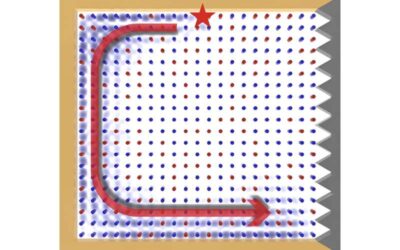
Photonic alloys, alloy-like materials combining two or more photonic crystals, are promising candidates for the development of structures that control the propagation of electromagnetic waves, also known as waveguides. Despite their potential, these materials...
Optics & Photonics
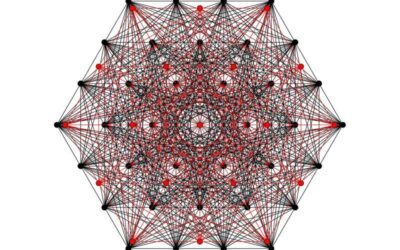
A framework to construct quantum spherical codes
To reliably perform complex, large-scale calculations, computing systems rely on so-called error correction schemes, techniques designed to protect information against errors. These techniques are perhaps even more essential when it comes to quantum computers, devices...
Researchers realize multiphoton electron emission with non-classical light
Strong field quantum optics is a rapidly emerging research topic, which merges elements of non-linear photoemission rooted in strong field physics with the well-established realm of quantum optics. While the distribution of light particles (i.e., photons) has been...
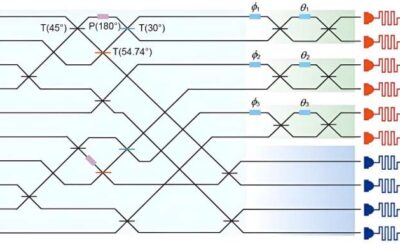
Demonstration of heralded three-photon entanglement on a photonic chip
Photonic quantum computers are computational tools that leverage quantum physics and utilize particles of light (i.e., photons) as units of information processing. These computers could eventually outperform conventional quantum computers in terms of speed, while also...
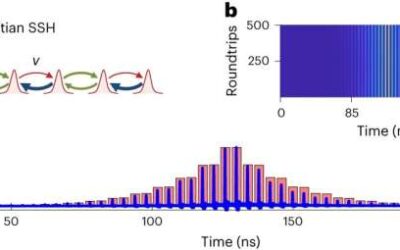
Using mode-locked lasers to realize and study non-Hermitian topological physics
Mode-locked lasers are advanced lasers that produce very short pulses of light, with durations ranging from femtoseconds to picoseconds. These lasers are widely used to study ultrafast and nonlinear optical phenomena, but they have also proved useful for various...
Researchers demonstrate multi-photon state transfer between remote superconducting nodes
Over the past few decades, quantum physicists and engineers have been trying to develop new, reliable quantum communication systems. These systems could ultimately serve as a testbed to evaluate and advance communication protocols.
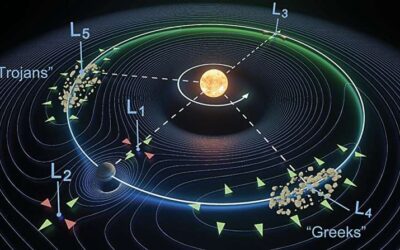
A Trojan approach to guide and trap light beams via Lagrange points
Reliably guiding and capturing optical waves is central to the functioning of various contemporary technologies, including communication and information processing systems. The most conventional approach to guide light waves leverages the total internal reflection of...
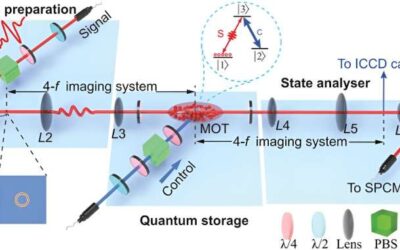
A new approach to realize highly efficient, high-dimensional quantum memories
Many physicists and engineers have been trying to develop highly efficient quantum technologies that can perform similar functions to conventional electronics leveraging quantum mechanical effects. This includes high-dimensional quantum memories, storage devices with...
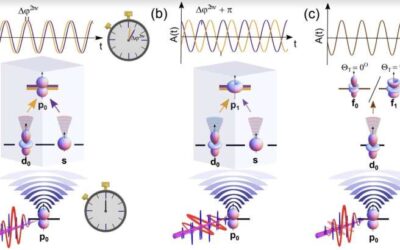
A method to resolve quantum interference between photoionization pathways with attosecond resolution
The field of attosecond physics was established with the mission of exploring light–matter interactions at unprecedented time resolutions. Recent advancements in this field have allowed physicists to shed new light on the quantum dynamics of charge carriers in atoms...
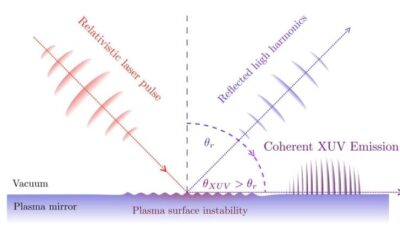
An anomalous relativistic emission arising from the intense interaction of lasers with plasma mirrors
Interactions between intense laser pulses and plasma mirrors have been the focus of several recent physics studies due to the interesting effects they produce. Experiments have revealed that these interactions can generate a non-linear physical process known as...