The Hall effect is a conduction phenomenon discovered by physicist Edwin Herbert Hall that describes the development of a transverse electric field in solid materials carrying electric current that are placed in a magnetic field perpendicular to this current. In the...
Condensed Matter
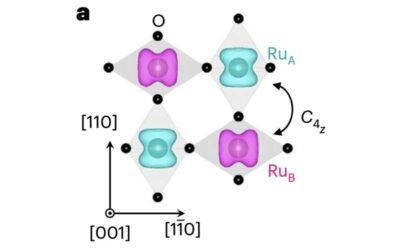
Study demonstrates tailored Ising superconductivity in intercalated bulk niobium diselenide
When 2D layered materials are made thinner (i.e., at the atomic scale), their properties can dramatically change, sometimes resulting in the emergence of entirely new features and in the loss of others. While new or emerging properties can be very advantageous for the...
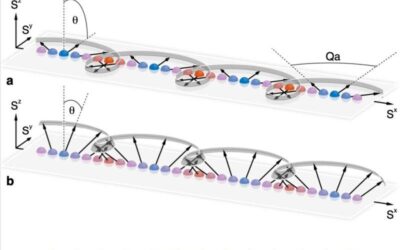
The experimental observation of long-lived phantom helix states in Heisenberg quantum magnets
Researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), the MIT-Harvard Center for Ultracold Atoms, Harvard University and Stanford University have recently unveiled the existence of unique helical spin states in Heisenberg quantum magnets. Their observations,...
Evidence of a new type of disordered quantum Wigner Solid
Physicists have been trying to determine the ground states of 2D electron systems at extremely low densities and temperatures for many decades now. The first theoretical predictions for these ground states were put forward by physicists Felix Bloch in 1929 and Eugene...
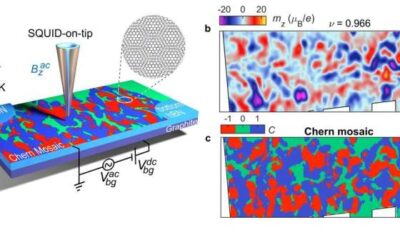
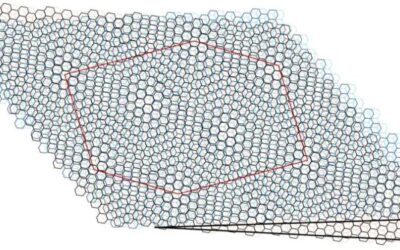
The observation of Chern mosaic and Berry-curvature magnetism in magic angle graphene
Researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science, the Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology and the National Institute for Material Science in Tsukuba (Japan) have recently probed a Chern mosaic topology and Berry-curvature magnetism in magic-angle graphene....
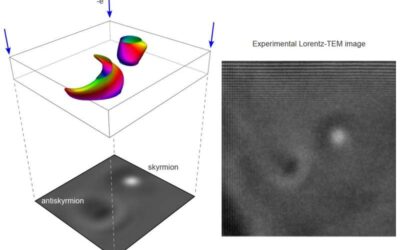
Study shows that skyrmions and antiskyrmions can coexist at different temperatures
Matching particles and antiparticles are small units of matter that have the same mass but opposite electric charges. Typically, these units of matter with opposite electric charge tend to annihilate one another.
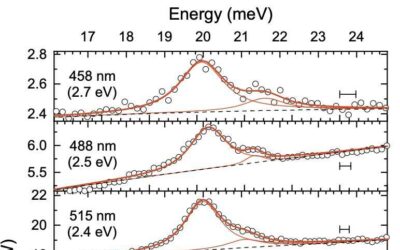
Study finds evidence of resonant Raman scattering from surface phonons of Cu(110)
Researchers at Johannes Kepler University in Linz have been investigating the physical properties of Cu(110), a surface attained when cutting a single copper crystal in a specific direction, for several years. Their most recent study, featured in Physical Review...
The direct detection of a topological phase transition through a sign change in the Berry curvature dipole
The Berry curvature and Chern number are crucial topological qualities of a quantum mechanical origin characterizing the electron wave function of materials. These two elements play a very important role in determining the properties of specific materials.
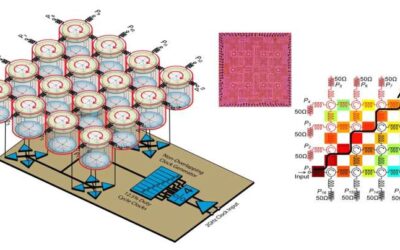
Chip-scale Floquet topological insulators to enhance 5G wireless communications
Floquet topological insulators are materials with topological phases that originate from tailored time-dependent perturbations of their crystal structure. These materials have been proved to feature highly unusual electron conduction properties. In recent years, there...
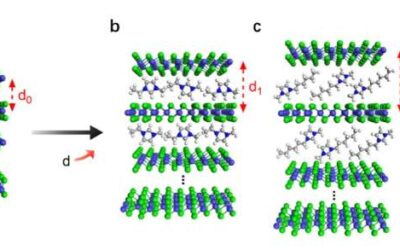
Remarkably strong pairing of charge carriers in bilayer antiferromagnetic Mott insulators
Over the past few years, many physicists and material scientists have been investigating superconductivity, the complete disappearance of electrical resistance observed in some solid materials. Superconductivity has so far been primarily observed in materials that are...