Studies that explore how the denser sections of atoms, known as atomic nuclei, interact with neutrons (i.e., particles with no electric charge) can have valuable implications both for the understanding of these atoms' underlying physics and for the development of...
PHYS.ORG
AMoRE experiment sets new limits on neutrinoless double beta decay of ¹⁰⁰Mo
In recent years, some large physics experiments worldwide have been trying to gather evidence of a nuclear process known as neutrinoless double beta (0νββ) decay. This is a rare process that entails the simultaneous decay of two neutrons in a nucleus into two protons,...
An experimental test of the nonlocal energy alteration between two quantum memories
Quantum technologies operate by leveraging various quantum mechanical effects, including entanglement. Entanglement occurs when two or more particles share correlated states even if they are distant.
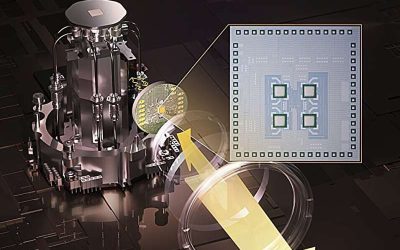
Wireless terahertz cryogenic interconnect minimizes heat-to-information transfer in quantum processors
Quantum computers, devices that process information leveraging quantum mechanical effects, could outperform classical computers in some complex optimization and computational tasks. However, before these systems can be adopted on a large-scale, some technical...
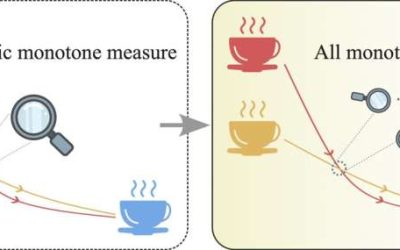
Thermomajorization theory provides new framework for quantifying mysterious Mpemba effect
The Mpemba effect is an intriguing physical phenomenon that causes some systems to cool faster when they are hot than when they are warm or colder. This effect was observed in various systems, including water, which sometimes freezes faster when it is hot than when it...
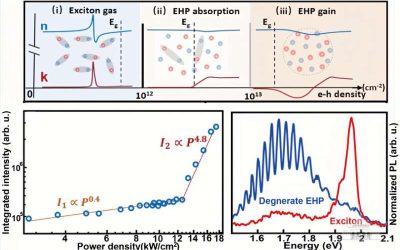
The first observation of amplified spontaneous emission from electron-hole plasma in 2D semiconductors
Amplified spontaneous emission is a physical phenomenon that entails the amplification of the light spontaneously emitted by excited particles, due to photons of the same frequency triggering further emissions. This phenomenon is central to the functioning of various...
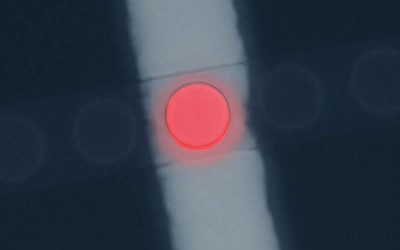
Boosting the response speed of quantum LEDs via an excitation memory effect
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are widely used electroluminescent devices that emit light in response to an applied electric voltage. These devices are central components of various electronic and optoelectronic technologies, including displays, sensors and...
Quantum entanglement wins: Researchers report quantum advantage in a simple cooperation game
Quantum systems hold the promise of tackling some complex problems faster and more efficiently than classical computers. Despite their potential, so far only a limited number of studies have conclusively demonstrated that quantum computers can outperform classical...
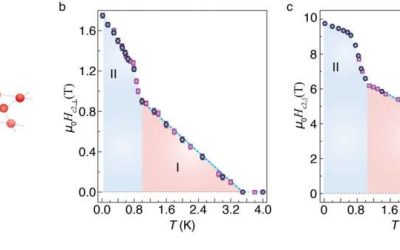
Physicists uncover two superconducting regimes in a Kagome lattice superconductor
Superconductivity, which entails an electrical resistance of zero at very low temperatures, is a highly desirable and thus widely studied quantum phenomenon. Typically, this state is known to arise following the formation of bound electron pairs known as Cooper pairs,...
A new protocol to image wave functions in continuous space
In recent years, physicists have been trying to better understand the behavior of individual quantum particles as they move in space. Yet directly imaging these particles with high precision has so far proved challenging, due to the limitations of existing microscopy...