When two-dimensional electron systems are subjected to magnetic fields at low temperatures, they can exhibit interesting states of matter, such as fractional quantum Hall liquids. These are exotic states of matter characterized by fractionalized excitations and the...
Condensed Matter
Two distinct exciton states observed in 2H stacked bilayer molybdenum diselenide
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have proved to be a promising platform for studying exotic quasiparticles, such as excitons. Excitons are bound states that emerge when an electron in a material absorbs energy and rises to a higher energy level, leaving a hole (i.e.,...
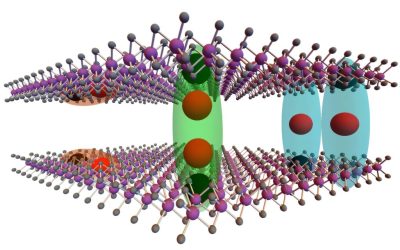
Two distinct exciton states observed in 2H stacked bilayer molybdenum diselenide
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have proved to be a promising platform for studying exotic quasiparticles, such as excitons. Excitons are bound states that emerge when an electron in a material absorbs energy and rises to a higher energy level, leaving a hole (i.e.,...
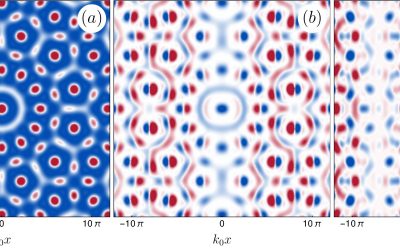
New physics theory to study low-energy excitations in quantum quasicrystals
Quasicrystals, exotic states of matter characterized by an ordered structure with non-repeating spatial patterns, have been the focus of numerous recent physics studies due to their unique organization and resulting symmetries. Among the quasicrystals that have...
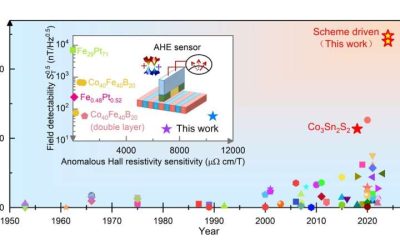
Mathematical model modulates the anomalous Hall angle in a magnetic topological semimetal
When an electric current passes through some materials, it generates a voltage perpendicular to the direction in which the current is flowing and of an applied magnetic field. This physical phenomenon, known as the anomalous Hall effect, has been linked to the...
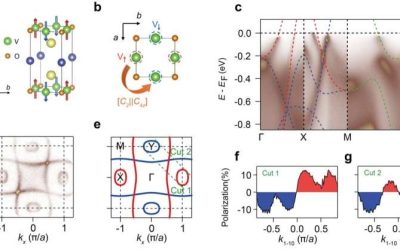
Layered room-temperature altermagnet shows promise for advanced spintronics
Traditionally, magnetic materials have been divided into two main categories: ferromagnets and antiferromagnets. Over the past few years, however, physicists have uncovered the existence of altermagnets, a new type of magnetic material that exhibits features of both...
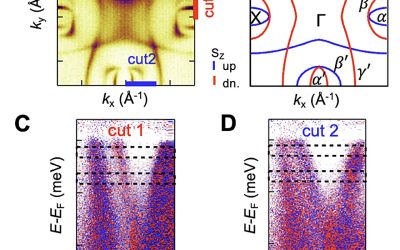
Physicists uncover a metallic altermagnet with d-wave spin splitting at room temperature
For many years, physics studies focused on two main types of magnetism, namely ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism. The first type entails the alignment of electron spins in the same direction, while the latter entails the alignment of electron spins in alternating,...
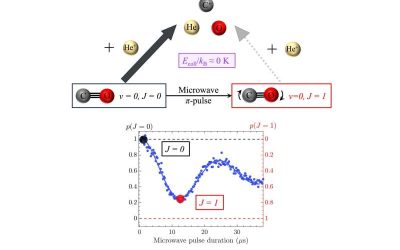
Microwave pulses can control ion-molecule reactions at near absolute zero
A key objective of ongoing research rooted in molecular physics is to understand and precisely control chemical reactions at very low temperatures. At low temperatures, the chemical reactions between charged particles (i.e., ions) and molecules unfold with highly...
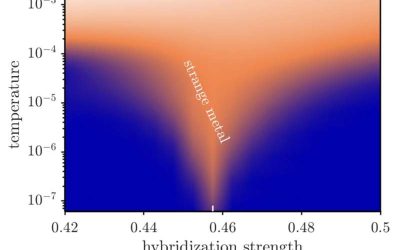
Study proposes new mechanism underpinning intrinsic strange metal behavior
Quantum critical points are thresholds that mark the transition of materials between different electronic phases at absolute zero temperatures, around which they often exhibit exotic physical properties.
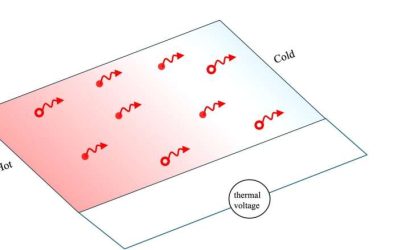
Thermopower-based technique can detect fractional quantum Hall states
If one side of a conducting or semiconducting material is heated while the other remains cool, charge carriers move from the hot side to the cold side, generating an electrical voltage known as thermopower.