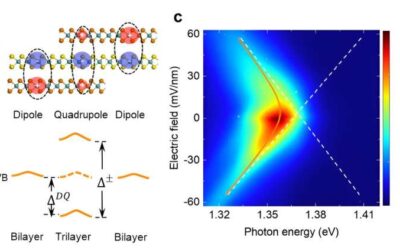
Light can excite electron and hole pairs inside semiconducting materials. If the attraction between a negatively charged electron and a positively charged hole (the antiparticle of electron in solid state physics) is strong, they stay bound together, forming states...
Condensed Matter
Researchers uncover unconventional charge carriers in a triangular-lattice Mott insulator
Mott insulators are a peculiar class of materials with structures that should theoretically conduct electricity, but that are instead insulators. These materials contain strongly correlated electrons, which can generate highly entangled many-body states marked by...
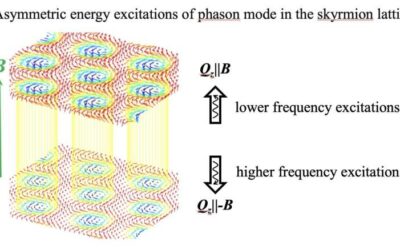
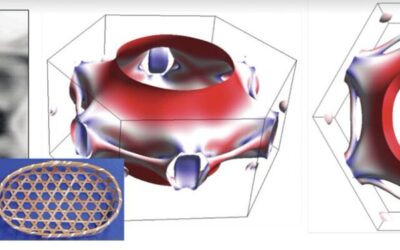
Study reveals an asymmetric dispersion of phason excitations in a skyrmion lattice
Magnetic skyrmions, statically stable magnetic quasiparticles with a topological charge, have been the focus of numerous recent studies, as they could support the development of so-called spintronics. These devices, which leverage the spin of electrons, could perform...
Study demonstrates many-body chemical reactions in a quantum degenerate gas
In recent years, physicists have been trying to attain the control of chemical reactions in the quantum degenerate regime, where de Broglie wavelength of particles becomes comparable to the spacing between them. Theoretical predictions suggest that many-body reactions...
Researchers observe ubiquitous superconductive diode effect in thin superconducting films
The so-called superconducting (SC) diode effect has recently attracted significant attention within the physics research community, due to its potential value for developing new technologies. This effect provides a key example of nonreciprocal superconductivity, as...
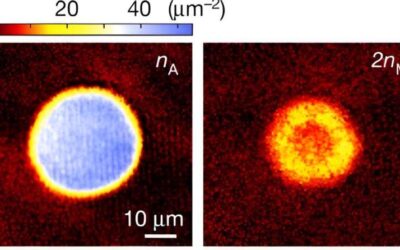
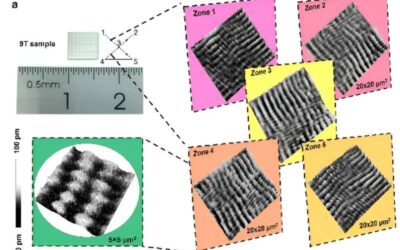
Millimeter-scale meron lattices that can serve as spin injectors for LEDs
Merons, topological structures based on in-plane magnetized magnetic materials, could have numerous valuable applications, particularly for carrying information or storing magnetic charge. Most past realizations of these structures, however, were limited in size and...
Study reports melting curve of superionic ammonia under icy planetary interior conditions
Icy planets, such as Uranus (U) and Neptune (N), are found in both our solar system and other solar systems across the universe. Nonetheless, these planets, characterized by a thick atmosphere and a mantle made of volatile materials (e.g., hydrogen water, ammonia,...
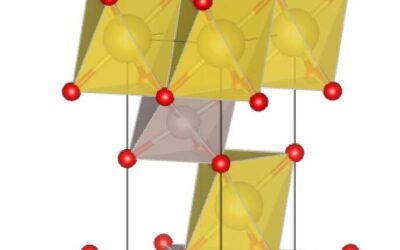
Mapping the curvature where electrons reside in Kagome materials
Kagome metals are a class of quantum materials with interesting properties that are characterized by a unique lattice structure resembling Japanese woven bamboo patterns of the same name (i.e., Kagome). Over the past decade, physicists have been using these materials...
The observation of a quantum disordered ground state in a triangular lattice magnet
Magnetic materials with a triangular lattice have been the focus of numerous research studies, as theoretical predictions suggest that they could exhibit spin liquid states. These are quantum phases of matter that present interesting characteristics, such as quantum...
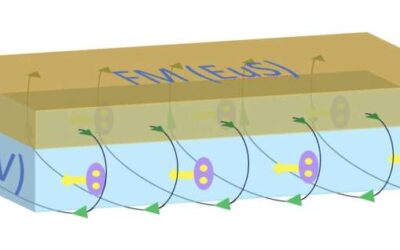
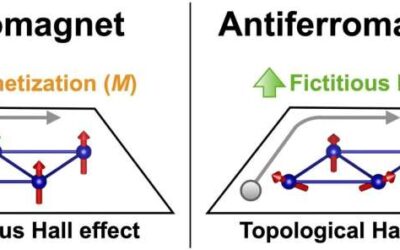
A spontaneous topological Hall effect driven by a non-coplanar antiferromagnetic order in van der Waals materials
Ferromagnets are materials that become magnetized and remain so while they are exposed to an external magnetic field. In these materials, electric currents typically induce a so-called transverse Hall voltage (i.e., a voltage resulting from the deflection of...