Perovskites, materials with a crystal structure that mirrors that of the mineral calcium titanate CaTiO₃, exhibit properties that are advantageous for developing various technologies. For instance, they have proved promising for designing photovoltaic (PV) systems and...
Condensed Matter
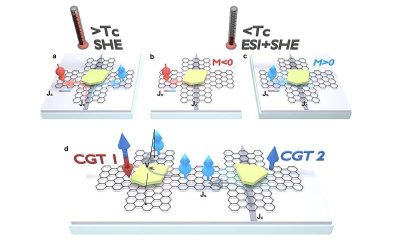
2D graphene spin valve leverages van der Waals magnet proximity for efficient spintronics
Graphene, particularly in its purest form, has long been considered a promising material for developing spintronic devices. These devices leverage the intrinsic angular momentum (i.e., spin), as opposed to the charge, of electrons to transmit and process data.
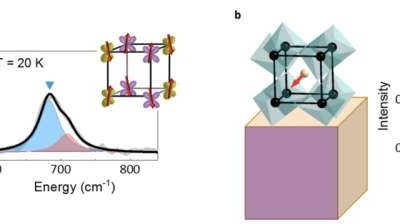
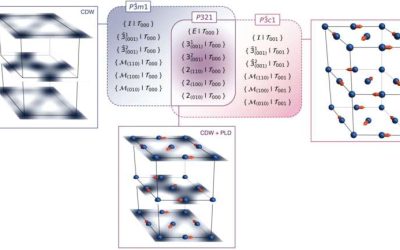
Physicists identify key mechanism behind chiral charge density wave in TiSe₂
Chirality is a property of some molecules, subatomic particles, living organisms and other physical or biological systems. This property entails a lack of mirror symmetry in these systems' underlying structures.
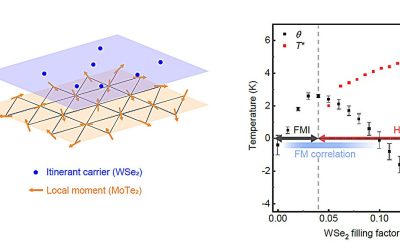
Physicists report emergence of ferromagnetism at onset of Kondo breakdown in moiré bilayer lattices
Moiré superlattices are materials consisting of two layers stacked on top of each other with either a small rotational misalignment or a lattice mismatch between them. The Kondo lattice model, on the other hand, describes systems in which conduction electrons interact...
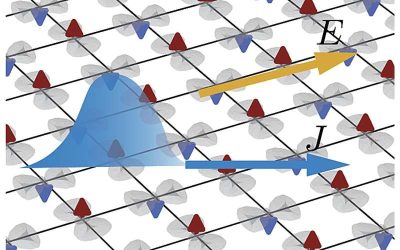
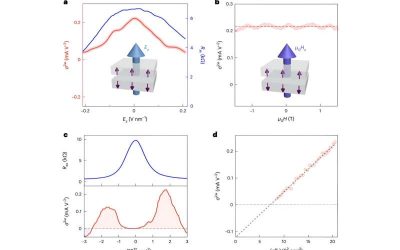
Physicists reveal nonlinear transport induced by quantum geometry in planar altermagnets
In recent years, many physicists and materials scientists have been studying a newly uncovered class of magnetic materials known as altermagnets. These materials exhibit a unique type of magnetism that differs from both conventional ferromagnetism and...
Theoretical study demonstrates existence of giant photocaloric effects in ferroelectric perovskites
Solid-state cooling is a promising alternative cooling technique that does not rely on the use of gases or liquids, like conventional refrigeration systems, but instead utilizes the properties of solid materials to refrigerate. This alternative cooling approach could...
Researchers observe an antiferromagnetic diode effect in even-layered MnBi₂Te₄
Antiferromagnets are materials in which the magnetic moments of neighboring atoms are aligned in an alternating pattern, resulting in no net macroscopic magnetism. These materials have interesting properties that could be favorable for the development of spintronic...
Findings hint at a superfluid phase in ²⁹F and ²⁸O
Data collected by the SAMURAI spectrometer at RIKEN's RI Beam Factory (RIBF) in Japan recently led to the detection of a rare fluorine (F) isotope, known as 30F. This has opened interesting possibilities for the study of rare nuclear structures and corresponding...
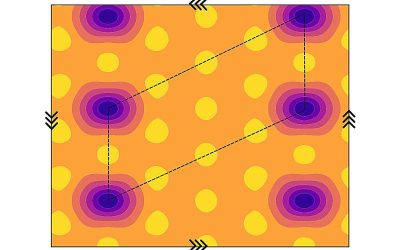
Study predicts a new quantum anomalous crystal in fractionally filled moiré superlattices
Moiré superlattices, structures that arise when two layers of two-dimensional (2D) materials are overlaid with a small twist angle, have been the focus of numerous physics studies. This is because they have recently been found to host novel fascinating unobserved...
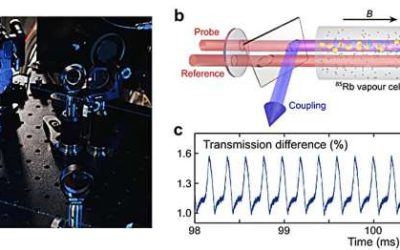
The experimental observation of a dissipative time crystal in a Rydberg gas
A dissipative time crystal is a phase of matter characterized by periodic oscillations over time, while a system is dissipating energy. In contrast with conventional time crystals, which can also occur in closed systems with no energy loss, dissipative time crystals...