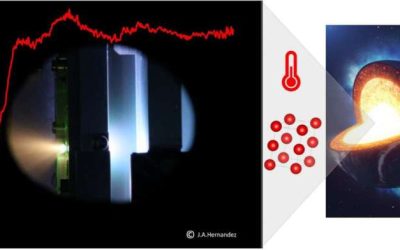
Iron is one of the main elements found in the Earth's inner core, which is characterized by extremely high temperatures and pressures. Determining how iron behaves in these extreme conditions could thus help to advance the current understanding of our home planet's...
PHYS.ORG
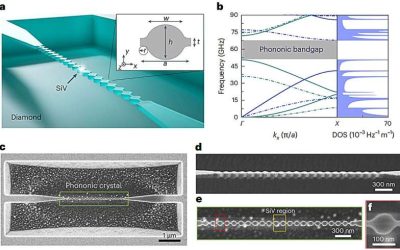
Newly fabricated crystals control interactions between high-frequency phonons and single quantum systems
Phonons, the quantum mechanical vibrations of atoms in solids, are often sources of noise in solid-state quantum systems, including quantum technologies, which can lead to decoherence and thus adversely impact their performance.
Scientists achieve direct experimental realization of dual-type entangling gates
To develop scalable and reliable quantum computers, engineers and physicists will need to devise effective strategies to mitigate errors in their quantum systems without adding complex additional components. A promising strategy to reduce errors entails the use of...
Quantum experiment generates long-range entanglement in 54-qubit system
The operation and performance of quantum computers relies on the ability to realize and control entanglement between multiple qubits. Yet entanglement between many qubits is inherently susceptible to noise and imperfections in quantum gates.
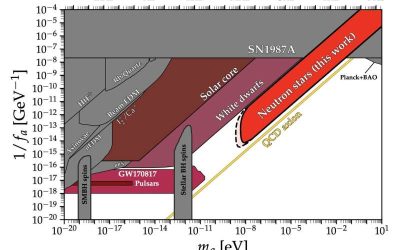
Neutron star cooling simulations set new constraints on light QCD axions
Neutron stars, the remnants of massive stars after a supernova explosion, have often been the focus of studies aimed at testing and unveiling exotic physics. This is because these stars are among the densest objects in the universe, so they host extremely high...
Resistance measurement approach successfully observes topological signatures in multiterminal Josephson junctions
Multiterminal Josephson junctions, nanoscale devices with unique electronic properties, comprise non-superconducting metallic material coupled to three or more superconducting leads. These devices have proved to be promising platforms for the exploration of...
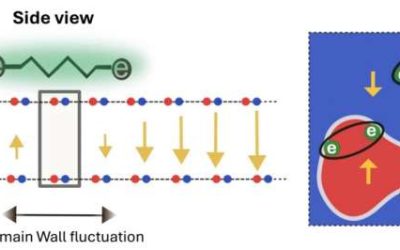
Domain wall fluctuations in 2D materials reveal a new mechanism of superconductivity
Two-dimensional (2D) van der Waals are made of atomically thin layers, held together by weak van der Waals forces. These materials have been the focus of numerous studies, as their unique properties make them ideal for studying various exotic and rare physical...
The LZ experiment’s first science run sets new constraints on dark matter interactions
The LUX ZEPLIN (LZ) Dark Matter experiment is a large research effort involving over 200 scientists and engineers at 40 institutions worldwide. Its key objective is to search for weakly interacting massive particles (WIMPs) by analyzing data collected by the LZ...
The first observation of time-domain oscillations between two distant semiconductor spin qubits
Quantum computing holds the promise of outperforming classical computing on some optimization and data processing tasks. The creation of highly performing large-scale quantum computers, however, relies on the ability to support controlled interactions between qubits,...
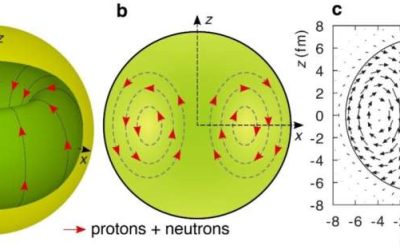
Nickel-58 nucleus may host elusive toroidal dipole excitations
Dipole toroidal modes are a unique set of excitations that are predicted to occur in various physical systems, ranging from atomic nuclei to metamaterials. What characterizes these excitations, or modes, is a toroidal distribution of currents, which results in the...