In 2015, astrophysicists discovered a system consisting of two compact stars orbiting each other: a pulsar (i.e., a highly magnetized rapidly rotating, light-emitting neutron star) and a so-called companion star. The companion star in this system has a mass that is...
PHYS.ORG
Optimal brain processing requires balance between excitatory and inhibitory neurons, study suggests
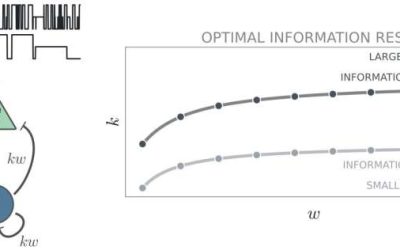
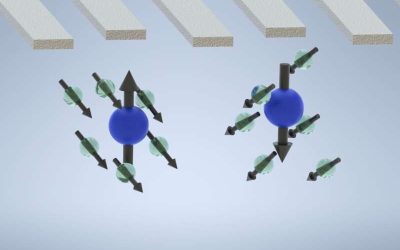
The brain's ability to process information is known to be supported by intricate connections between different neuron populations. A key objective of neuroscience research has been to delineate the processes via which these connections influence information processing.
Quantum algorithm excels at finding local minima of many-body systems
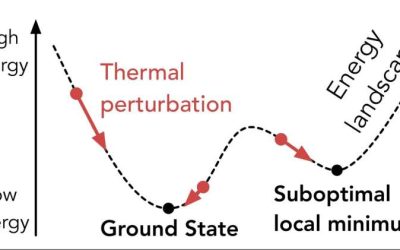
Many physicists and engineers have recently been trying to demonstrate the potential of quantum computers for tackling some problems that are particularly demanding and are difficult to solve for classical computers. A task that has been found to be challenging for...
Meta-analysis uncovers public’s skill in detecting fake news, but skepticism towards true news persists
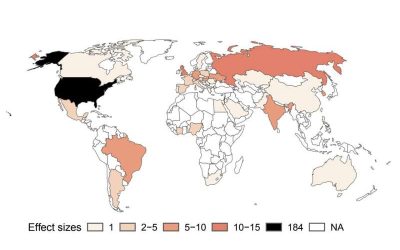
While the internet has made accessing information and updates on what is happening in the world extremely easy, it has also facilitated the proliferation of fake news. Over the past decades, fake news has thus become a heated topic of debate, with some social media...
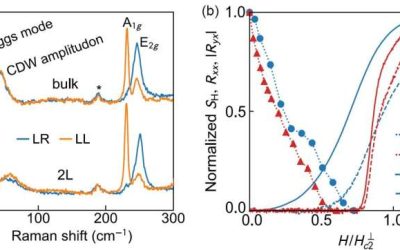
Researchers discover magnetic equivalent of the Lyddane-Sachs-Teller relation
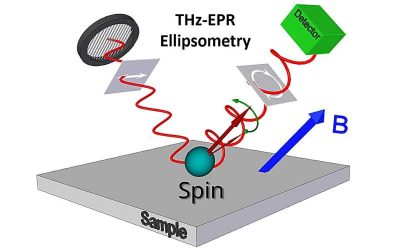
Materials are known to interact with electromagnetic fields in different ways, which reflect their structures and underlying properties. The Lyddane-Sachs-Teller relation is a physics construct that describes the relationship between a material's static and dynamic...
A new approach to reduce decoherence in superconducting qudit-based quantum processors
Quantum computers, which operate leveraging quantum mechanics effects, could soon outperform traditional computers in some advanced optimization and simulation tasks. Most quantum computing systems developed so far store and process information using qubits (quantum...
Atomically thin NbSe₂ demonstrates resilient superconducting fluctuations
Superconductivity is an intriguing property observed in some materials, which entails the ability to conduct electric current combined with an electrical resistance of zero at low temperatures. Physicists have observed this property in various solid materials with...
First dark matter search using WINERED spectrograph sets new lifetime constraints
Dark matter is an elusive type of matter that does not emit, absorb or reflect light and is thus impossible to detect using conventional techniques employed in particle physics. In recent years, groups of physicists worldwide have been trying to observe this matter...
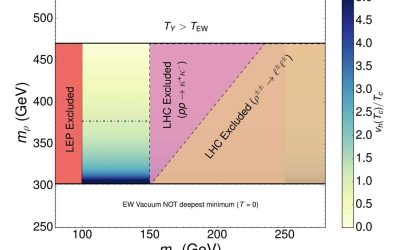
Hypercharge breaking scenarios could explain the baryon asymmetry of the universe
The Standard Model (SM), the main physics framework describing elementary particles and the forces driving them, outlines key patterns in physical interactions referred to as gauge symmetries. One of the symmetries it describes is the so-called U(1)Y hypercharge:...
Newly realized nuclear-spin dark state promises reduced quantum decoherence
Quantum computers, which operate leveraging quantum mechanics phenomena, could eventually tackle some optimization and computational problems faster and more efficiently than their classical counterparts. Instead of bits, the fundamental units of information in...