Neutrinos are tiny and neutrally charged particles accounted for by the Standard Model of particle physics. While they are estimated to be some of the most abundant particles in the universe, observing them has so far proved to be highly challenging, as the...
General Physics
A quantum radar that outperforms classical radar by 20%
Quantum technologies, a wide range of devices that operate by leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics, could significantly outperform classical devices on some tasks. Physicists and engineers worldwide have thus been working hard to achieve this long-sought...
PandaX sets new constraints on the search for light dark matter via ionization signals
Teams of physicists worldwide have been trying to detect dark matter, an elusive type of matter that does not emit, absorb, or reflect light. Due to its lack of interactions with electromagnetic forces, this matter is very difficult to observe directly, thus most...
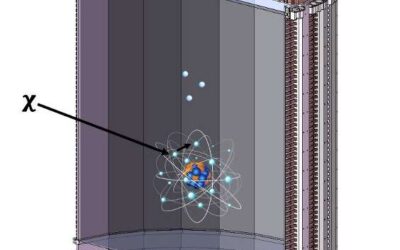
New method to search for strongly interacting dark matter inside neutrino detectors
Physicists worldwide are trying to detect dark matter (DM) particles and their interactions with visible matter using various strategies and detectors. As these particles do not emit, reflect or absorb light, they have so far proved to be very difficult to observe,...
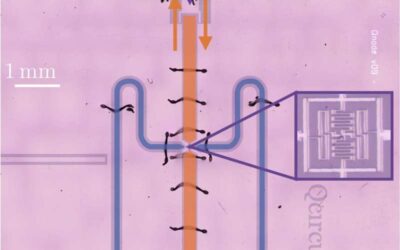
A solid-state quantum microscope that controls the wave functions of atomic quantum dots in silicon
Over the past decades, physicists and engineers have been trying to develop various technologies that leverage quantum mechanical effects, including quantum microscopes. These are microscopy tools that can be used to study the properties of quantum particles and...
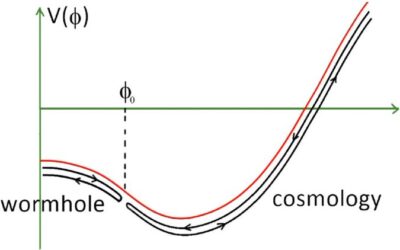
Could quantum gravity models arising from holography explain cosmological acceleration?
Theoretical physicists have long been trying to devise a complete theory of gravity that would also account for quantum mechanics phenomena, as existing models do not. Such a theory could collectively explain the many intricate physical and cosmological phenomena...
A new approach to controlling the properties of turbulence
Turbulence, a fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in flow velocity and pressure, has been the topic of countless physics studies. Although turbulence is a very common phenomenon that occurs in nature, manipulating it and controlling its properties had so far...
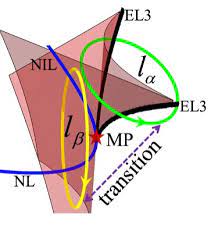
Study reveals the existence of the swallowtail catastrophe in non-Hermitian systems
Researchers from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Xiangtan University and Southern University of Science and Technology recently unveiled a possible connection between catastrophe theory, an area of mathematics that focuses on modeling sudden...
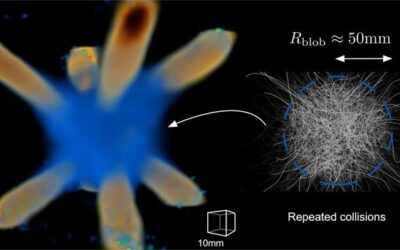
The first experimental observation of subpicosecond electron bunches originating from an ultracold source
Identifying new sources that produce electrons faster could help to advance the many imaging techniques that rely on electrons. In a recent paper published in Physical Review Letters, a team of researchers at Eindhoven University of Technology demonstrated the...
The realization of a continuous time crystal based on a photonic metamaterial
A time crystal, as originally proposed in 2012, is a new state of matter in which the particles are in continuous oscillatory motion. Time crystals break time-translation symmetry. Discrete time crystals do so by oscillating under the influence of a periodic external...