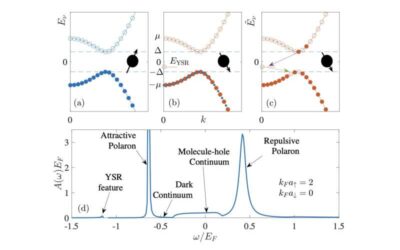
Physicists studying quantum many-body physics very rarely reach exact solutions or conclusions, particularly in more than one dimension. This is also true for the Fermi polaron problem, describing instances in which the many-body quantum background is a...
General Physics
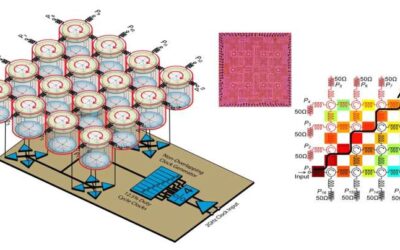
Chip-scale Floquet topological insulators to enhance 5G wireless communications
Floquet topological insulators are materials with topological phases that originate from tailored time-dependent perturbations of their crystal structure. These materials have been proved to feature highly unusual electron conduction properties. In recent years, there...
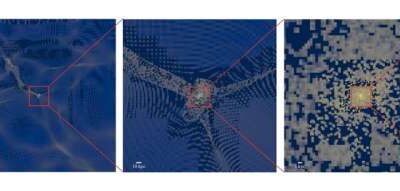
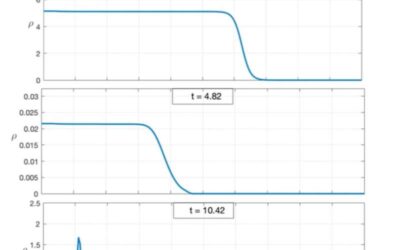
Astrophysicists simulate a fuzzy dark matter galactic halo
Dark matter is a type of matter in the universe that does not absorb, reflect or emit light, which makes it impossible to directly detect. In recent years, astrophysicists and cosmologists worldwide have been trying to indirectly detect this elusive type of matter, to...
Searching for cosmic-ray boosted sub-GeV dark matter using data from the PandaX-II experiment
Physicists worldwide are continuing their search for dark matter, an elusive type of matter that does not absorb, reflect or emit light and is believed to make up most of the matter in the universe. A type of dark matter that many teams have been specifically looking...
Using renormalization group methods to study how the brain processes information
Past neuroscience research suggests that biological neural networks in the brain could self-organize into a critical state. In physics, a critical state is essentially a point that marks the transition between ordered and disordered phases of matter.
Theoretical model offers a new perspective on black hole formation and evolution
Black holes are regions in space characterized by gravitational fields so intense that no matter or radiation can escape from them. They are solutions to Einstein's field equations, with a point of unphysical infinite density at their center.
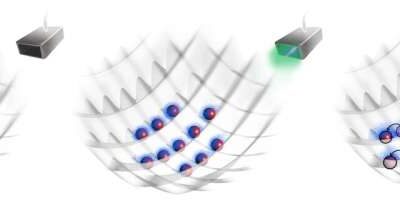
Study introduces loss-free matter-wave polaritons in an optical lattice system
Polaritons are quasiparticles that are formed when photons couple strongly with excitations of matter. These quasi-particles, which are half-light and half-matter, underpin the functioning of a wide range of emergent photonic quantum systems, including...
Borexino gathers the first directional measurement of sub-MeV solar neutrinos using a monolithic scintillation detector
Borexino is a large-scale particle physics experiment that collected data until October 2021. Its key mission was to study low energy (sub-MeV) solar neutrinos using the Borexino detector, the world's most radio-pure liquid scintillator calorimeter, located at the...
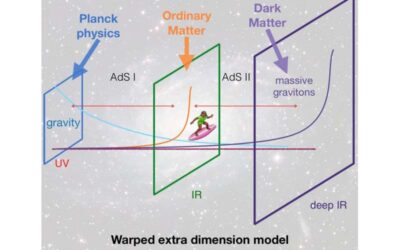
Could massive gravitons be viable dark matter candidates?
Today, many research teams worldwide are trying to detect dark matter, an invisible substance that is believed to account for most of the matter in the universe. As does not reflect or emit light, its presence has been indirectly revealed via its gravitational...
The IceCube Collaboration sets the most restrictive constraints on relic magnetic monopoles from the early universe
Recent technological advances have enabled the development of increasingly advanced telescope and astrophysical instruments. This includes the IceCube telescope, which was originally built to detect and examine high-energy neutrinos in the universe.