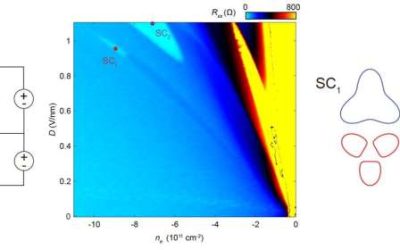
Superconductivity is a widely sought after material property, which entails an electrical resistance of zero below a specific critical temperature. So far, it has been observed in various materials, including recently in so-called multilayer graphene allotropes (i.e.,...
PHYS.ORG
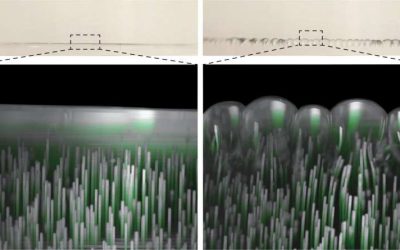
Study unveils new extrusion-induced instabilities in viscoelastic materials
Soft viscoelastic solids are flexible materials that can return to their original shape after being stretched. Due to the unique properties driving their deformation, these materials can sometimes behave and change shape in unexpected ways.
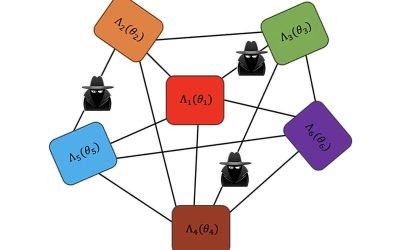
A newly proposed protocol to boost privacy in quantum sensor networks
Devices that leverage quantum mechanics effects, broadly referred to as quantum technologies, could help to tackle some real-world problems faster and more efficiently. In recent years, physicists and engineers have introduced various promising quantum technologies,...
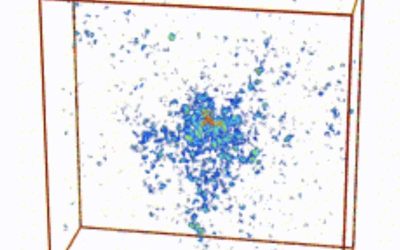
Simulations reveal Anderson transition for light in 3D disordered systems
The Anderson transition is a phase transition that occurs in disordered systems, which entails a shift from a diffusive state (i.e., in which waves or particles are spread out) to a localized state, in which they are trapped in specific regions. This state was first...
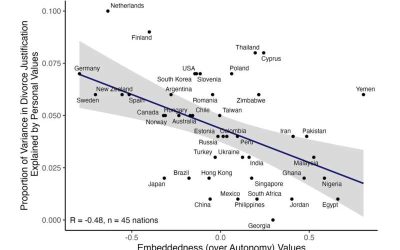
Divorce can be predicted by interactions between cultural and personal values, study finds
Divorce, the legal dissolution of marriage, can be driven by a variety of factors, ranging from changes in the economic status or health conditions of spouses to contrasting values. The end of a marriage can often be challenging to process. Thus, it can have adverse...
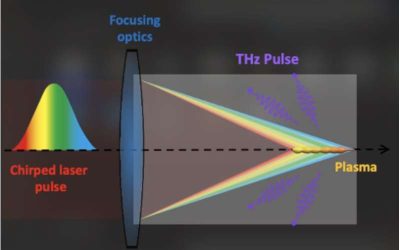
A promising technique to steer laser-produced THz radiation in air
Terahertz radiation (THz), electromagnetic radiation with frequencies ranging from 0.1 and 10 THz, is central to the functioning of various technologies, including imaging, sensing and spectroscopy tools. While THz radiation waves have been manipulated in different...
The ALPHA experiment moves towards the increasingly precise study of antihydrogen
Antimatter is a fascinating kind of matter made up of antiparticles, which have a mass equivalent to that of their normal matter counterparts, yet they exhibit an opposite charge and distinct quantum properties.
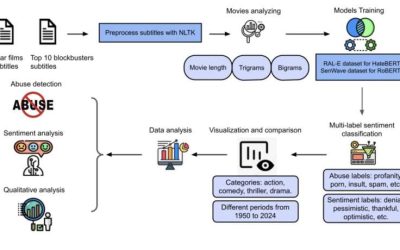
AI-driven dialogue analysis confirms popular movies have grown more violent over the past 70 years
Movies often reflect the predominant societal and cultural values at the time they were shot. These values can be expressed in various elements of a film, including the interactions between characters, their communication styles and their characterizing traits.
Researchers observe a phase transition in a 1D chain of atoms using a quantum simulator
Phase transitions, shifts between different states of matter, are widely explored physical phenomena. So far, these transitions have primarily been studied in three-dimensional (3D) and two-dimensional (2D) systems, yet theories suggest that they could also occur in...
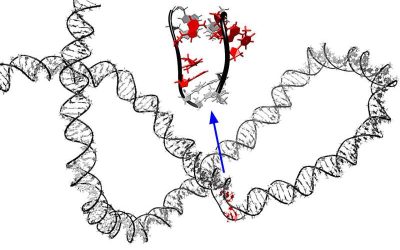
Molecular simulations provide new insights into the dynamics of supercoiled DNA
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), the molecular "blueprint" carrying the genetic instructions that influence the growth, development, reproduction and predispositions of individual humans, can undergo different types of mechanical stress inside cells. For instance, it can...