Magnetic and electric dipoles, objects with two oppositely charged ends, have a similar symmetrical structure. One might thus assume that they exhibit similar internal structures and physical states.
Condensed Matter
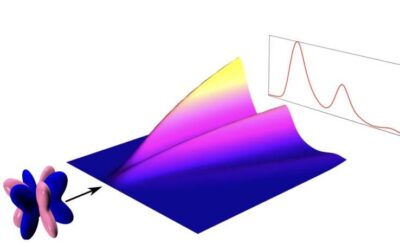
Study outlines spectroscopic signatures of fractionalization in octupolar quantum spin ice
Quantum spin liquids are fascinating quantum systems that have recently attracted significant research attention. These systems are characterized by a strong competition between interactions, which prevents the establishment of a long-range magnetic order, such as...
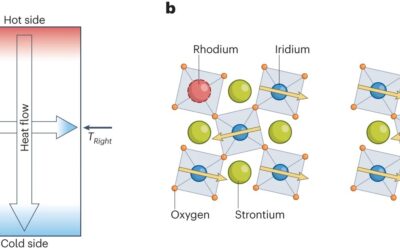
Evidence of phonon chirality from impurity scattering in the antiferromagnetic insulator strontium iridium oxide
The thermal hall effect (THE) is a physical phenomenon characterized by tiny transverse temperature differences occurring in a material when a thermal current passes through it and a perpendicular magnetic field is applied to it. This effect has been observed in a...
Evidence that atomically thin hafnium telluride is an excitonic insulator
The condensation of excitons with non-zero momentum can give rise to so-called charge density waves (CDW). This phenomenon can prompt the transition of materials into a fascinating new quantum phase, known as an excitonic insulator.
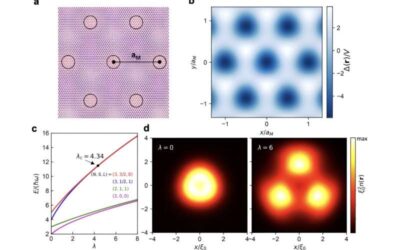
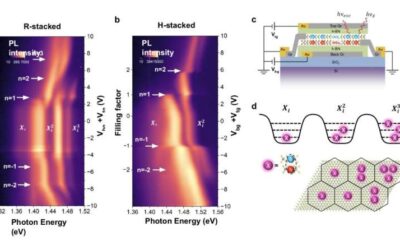
Exploring new physics arising from electron interactions in semiconductor moiré superlattices
Semiconductor moiré superlattices are fascinating material structures that have been found to be promising for studying correlated electron states and quantum physics phenomena. These structures, made up of artificial atom arrays arranged in a so-called moiré...
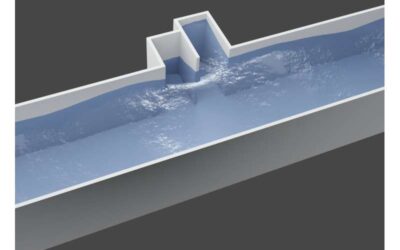
A strategy to realize the efficient resonant absorption of guided water waves
The absorption of water waves is the process through which water waves lose their energy, thus reducing their impact on shores or other solid structures surrounding them. Enabling this absorption process in real-world settings could help protect coasts and structures...
The formation of an excitonic Mott insulator state in a moiré superlattice
When a negatively charged electron and a positively charged hole in a pair remain bound together following excitation by light, they produce states known as excitons. These states can influence the optical properties of materials, in turn enabling their use for...
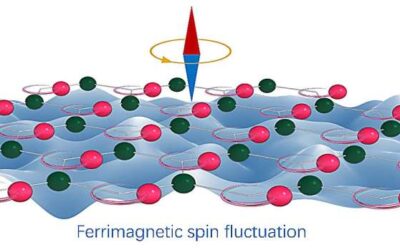
Study uncovers giant fluctuation-enhanced phonon magnetic moments in a polar antiferromagnet
Phonons, quasi-particles associated with sounds or lattice vibrations, can carry momentum and angular momentum. However, these quasi-particles are commonly considered to possess negligible magnetic moments.
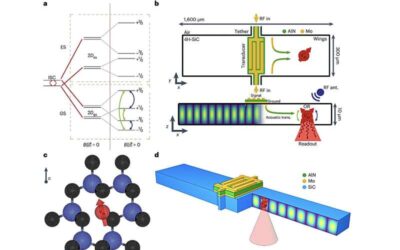
A strategy for the spin-acoustic control of silicon vacancies in a 4H silicon carbide-based bulk acoustic resonator
Bulk acoustic resonators—stacked material structures inside which acoustic waves resonate—can be used to amplify sounds or filter out undesired noise. These resonators have found wide use in today's RF telecommunication, like Front-End Modules (FEM) in iPhones. They...
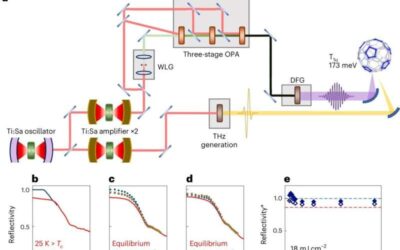
A strategy to enhance the light-driven superconductivity of K₃C₆₀
Superconductivity is the ability of some materials to conduct a direct electrical current (DC) with almost no resistance. This property is highly sought after and favorable for various technological applications, as it could boost the performance of different...