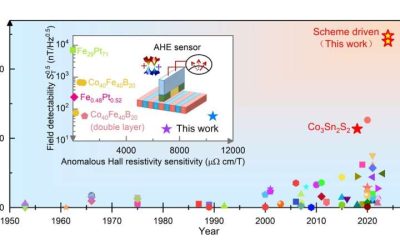
When an electric current passes through some materials, it generates a voltage perpendicular to the direction in which the current is flowing and of an applied magnetic field. This physical phenomenon, known as the anomalous Hall effect, has been linked to the...
Condensed Matter
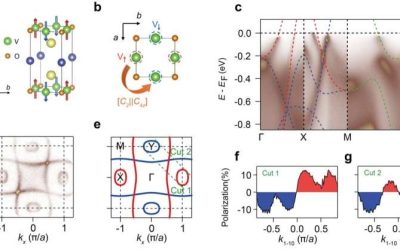
Layered room-temperature altermagnet shows promise for advanced spintronics
Traditionally, magnetic materials have been divided into two main categories: ferromagnets and antiferromagnets. Over the past few years, however, physicists have uncovered the existence of altermagnets, a new type of magnetic material that exhibits features of both...
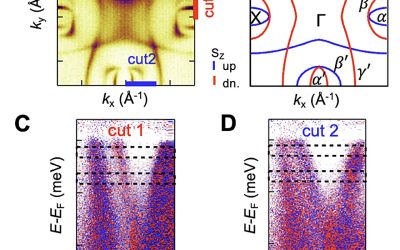
Physicists uncover a metallic altermagnet with d-wave spin splitting at room temperature
For many years, physics studies focused on two main types of magnetism, namely ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism. The first type entails the alignment of electron spins in the same direction, while the latter entails the alignment of electron spins in alternating,...
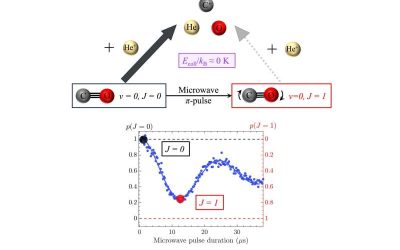
Microwave pulses can control ion-molecule reactions at near absolute zero
A key objective of ongoing research rooted in molecular physics is to understand and precisely control chemical reactions at very low temperatures. At low temperatures, the chemical reactions between charged particles (i.e., ions) and molecules unfold with highly...
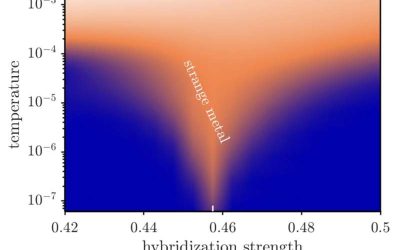
Study proposes new mechanism underpinning intrinsic strange metal behavior
Quantum critical points are thresholds that mark the transition of materials between different electronic phases at absolute zero temperatures, around which they often exhibit exotic physical properties.
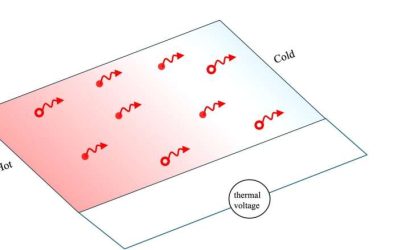
Thermopower-based technique can detect fractional quantum Hall states
If one side of a conducting or semiconducting material is heated while the other remains cool, charge carriers move from the hot side to the cold side, generating an electrical voltage known as thermopower.
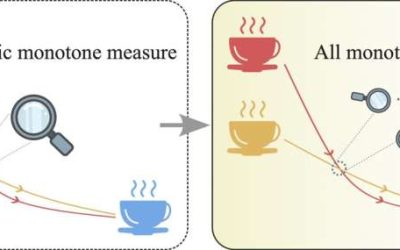
Thermomajorization theory provides new framework for quantifying mysterious Mpemba effect
The Mpemba effect is an intriguing physical phenomenon that causes some systems to cool faster when they are hot than when they are warm or colder. This effect was observed in various systems, including water, which sometimes freezes faster when it is hot than when it...
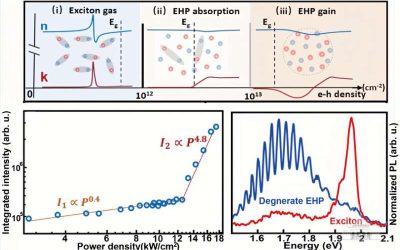
The first observation of amplified spontaneous emission from electron-hole plasma in 2D semiconductors
Amplified spontaneous emission is a physical phenomenon that entails the amplification of the light spontaneously emitted by excited particles, due to photons of the same frequency triggering further emissions. This phenomenon is central to the functioning of various...
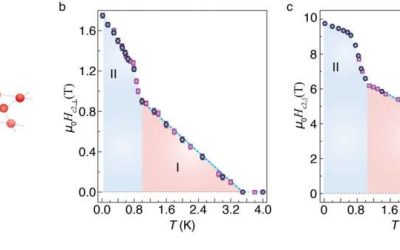
Physicists uncover two superconducting regimes in a Kagome lattice superconductor
Superconductivity, which entails an electrical resistance of zero at very low temperatures, is a highly desirable and thus widely studied quantum phenomenon. Typically, this state is known to arise following the formation of bound electron pairs known as Cooper pairs,...
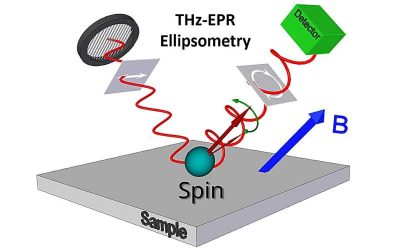
Researchers discover magnetic equivalent of the Lyddane-Sachs-Teller relation
Materials are known to interact with electromagnetic fields in different ways, which reflect their structures and underlying properties. The Lyddane-Sachs-Teller relation is a physics construct that describes the relationship between a material's static and dynamic...