Researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, and Ohio state University recently carried out a study examining the possible effects of a first-order phase transition in a confining dark sector with heavy dark quarks. Using...
General Physics
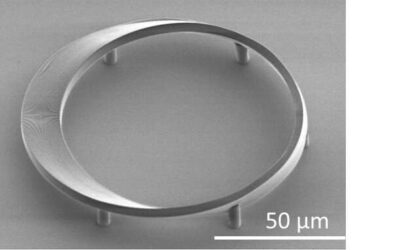
Möbius strip microlasers for non-Euclidean photonics applications
Photonics is a branch of technology development that specializes in the creation of devices that can generate, detect or manipulate light. Recently, researchers at Université Paris-Saclay coined a new term for a new photonics sub-field called non-Euclidean photonics.
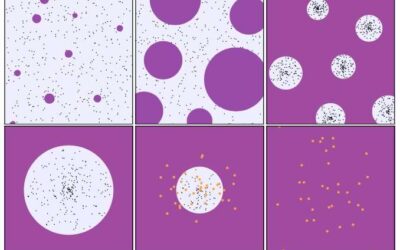
Study explores the origin of clonal dominance in excitable cell networks
Clonal dominance is a phenomenon that occurs when descendants (i.e., clones) of one or more founder cells in an organism contribute disproportionally to the system's final structure as the tissue grows. This phenomenon is associated with numerous biological processes,...
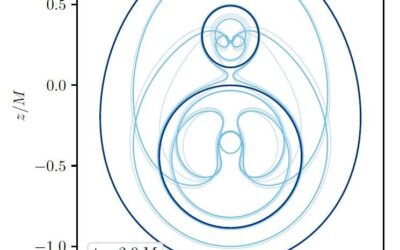
Study shows what happens to apparent horizons when binary black holes merge
Binary black hole mergers are fascinating cosmological events, which have been theorized to be the among the strongest sources of gravitational waves in the universe. While astrophysicists have carried out extensive research focusing on these events, many questions...
A strategy to control the spin polarization of electrons using helium
Spintronics, also known as spin electronics, is a research field that explores how the intrinsic spin of electrons and its magnetic moment can be exploited by devices. Spintronic devices are promising for a wide range of applications, particularly for efficiently...
Study demonstrates the potential of a quantum computer comprised of a small processor and a storage unit
Quantum computing systems, computer systems that are based on the key principles of quantum theory, could significantly outperform conventional computing systems, both in terms of speed and performance. Over the past decade or so, many physicists worldwide have thus...
A new theory to test hypotheses and methods for exoplanet detection
Countless astrophysicists and astronomers are actively searching for unobserved celestial bodies in the universe, as detecting these bodies could improve our understanding of space and help to address unanswered astrophysical questions. Among these elusive objects are...
Study demonstrates the robust storage of qubits in ultracold polar molecules
Molecules have a very intricate and rich structure, which allows them to rotate and vibrate freely. As a result, they have an almost limitless space in which computer scientists could encode quantum information. In addition to their vast internal space, molecules are...
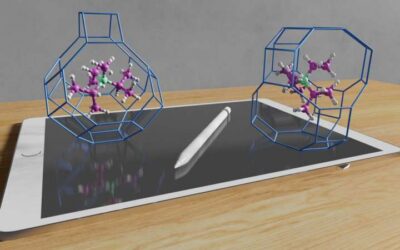
A strategy to control phase selectivity in templated zeolite synthesis
Zeolites, groups of minerals comprising of hydrated aluminosilicates, are known to be highly promising materials for a number of applications. For instance, they can be used as catalysts, cation exchangers and molecular sieves.
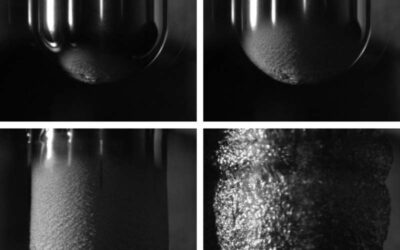
Study unveils the minimum temperature for droplets levitating from smooth surfaces
The Leidenfrost effect is a well-known physical phenomenon first discovered in 1756. It occurs when a liquid is in the proximity of a surface that is significantly warmer than its boiling point. This produces an insulating vapor layer that prevents the liquid from...