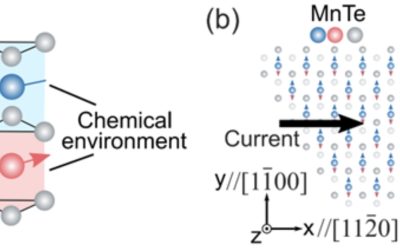
A promising pathway for the electrical switching of altermagnetism
The ability to switch magnetism, or, in other words, to change the orientation of a material's magnetic moments, using only electricity, could open new opportunities for the efficient storage of data in hard drives and other magnetic memory devices. While the...
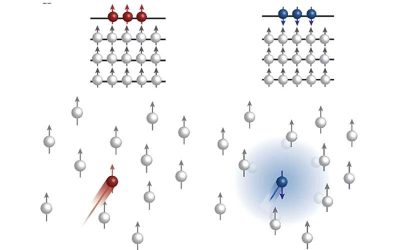
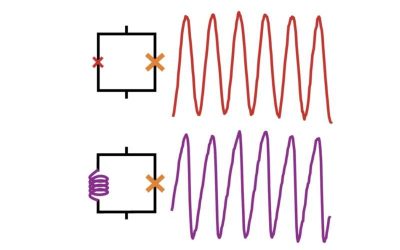
A new mechanism to realize spin-selective transport in tungsten diselenide
Spintronics are promising devices that work utilizing not only the charge of electrons, like conventional electronics, but also their spin (i.e., their intrinsic angular momentum). The development of fast and energy-efficient spintronic devices greatly depends on the...
TaIrTe₄ photodetectors show promise for highly sensitive room-temperature THz sensing
Terahertz radiation (THz), electromagnetic radiation with frequencies ranging between 0.1 and 10 THz, could be leveraged to develop various new technologies, including imaging and communication systems. So far, however, a lack of fast and sensitive detectors that can...
Twisted trilayer graphene shows high kinetic inductance
Superconductivity is an advantageous physical phenomenon observed in some materials, which entails an electrical resistance of zero below specific critical temperatures. This phenomenon is known to arise following the formation of so-called Cooper pairs (i.e., pairs...
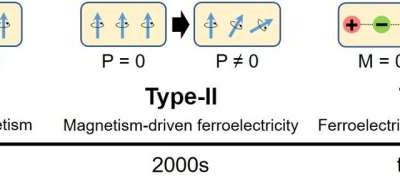
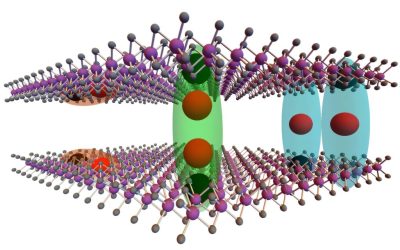
Study predicts existence of Type-III multiferroics, which exhibit ferroelectricity-driven magnetism
Multiferroics are materials that exhibit more than one ferroic property, typically ferroelectricity (i.e., a spontaneous electric polarization that can be reversed by electric fields) and ferromagnetism (i.e., the spontaneous magnetic ordering of electron spins)....
Using a fermionic neural network to find the ground state of fractional quantum Hall liquids
When two-dimensional electron systems are subjected to magnetic fields at low temperatures, they can exhibit interesting states of matter, such as fractional quantum Hall liquids. These are exotic states of matter characterized by fractionalized excitations and the...
Two distinct exciton states observed in 2H stacked bilayer molybdenum diselenide
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have proved to be a promising platform for studying exotic quasiparticles, such as excitons. Excitons are bound states that emerge when an electron in a material absorbs energy and rises to a higher energy level, leaving a hole (i.e.,...
Two distinct exciton states observed in 2H stacked bilayer molybdenum diselenide
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have proved to be a promising platform for studying exotic quasiparticles, such as excitons. Excitons are bound states that emerge when an electron in a material absorbs energy and rises to a higher energy level, leaving a hole (i.e.,...
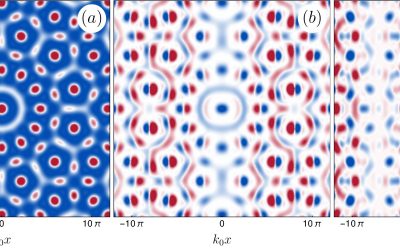
New physics theory to study low-energy excitations in quantum quasicrystals
Quasicrystals, exotic states of matter characterized by an ordered structure with non-repeating spatial patterns, have been the focus of numerous recent physics studies due to their unique organization and resulting symmetries. Among the quasicrystals that have...